

Syndromes with musculoskeletal implications were diagnosed in 328,600 children and adolescent health care visits in 2012, of which 126,300 had a primary diagnosis of a syndrome condition. About 1 in 10 (9%) children and adolescents with any syndrome with musculoskeletal implications diagnoses were hospitalized (29,800), but less than 1% (600) with a primary diagnosis of a syndrome with musculoskeletal implications had a hospital discharge. (Reference Table 7.1.1 PDF [1] CSV [2] and Table 7.1.2 PDF [3] CSV [4])
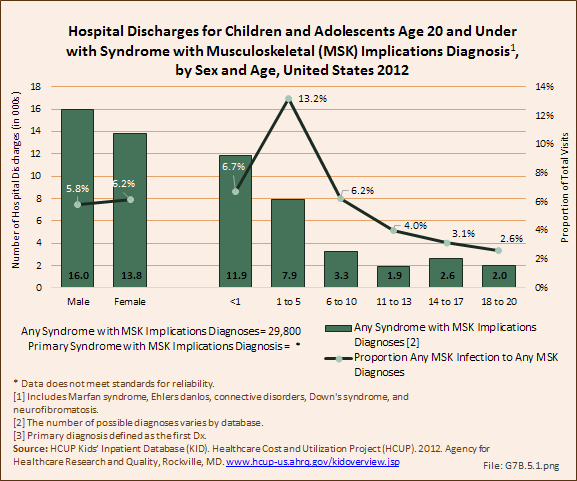
Males, more than females, had a hospital discharge with any syndrome with musculoskeletal implications diagnoses. Infants and young children under the age of 5 years had the highest rate of hospitalization for any diagnoses of syndromes with musculoskeletal implications. The number of hospitalizations with a primary diagnosis was too small for analysis by sex and age.
Any diagnoses of syndromes with musculoskeletal implications accounted for 6% of hospitalizations for any musculoskeletal condition diagnosis, and 0.4% of all hospitalizations for any health care condition. Hospitalizations with a primary diagnosis were 0.1% of all musculoskeletal diagnoses. (Reference Table 7.6 PDF [5] CSV [6])
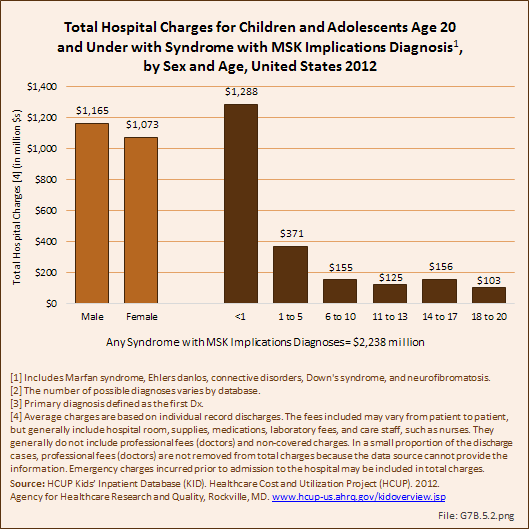
Total charges averaged $75,100 for a mean 8.1-day stay when children and adolescents were hospitalized with a diagnosis of a syndrome with musculoskeletal implications condition along with other medical conditions. With a primary syndrome diagnosis, the stay was slightly longer (8.7 days), and mean charges were higher at $100,800. Mean charges and length of stay were highest for the youngest patients, those under 1 year of age. Total hospital charges for primary syndrome with musculoskeletal implications discharges in 2012 were $60.5 million. (Reference Table 7.6 PDF [5] CSV [6])
Links:
[1] https://bmus.latticegroup.com/docs/T7.1.1.pdf
[2] https://bmus.latticegroup.com/docs/T7.1.1.csv
[3] https://bmus.latticegroup.com/docs/T7.1.2.pdf
[4] https://bmus.latticegroup.com/docs/T7.1.2.csv
[5] https://bmus.latticegroup.com/docs/T7.6.pdf
[6] https://bmus.latticegroup.com/docs/T7.6.csv