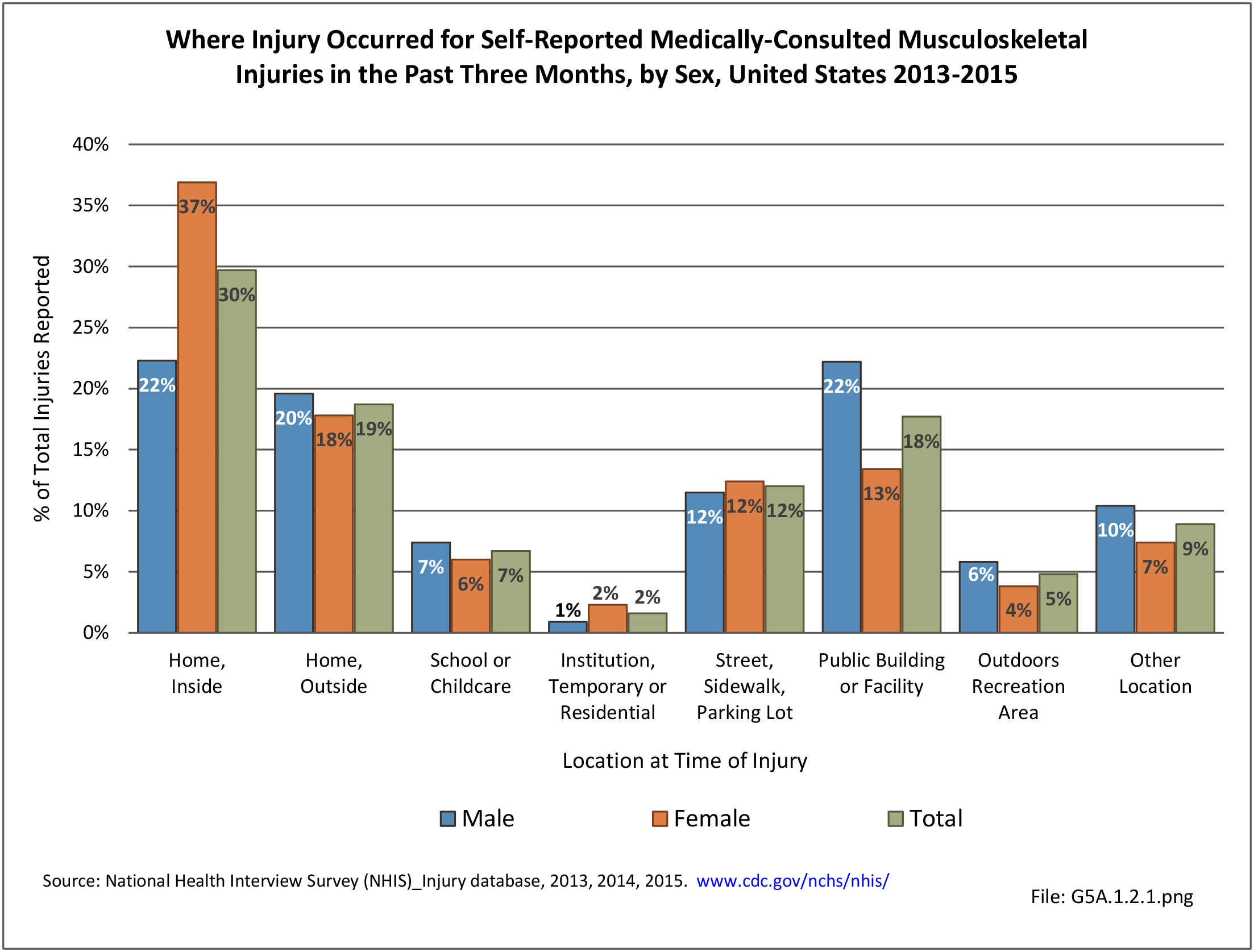
An injury is a general term referring to damage to the body, and can be caused by accidents, falls, weapons, sports, and other incidents. Injuries may affect many parts of the body, including the brain, the extremities, and internal organs. Wounds are injuries that break the skin or other body tissues, and include cuts, scrapes, and punctured skin. This document is focused on injuries to the extremities and spine, referred to as musculoskeletal injuries throughout this document.
Injuries are reported for six different categories, with each having a somewhat different focus and data source(s) specific to the category of injury. To address the broadest picture, this chapter includes the following sections.
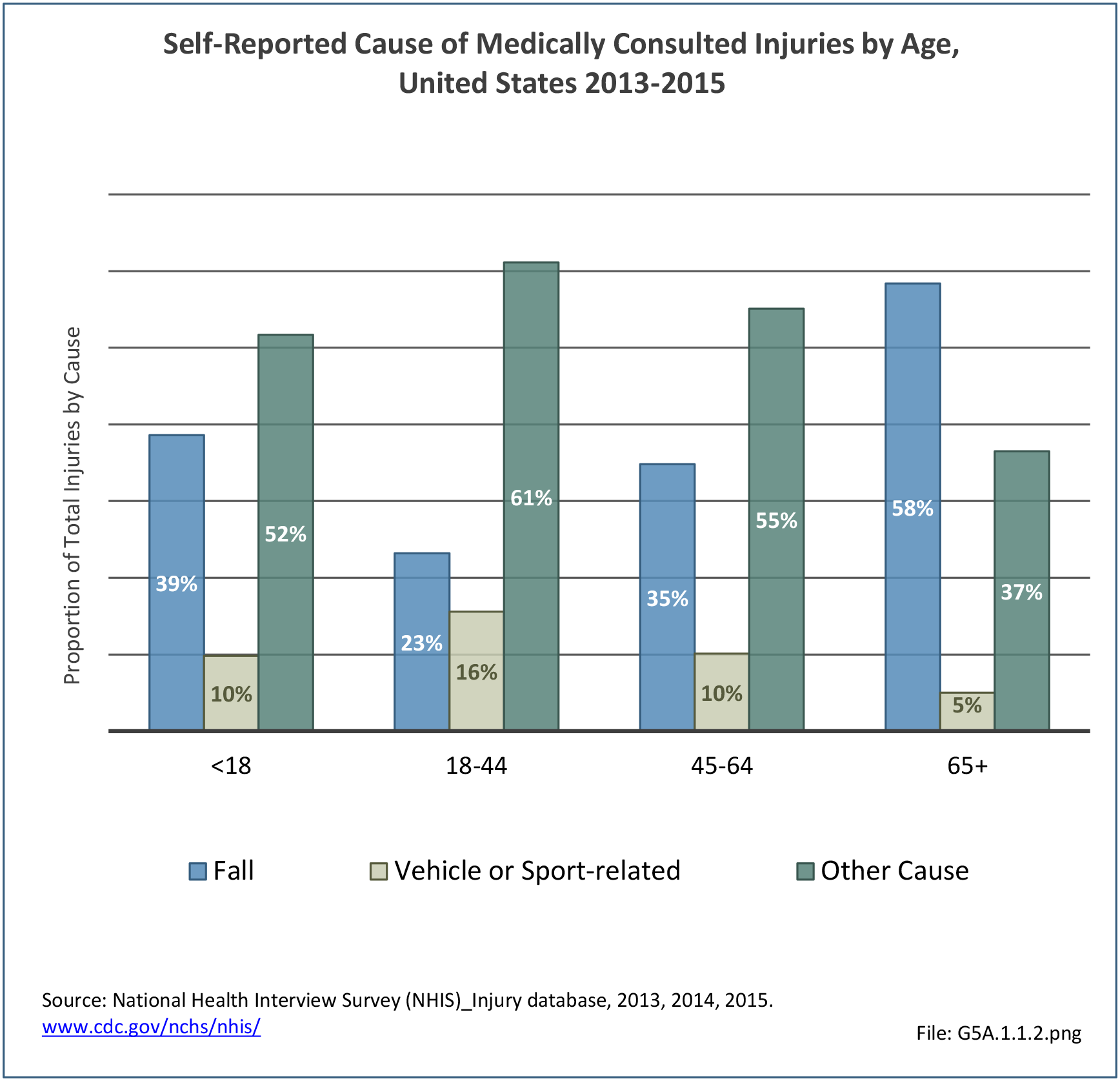
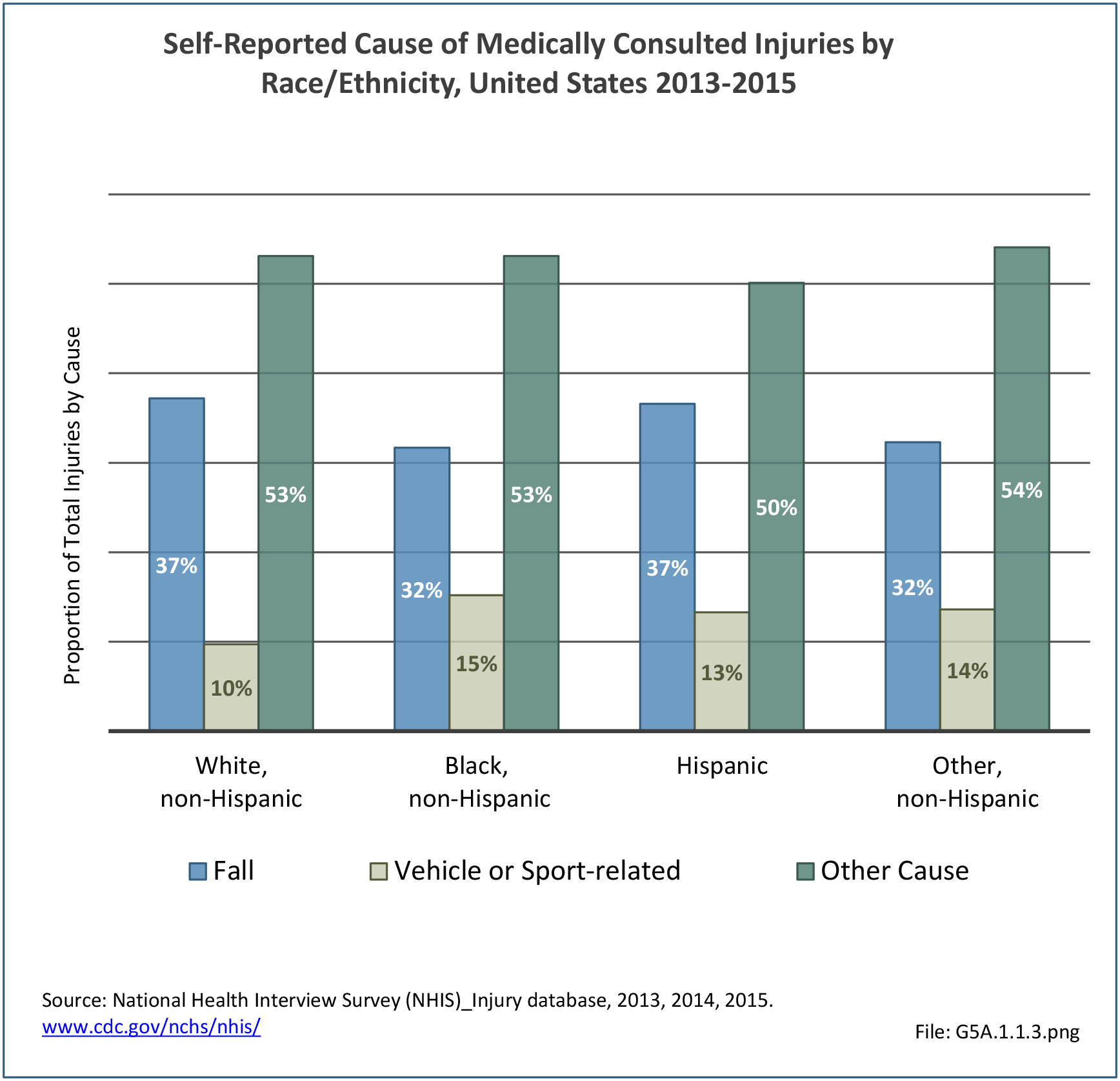
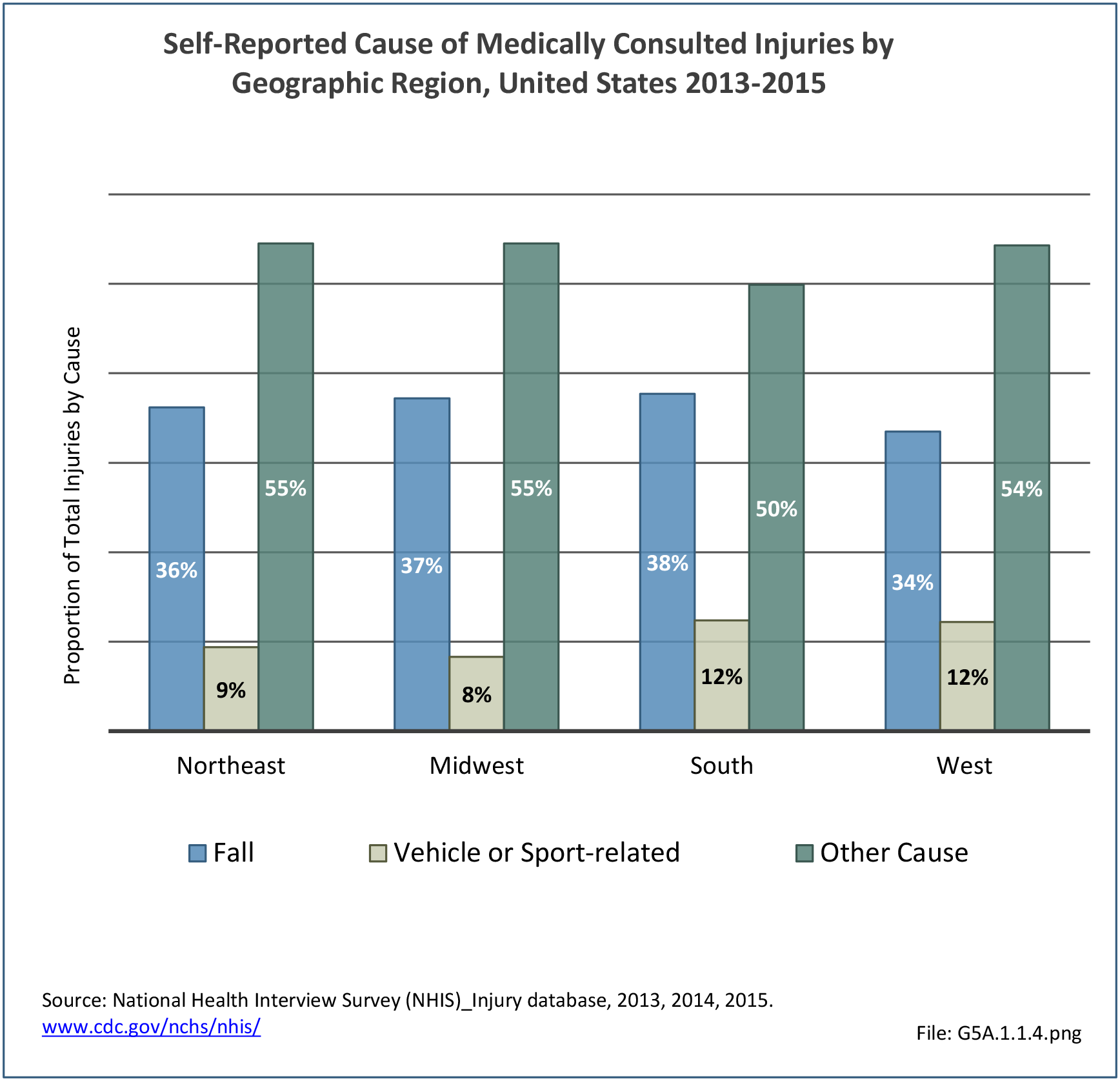
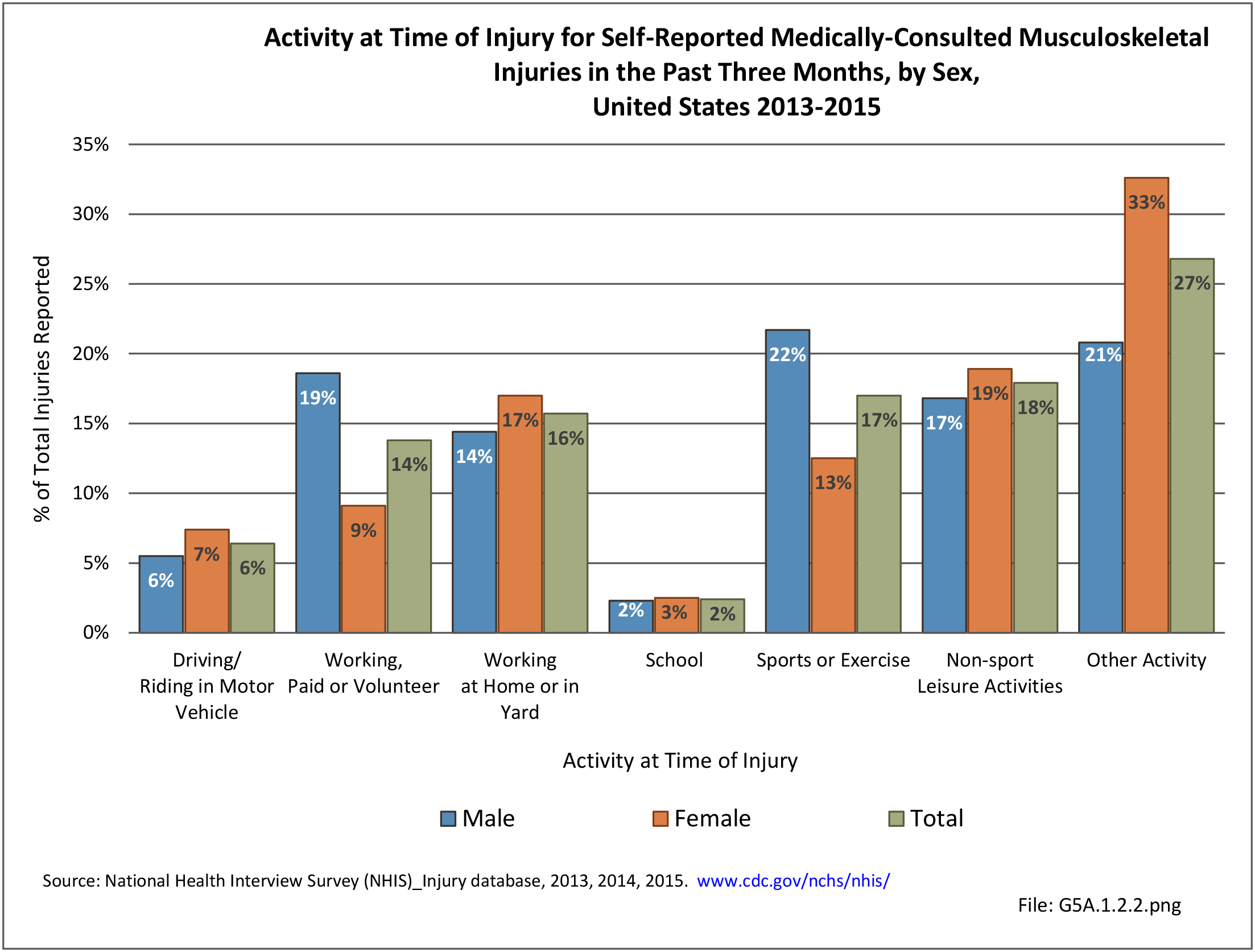
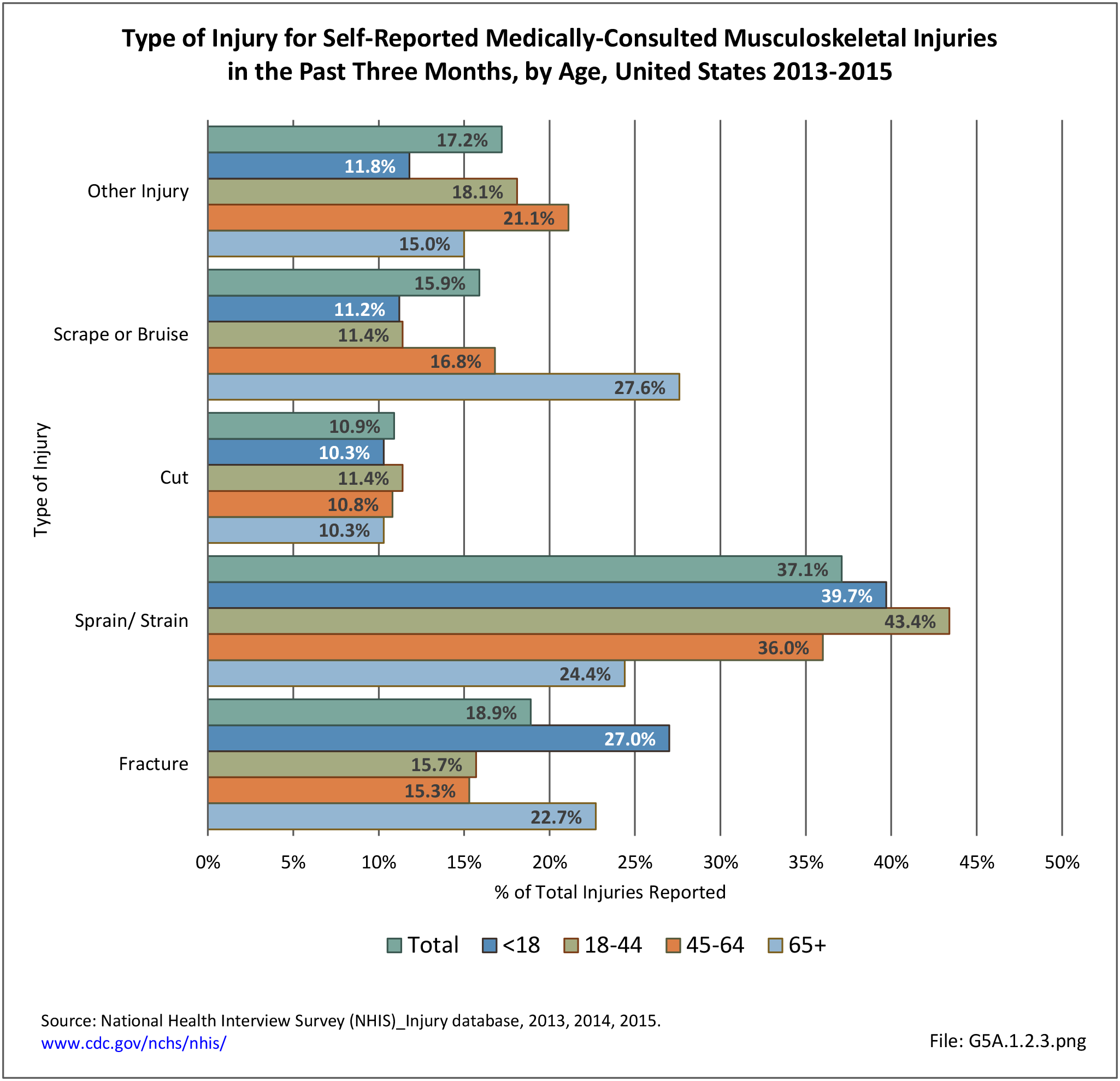
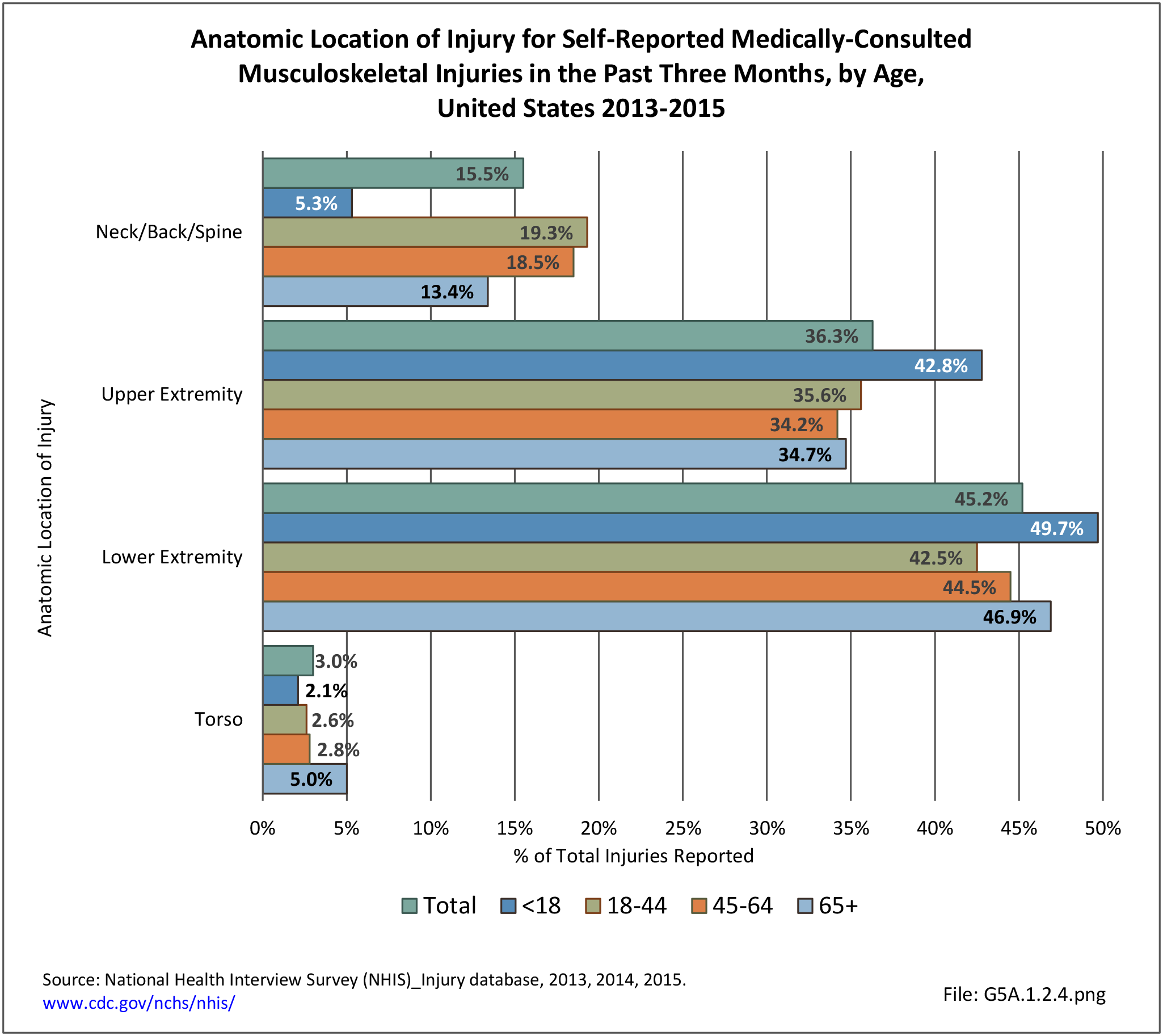
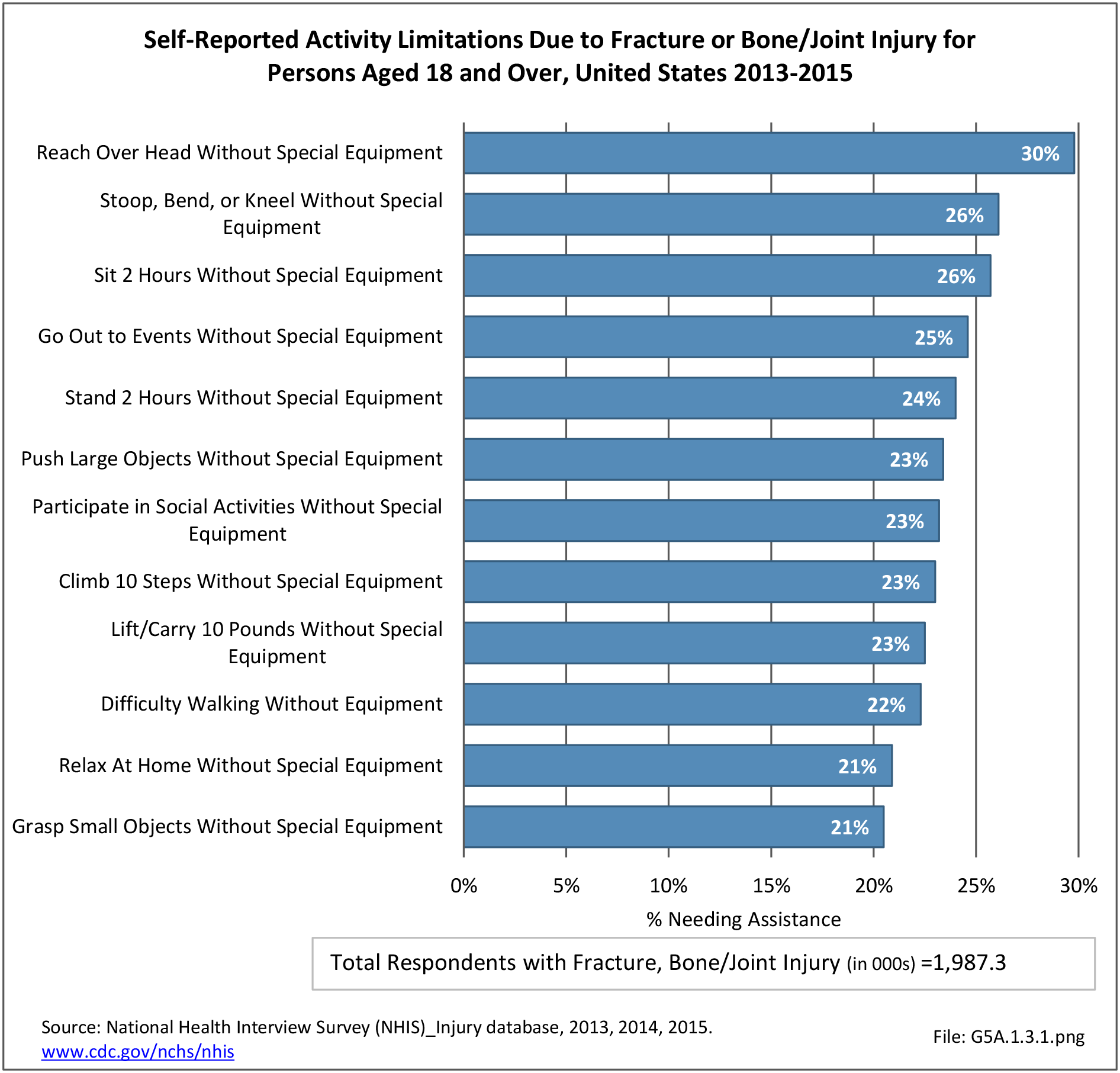
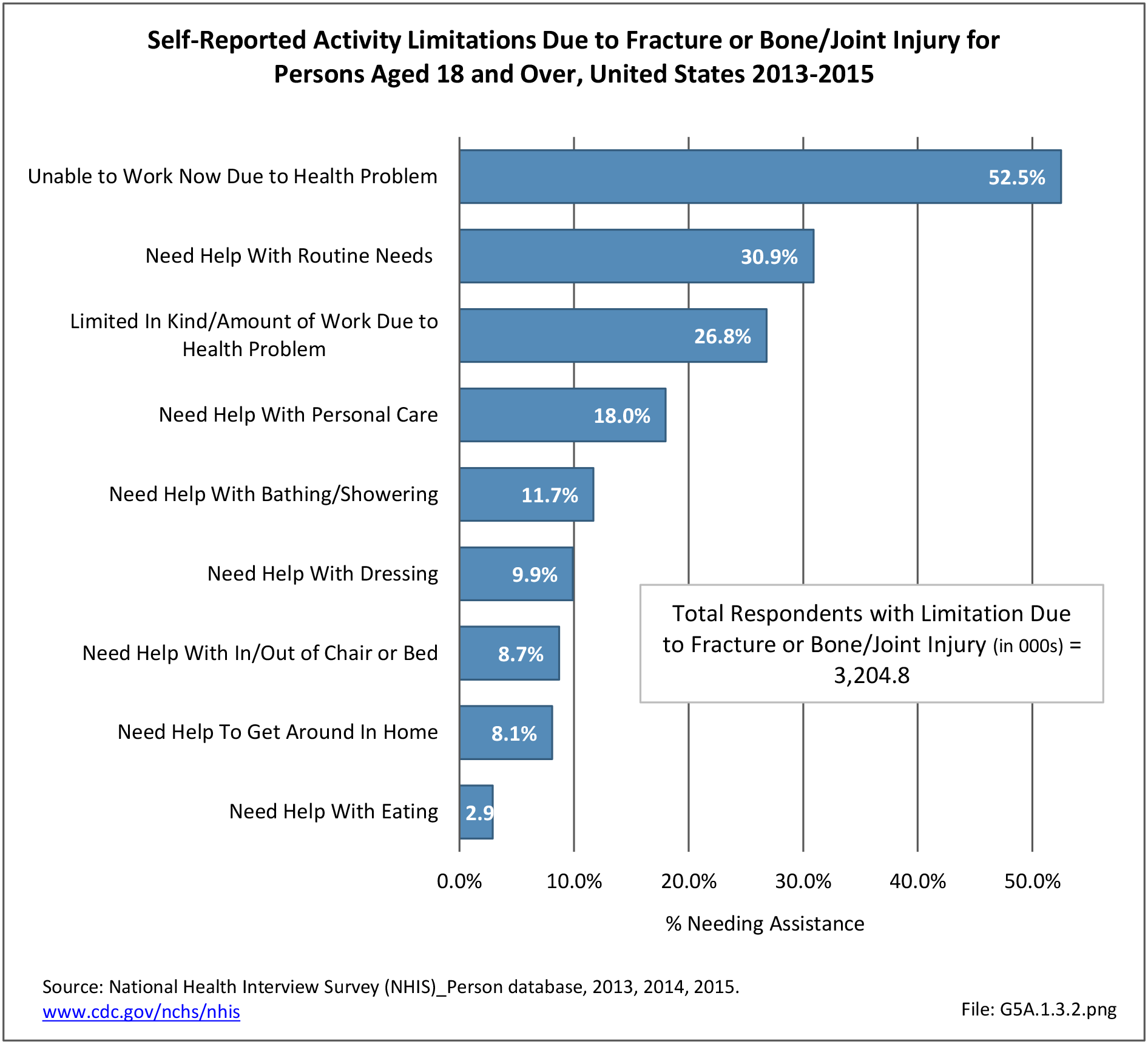
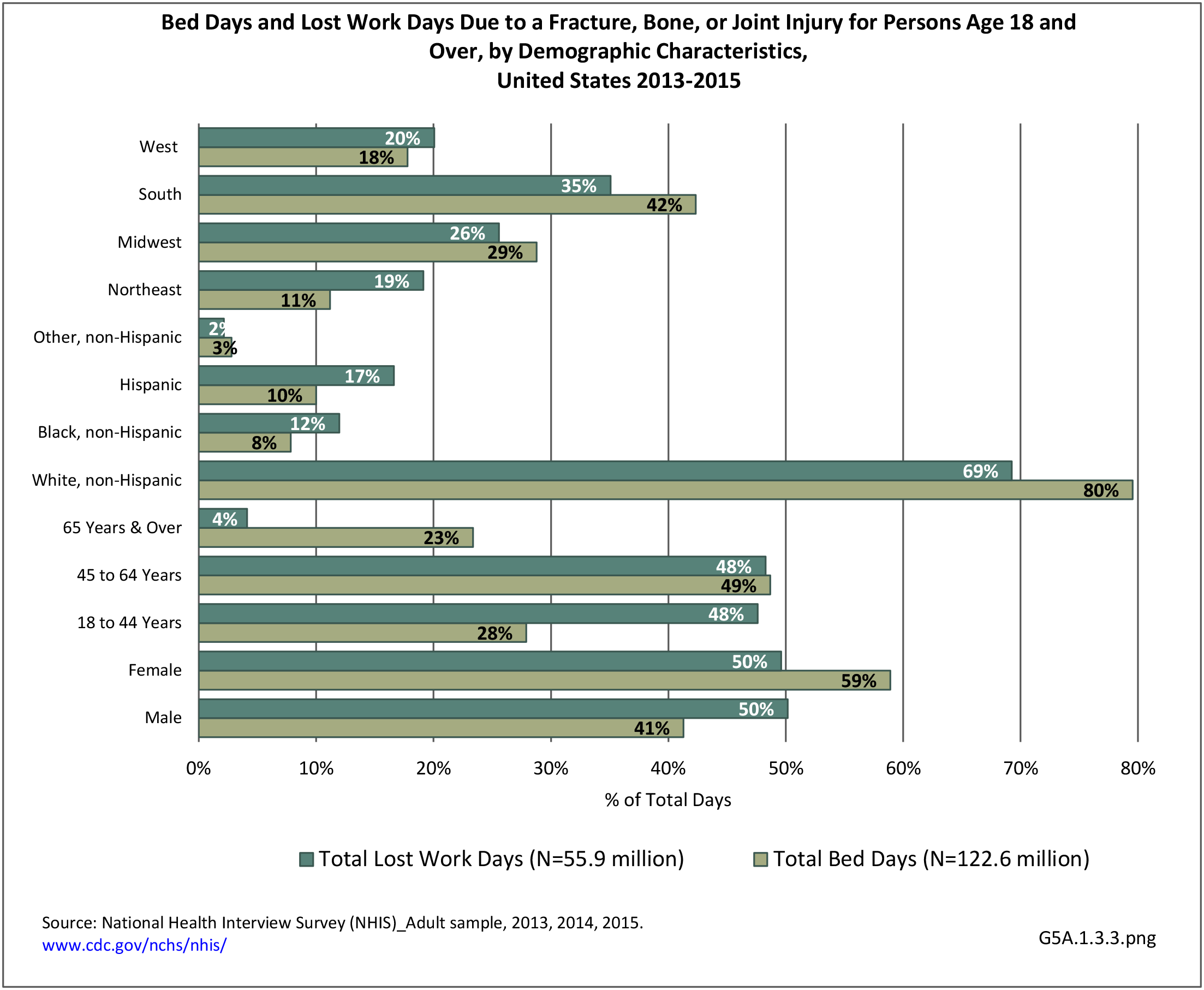
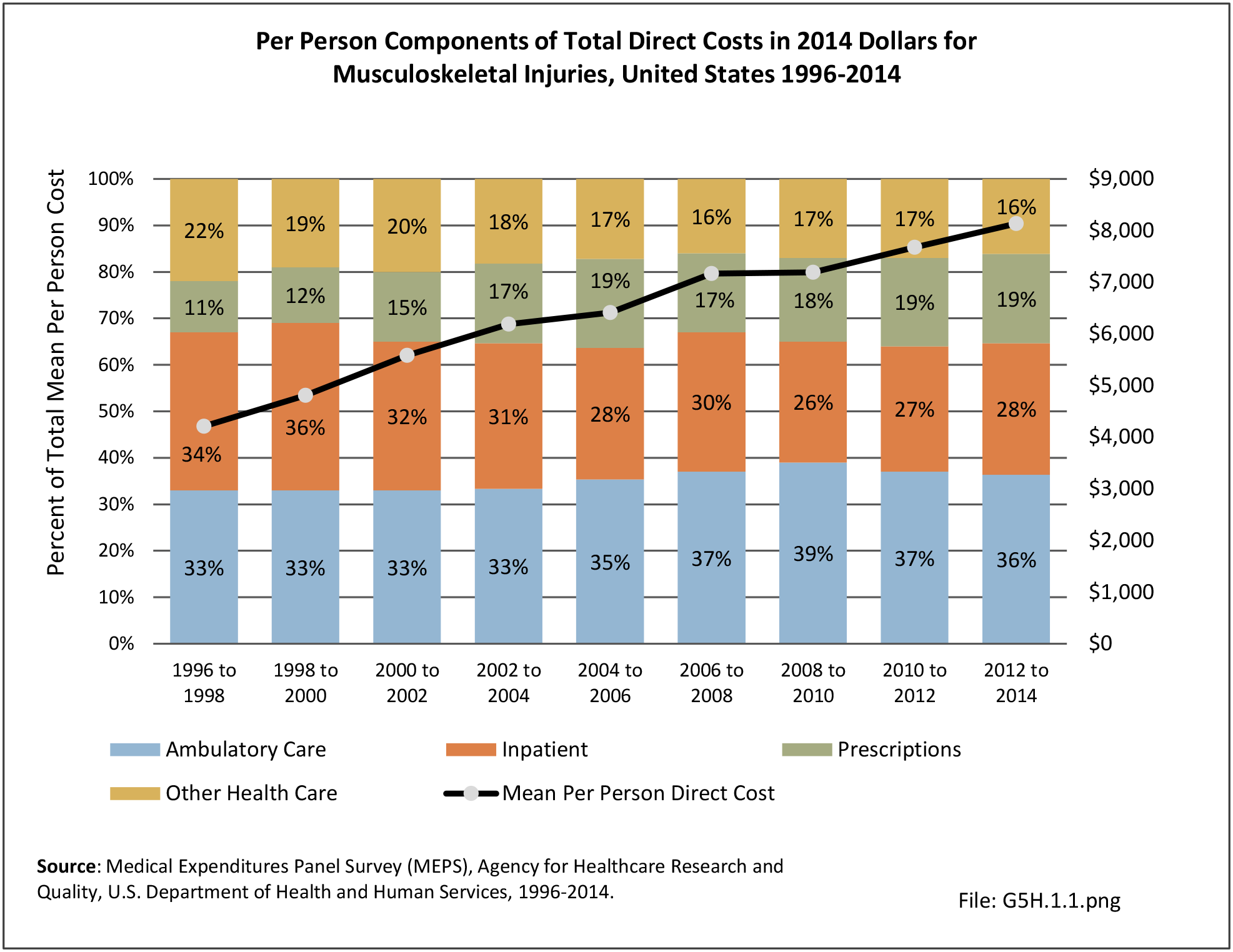
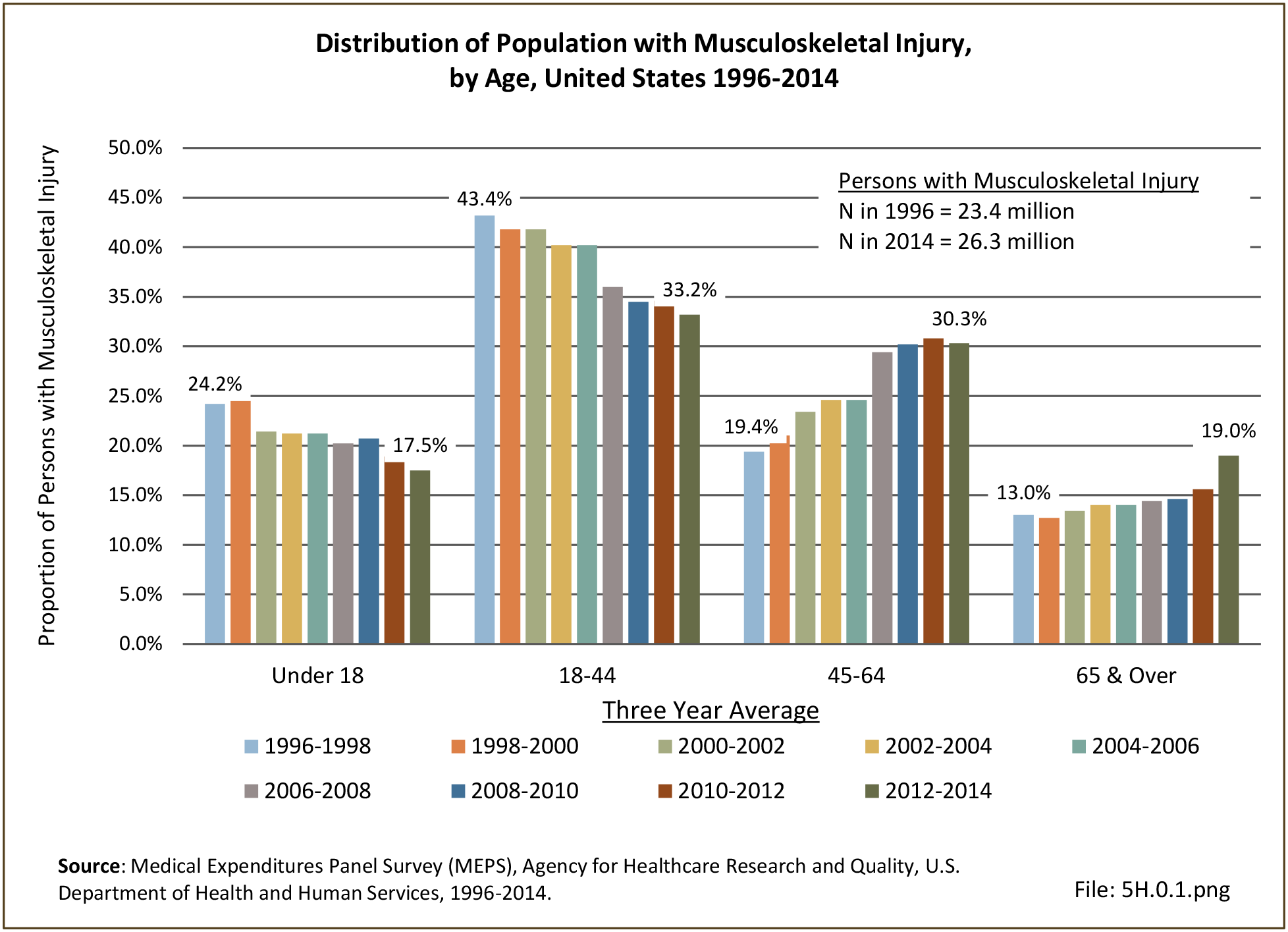
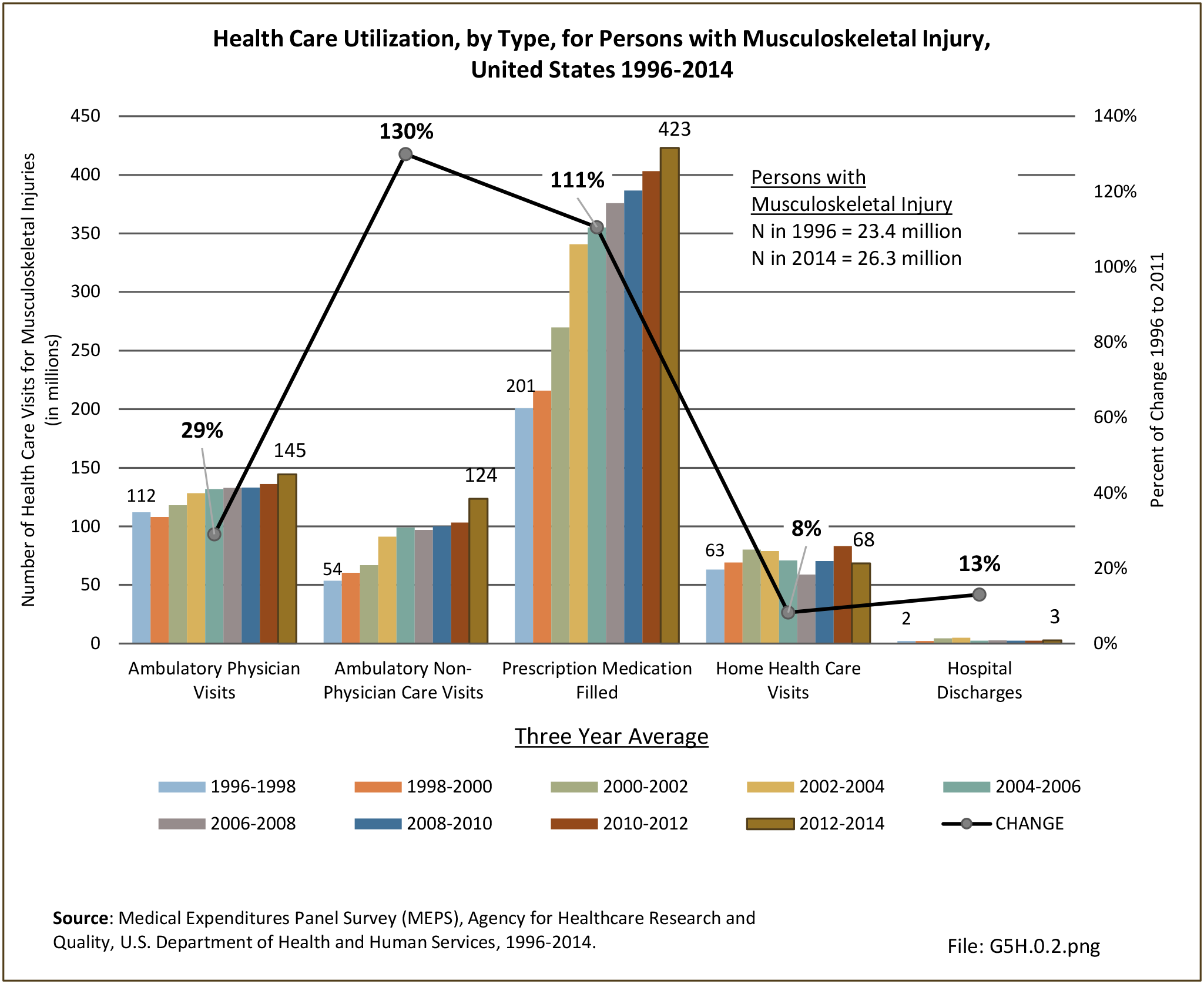
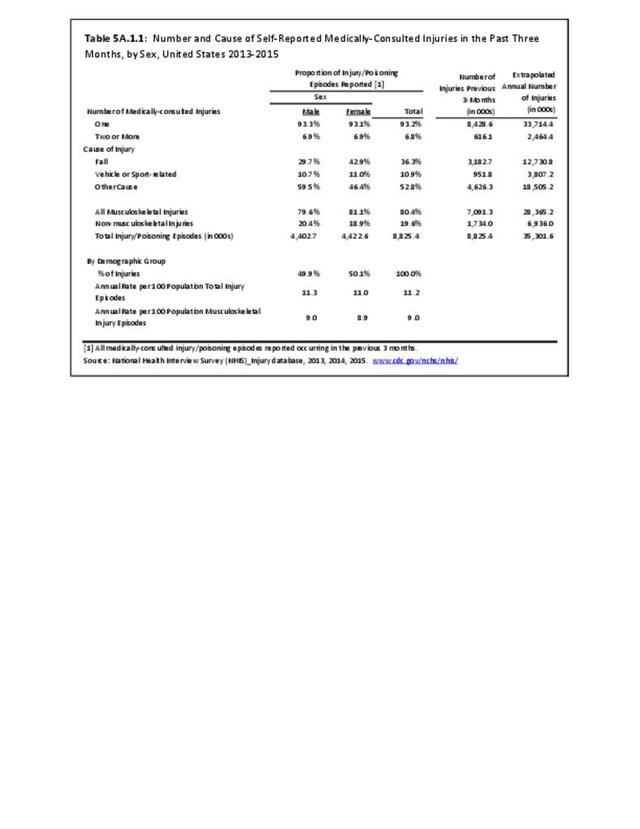
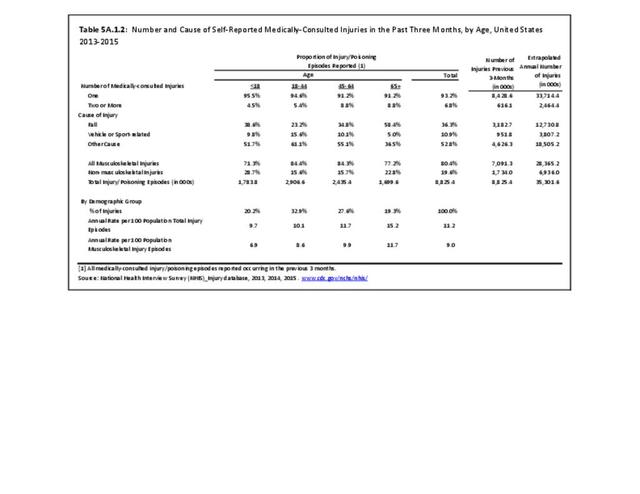
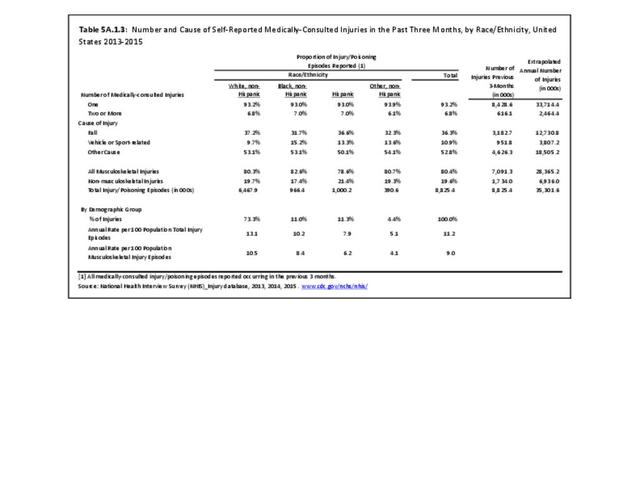
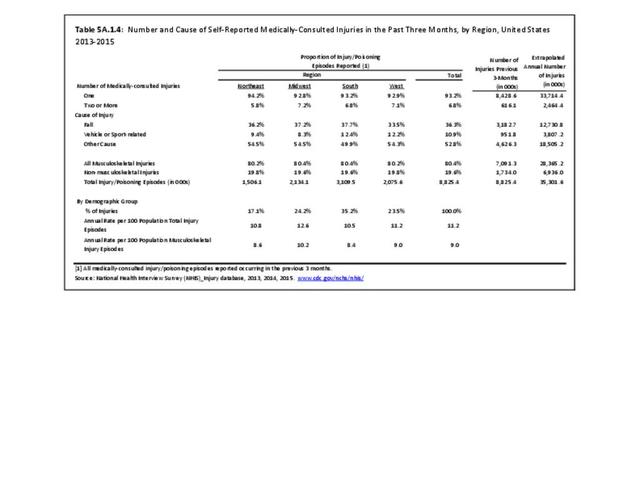
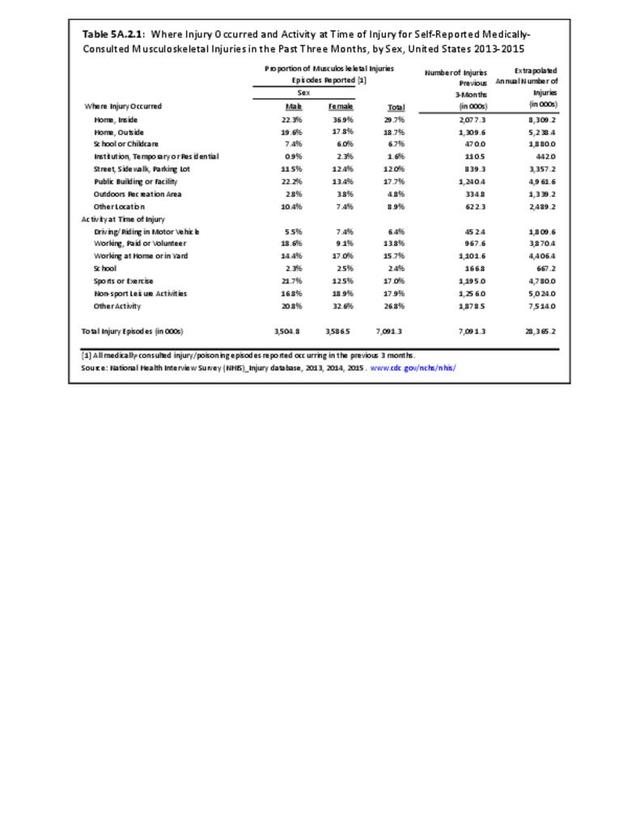
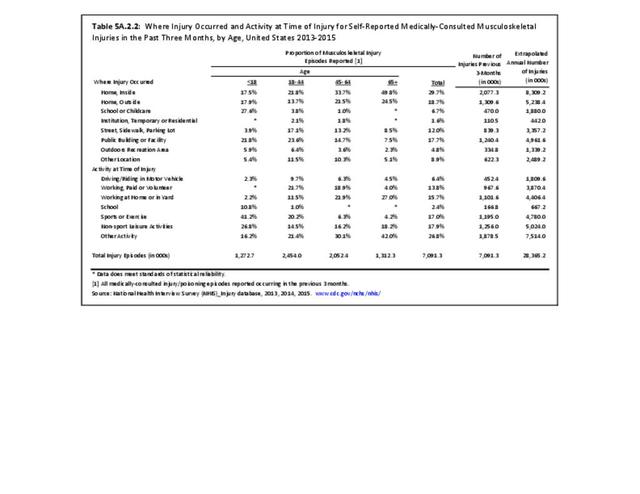
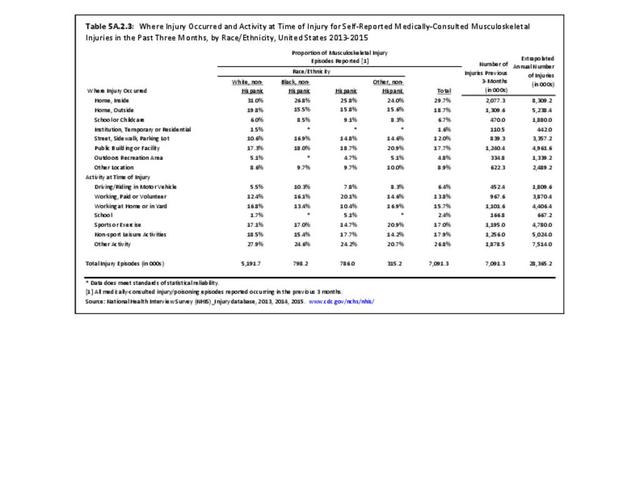
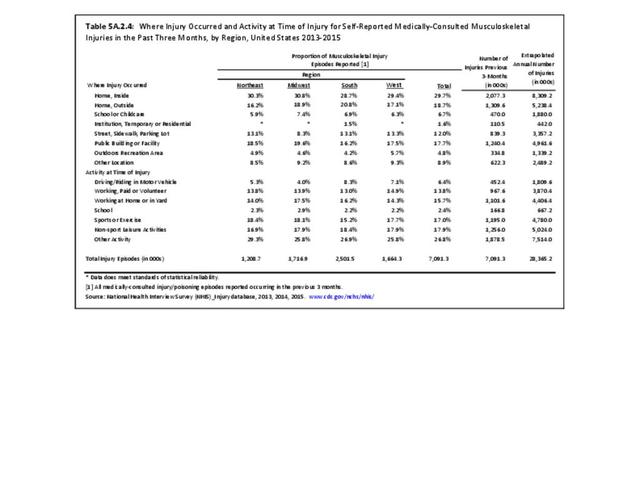
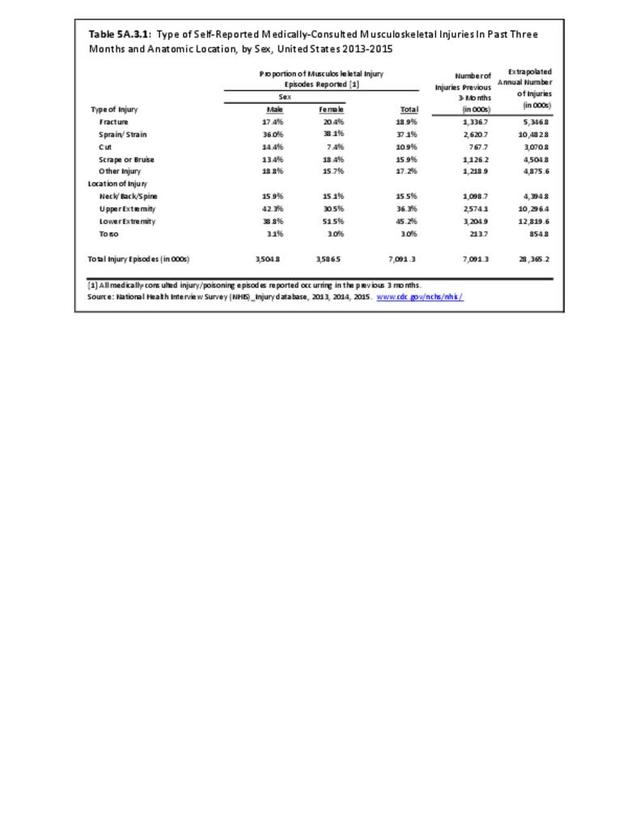
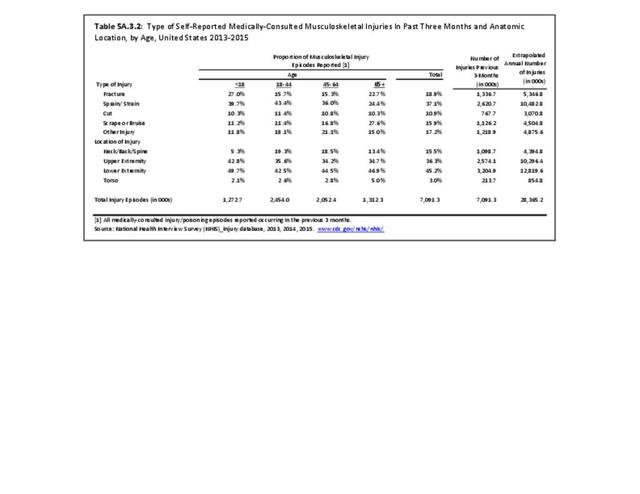
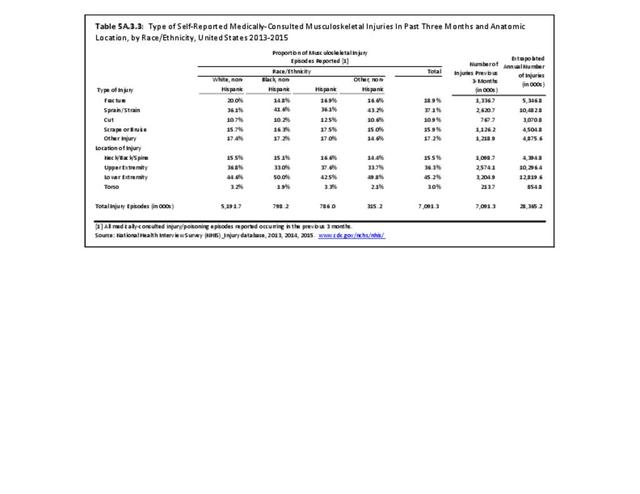
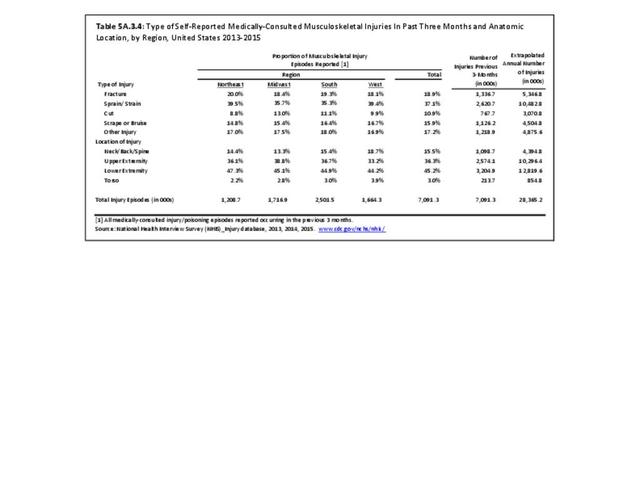
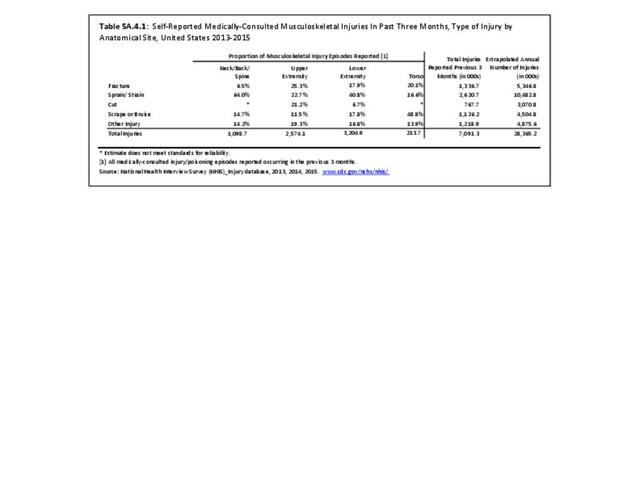
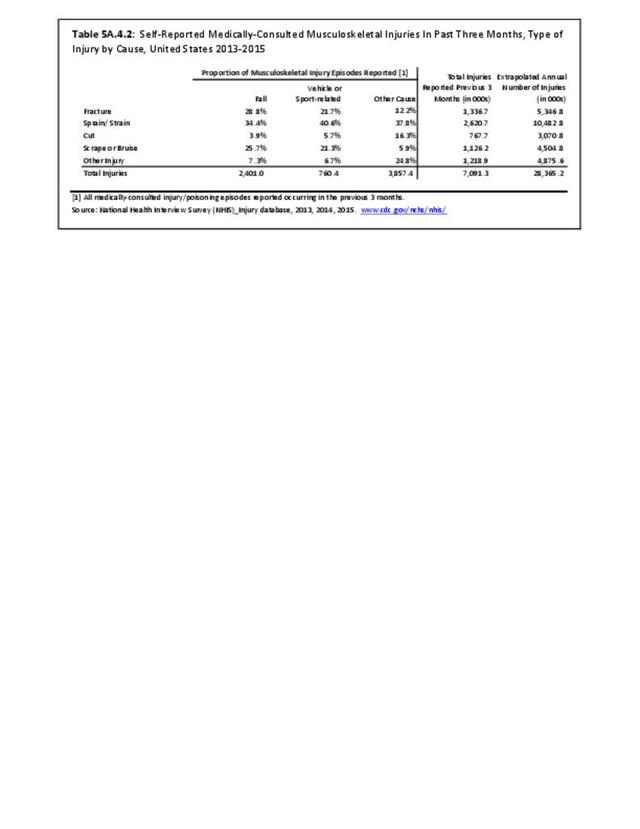
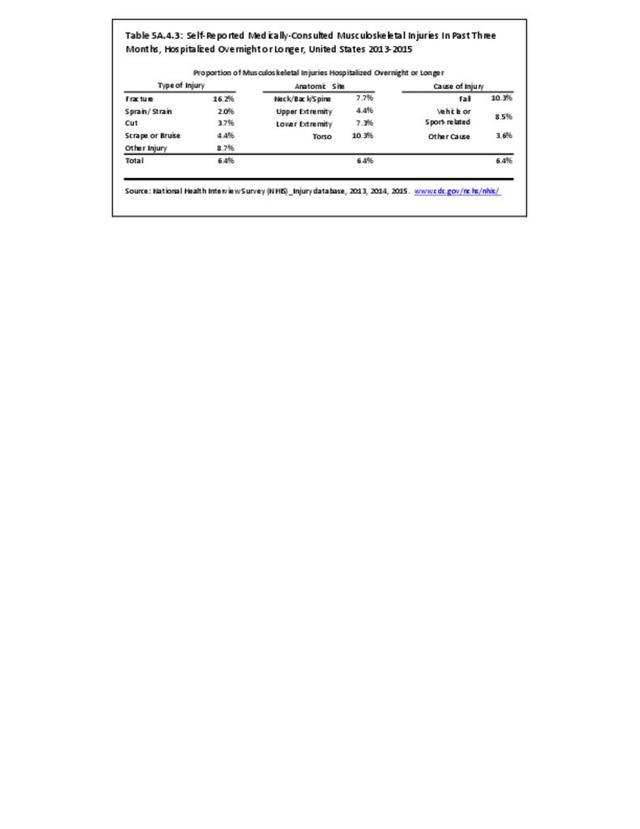
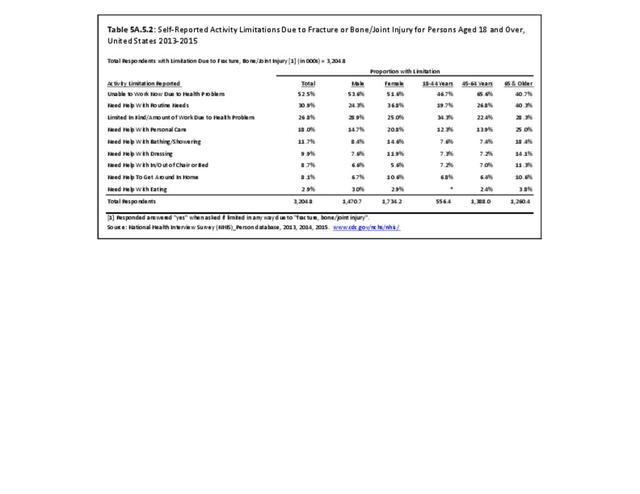
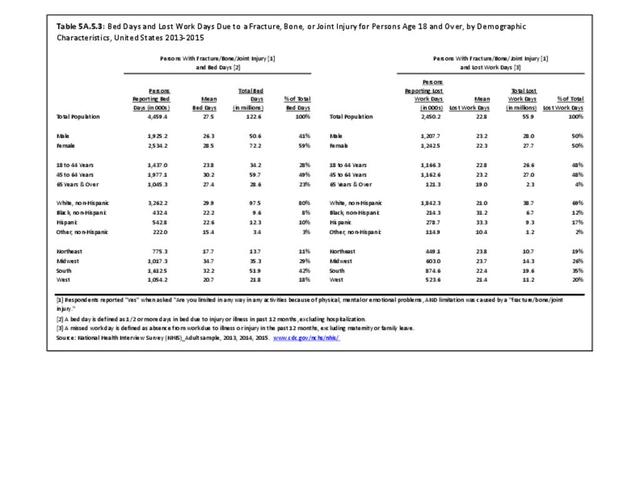
Self-reported Injuries: Data for this topic is based primarily on the National Health Interviews Survey (NHIS), conducted annually since 1957 by the National Center for Health Statistics, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US Department of Health and Human Services. The survey includes self-reported questions on medical conditions, health insurance, doctor’s office visits, and physical activity and other health behaviors. Because of small sample sizes for some conditions, data is often merged for three years, the result being an average across the time period.
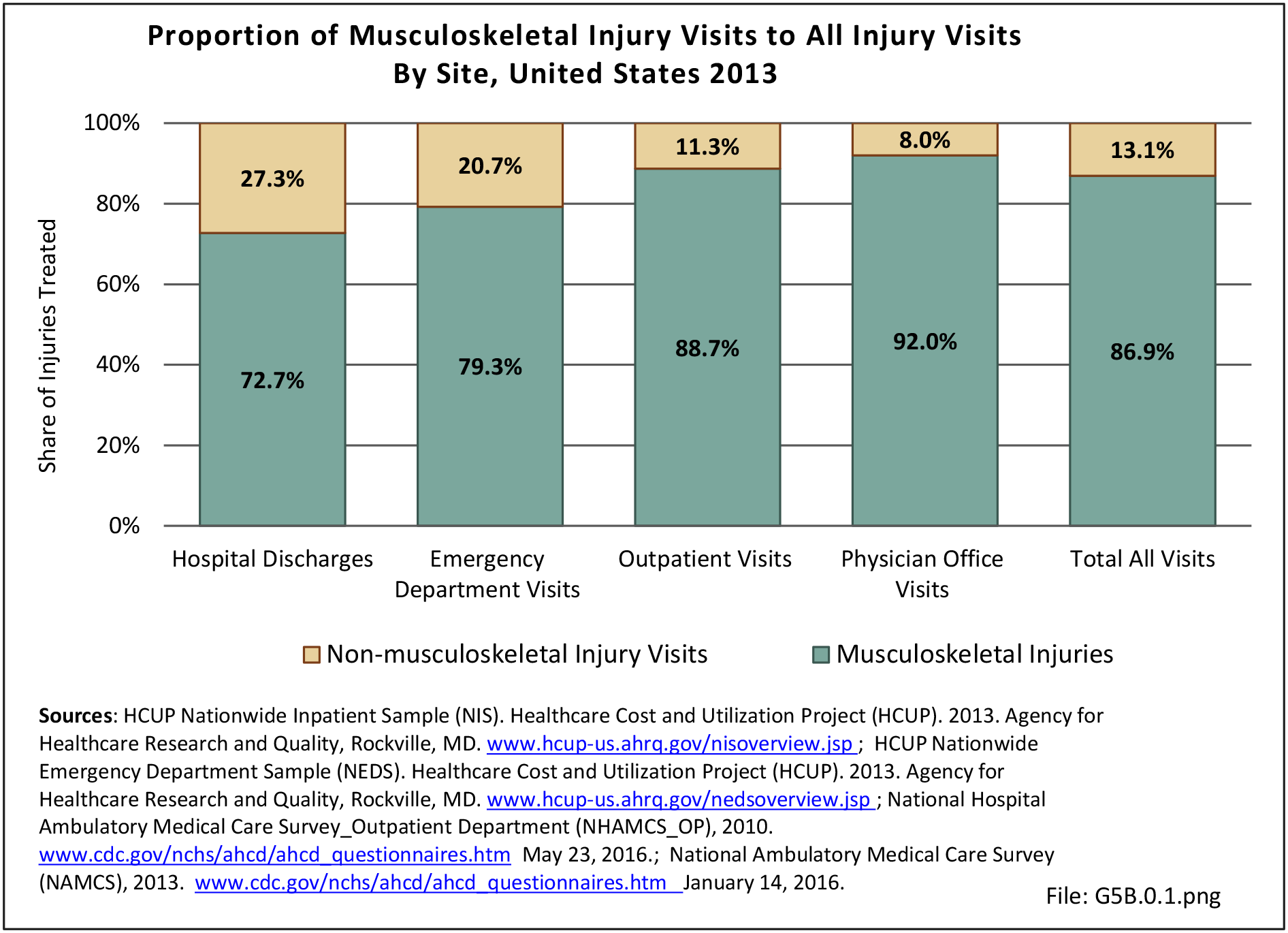
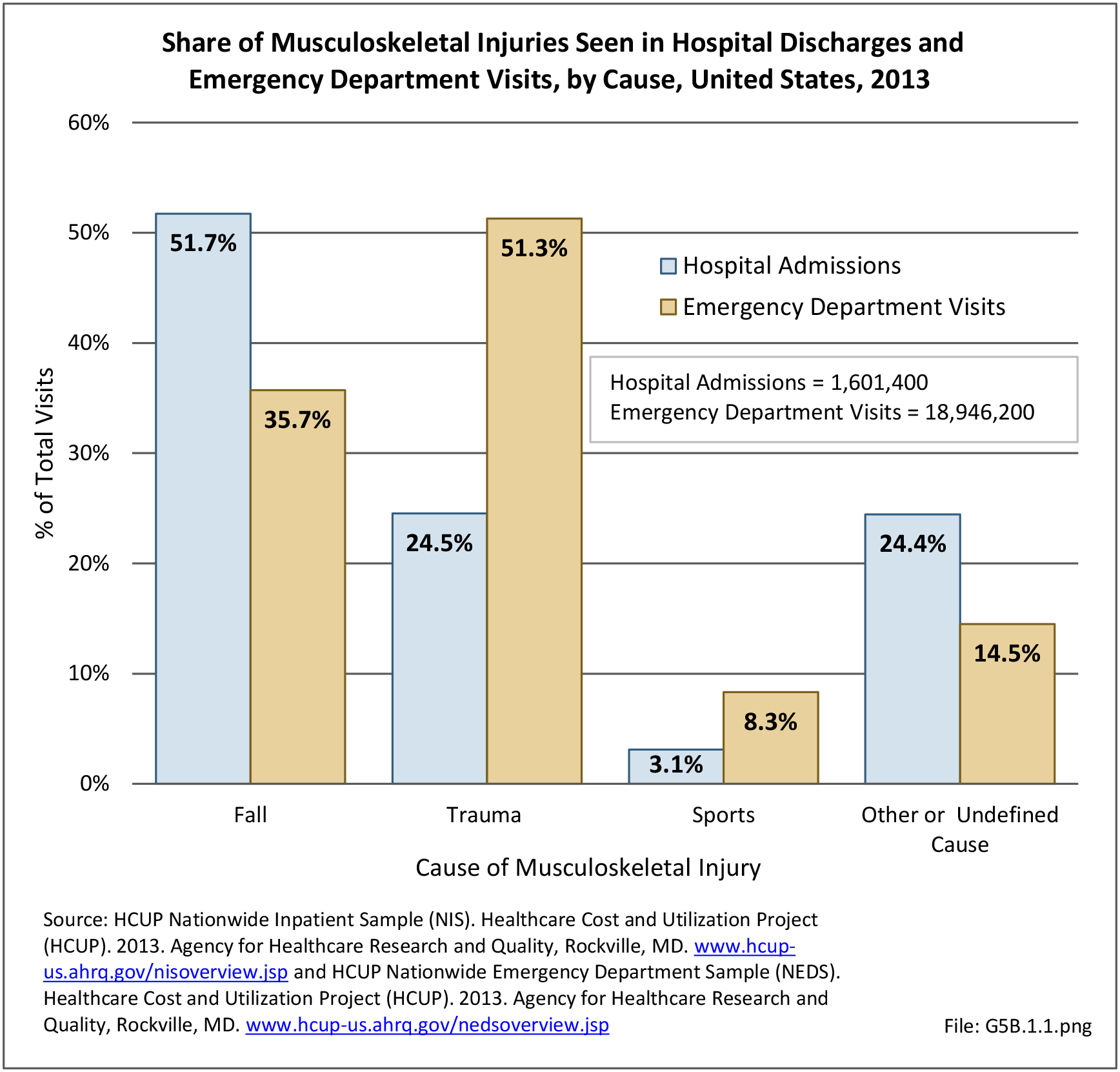
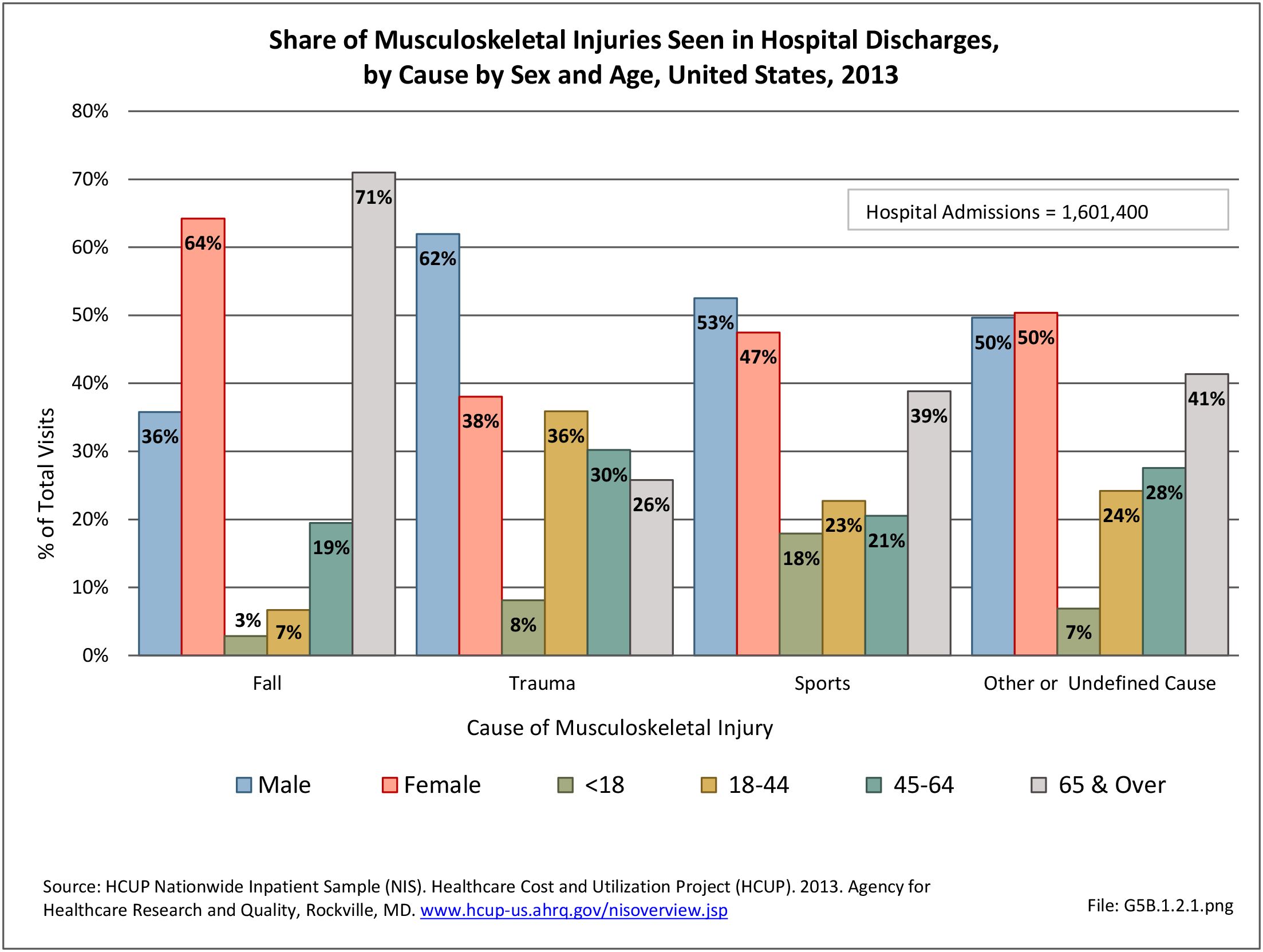
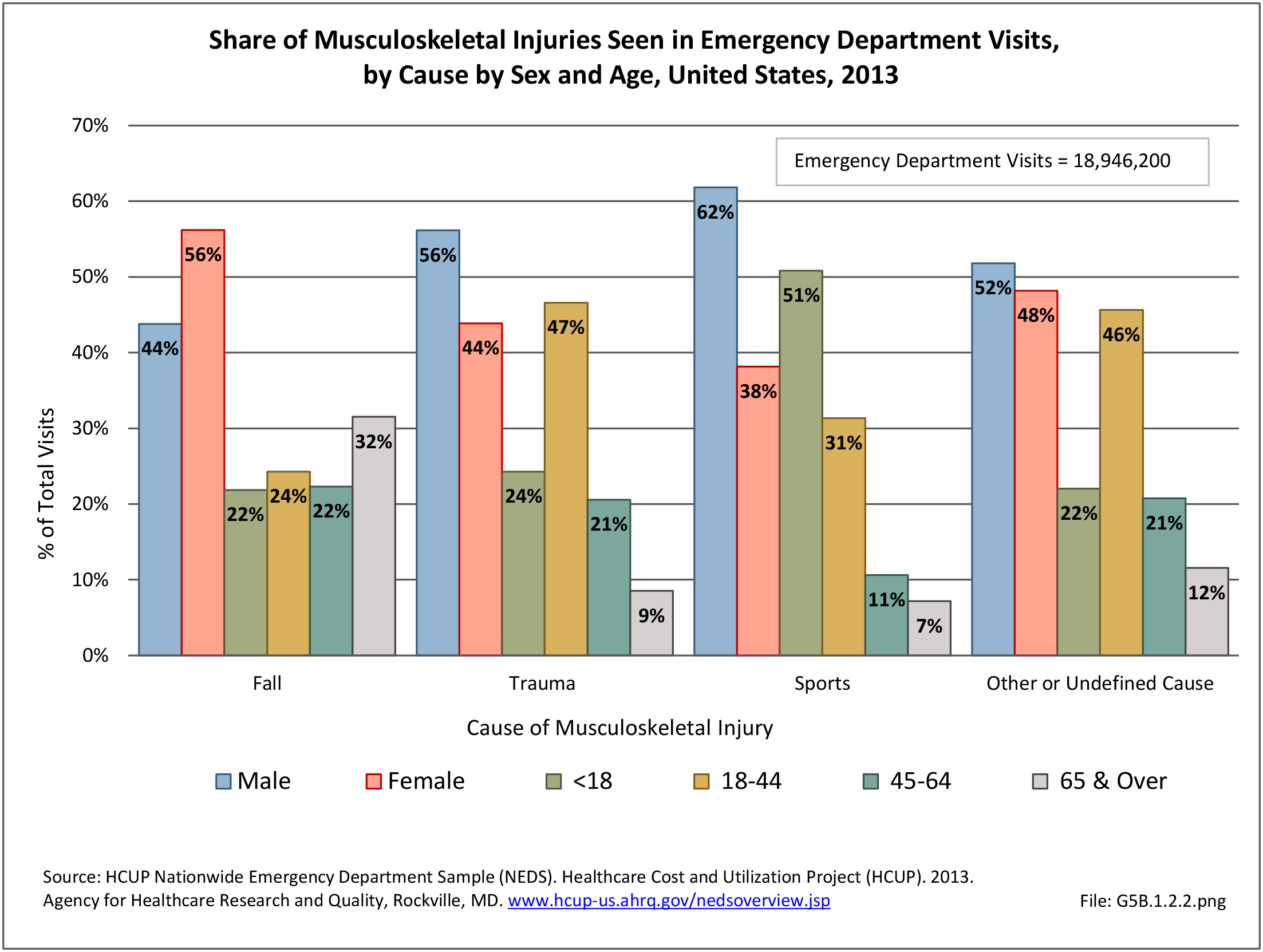
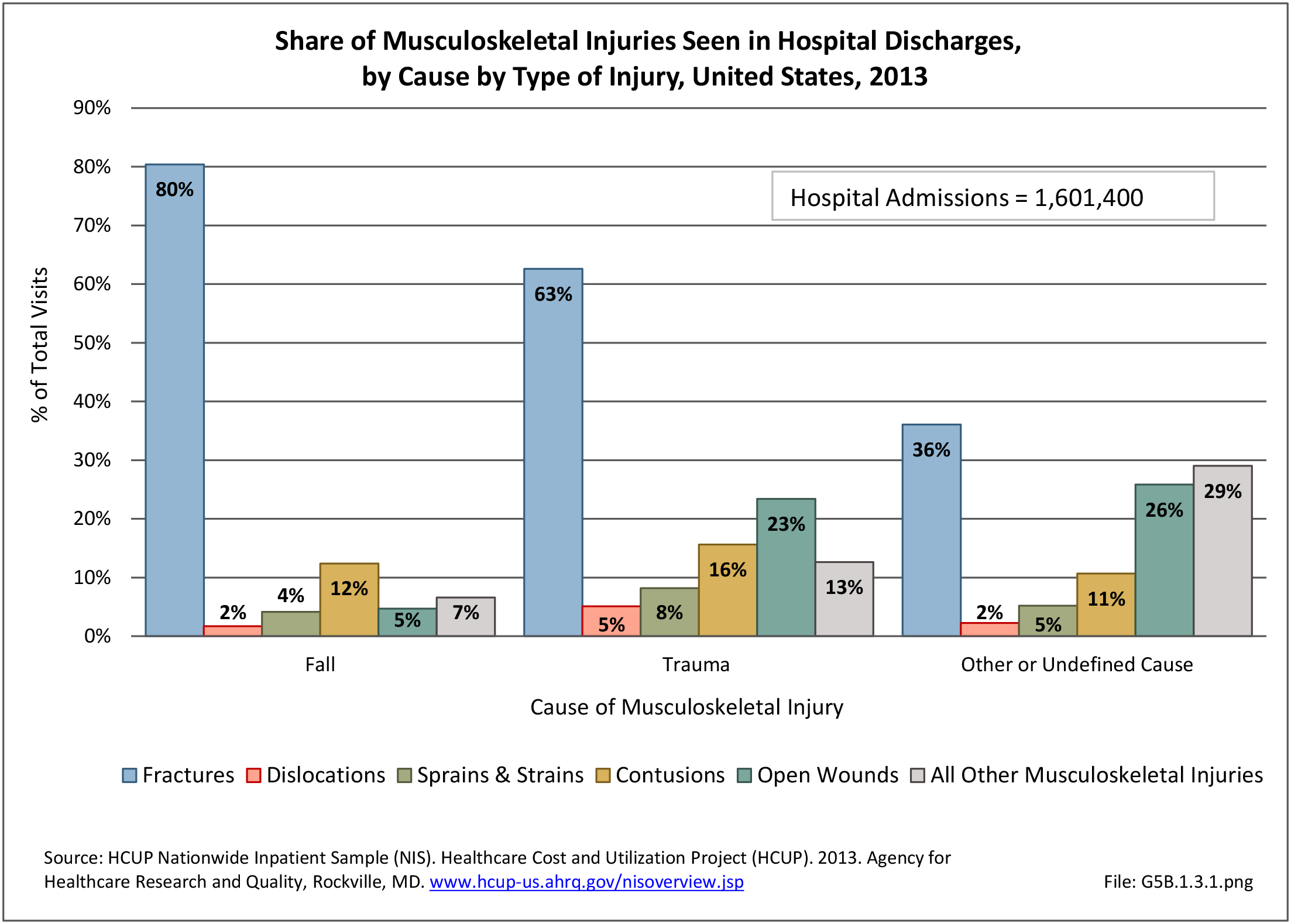
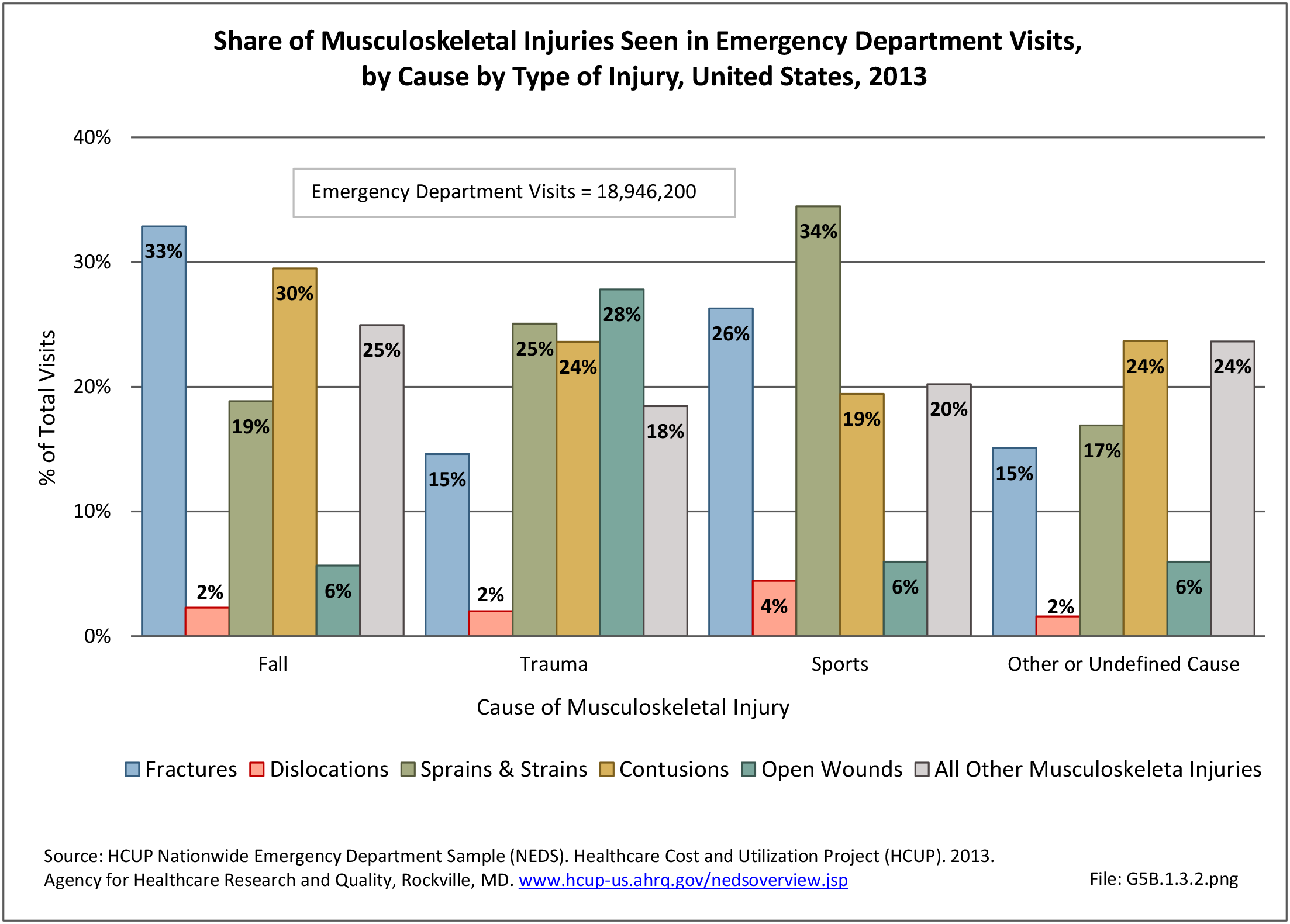
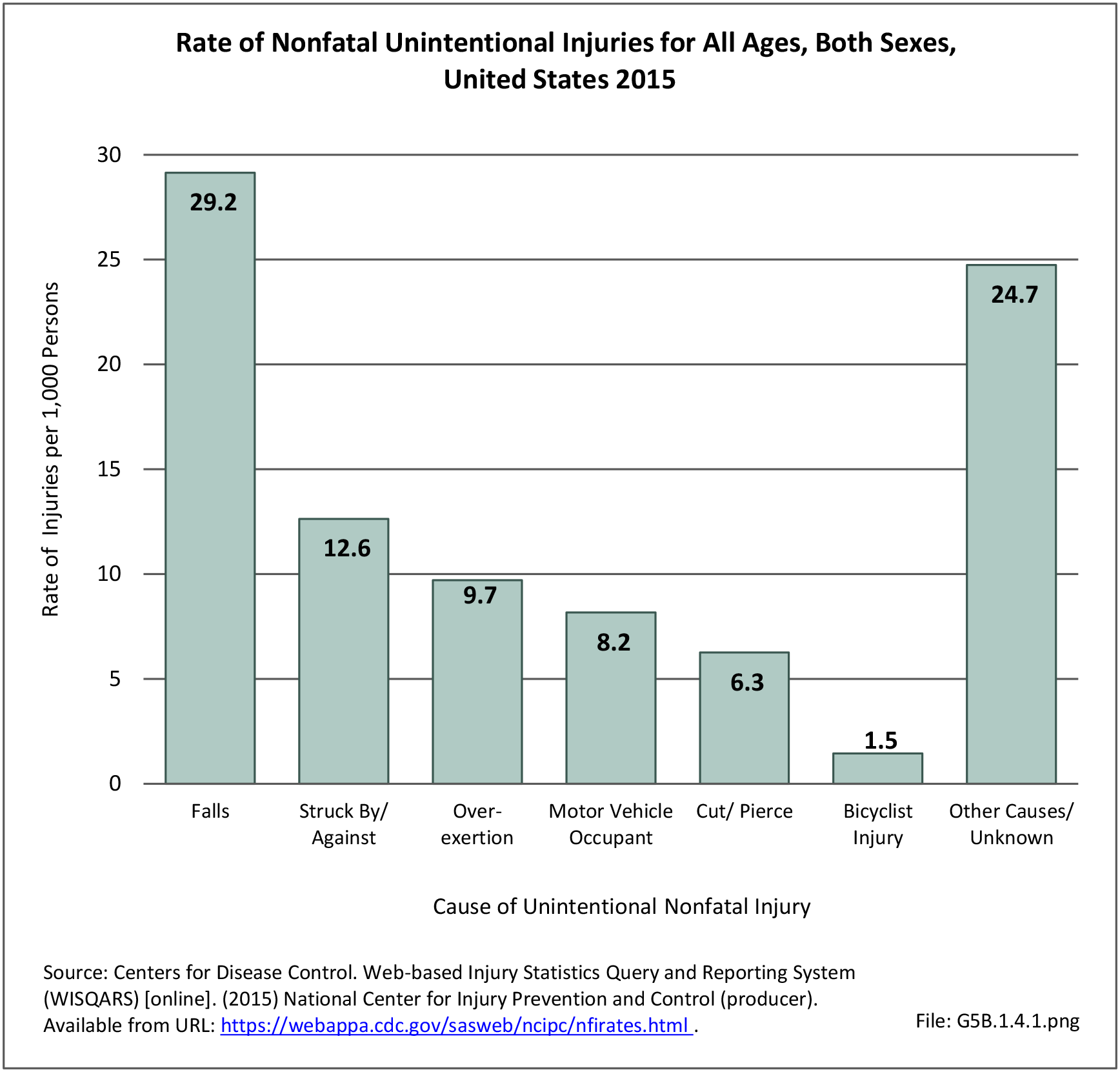
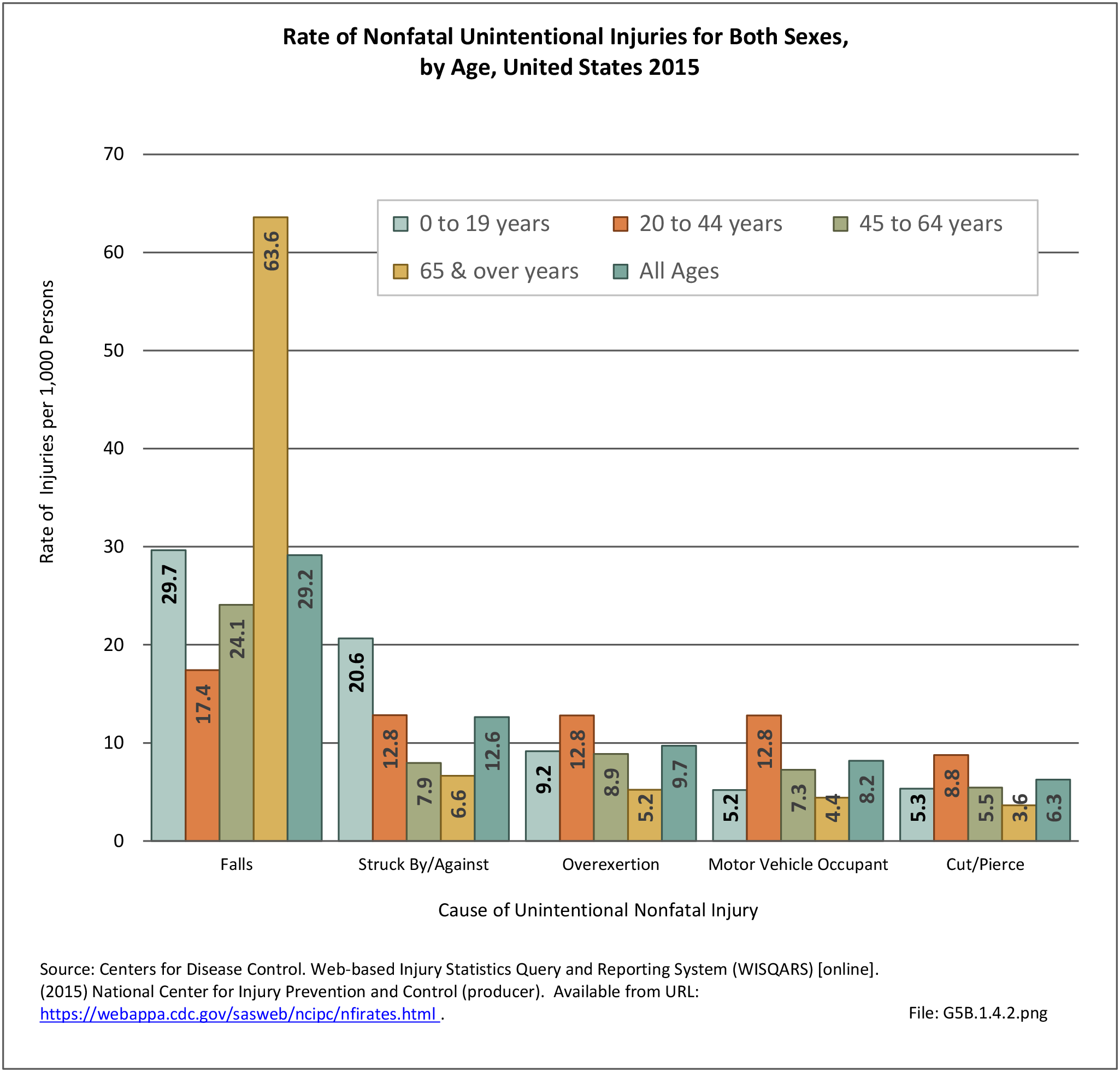
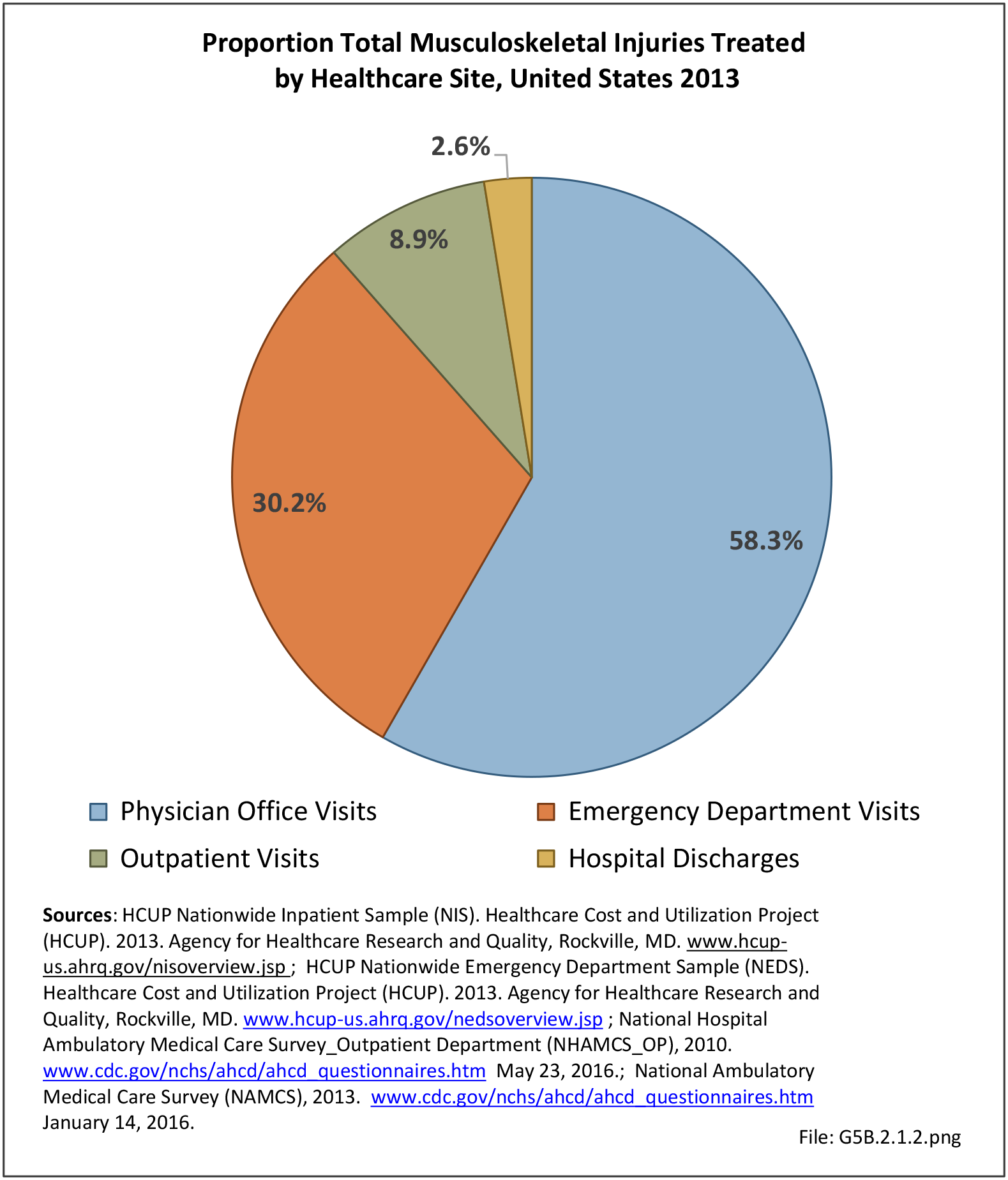
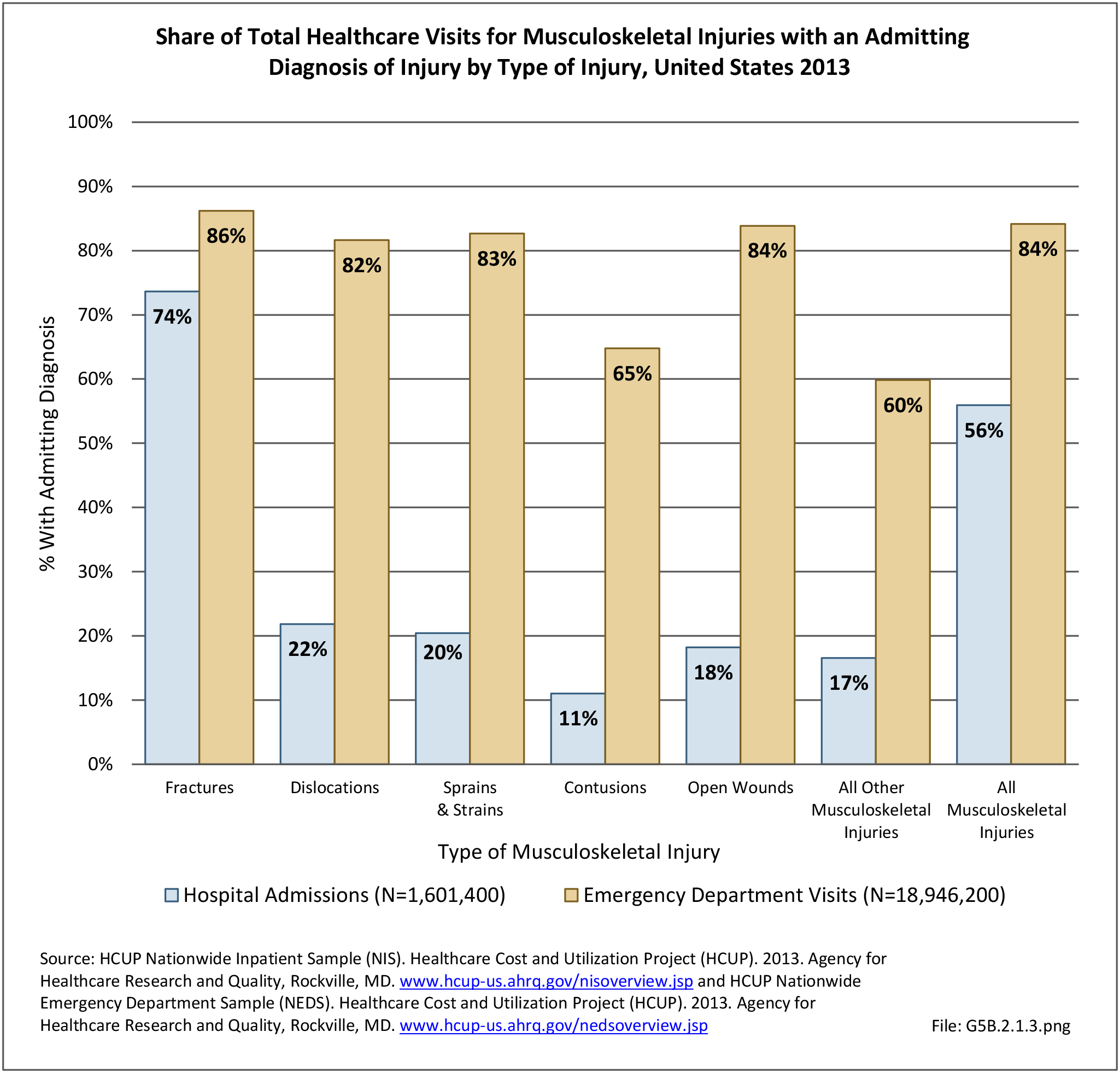
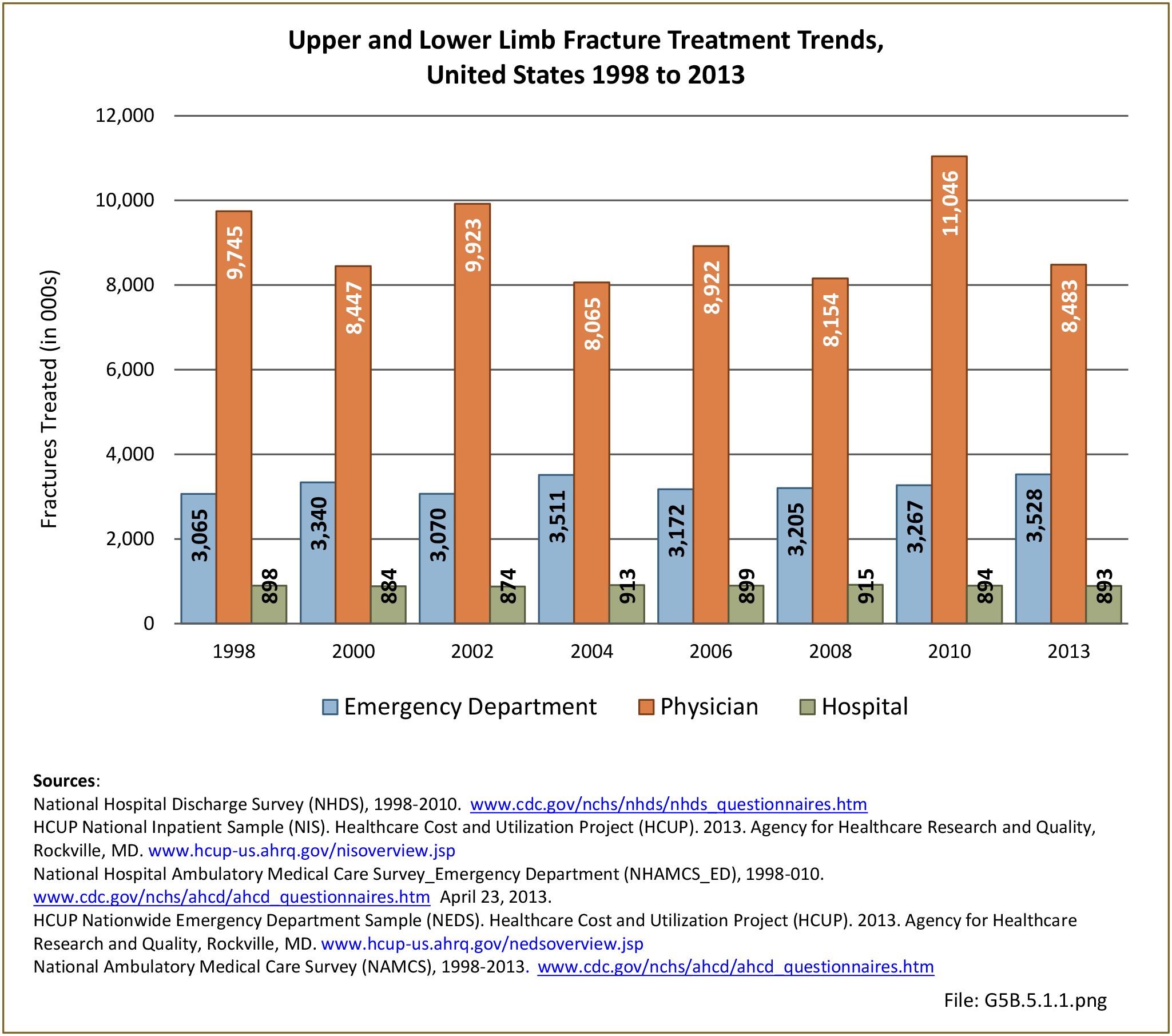
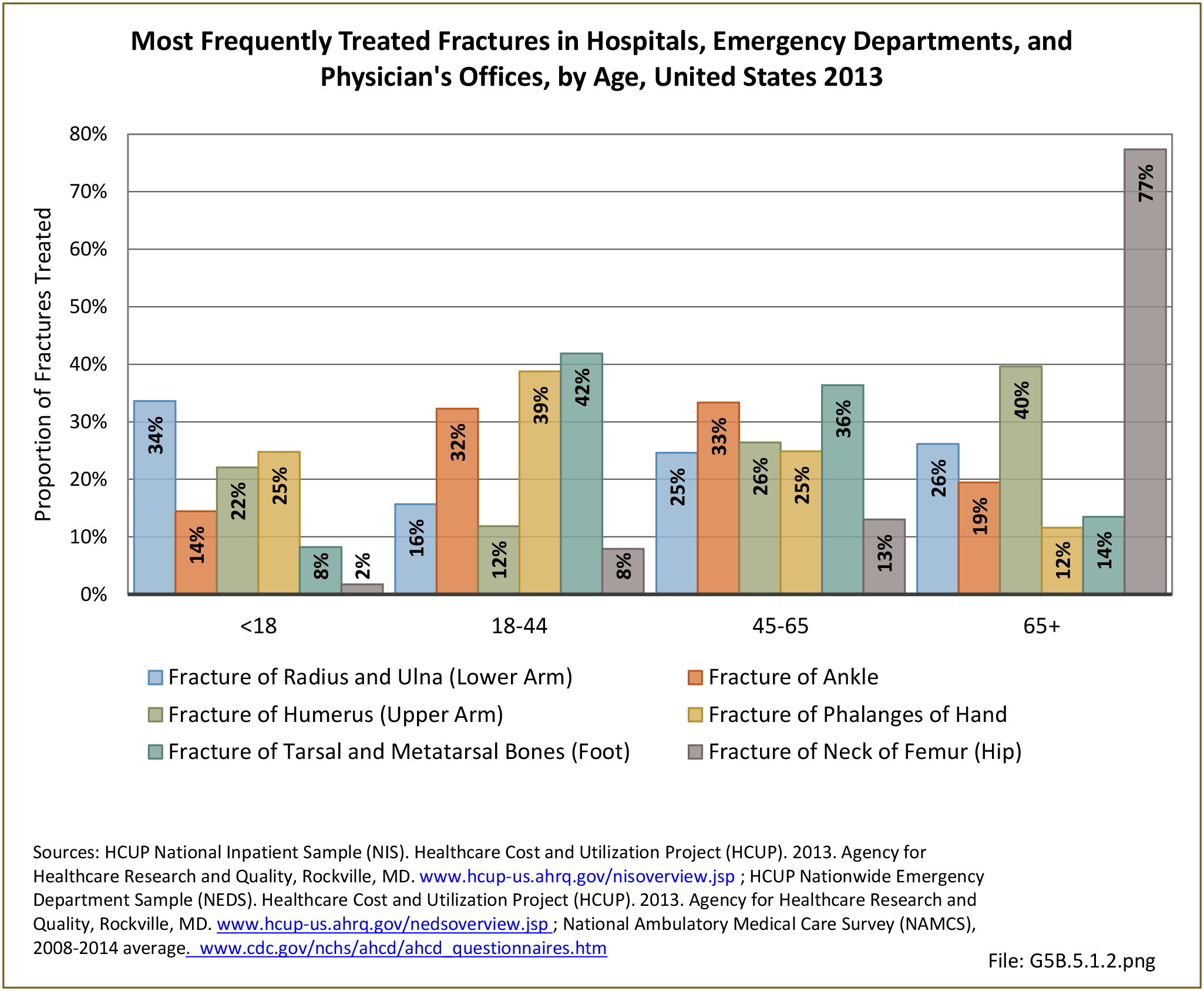
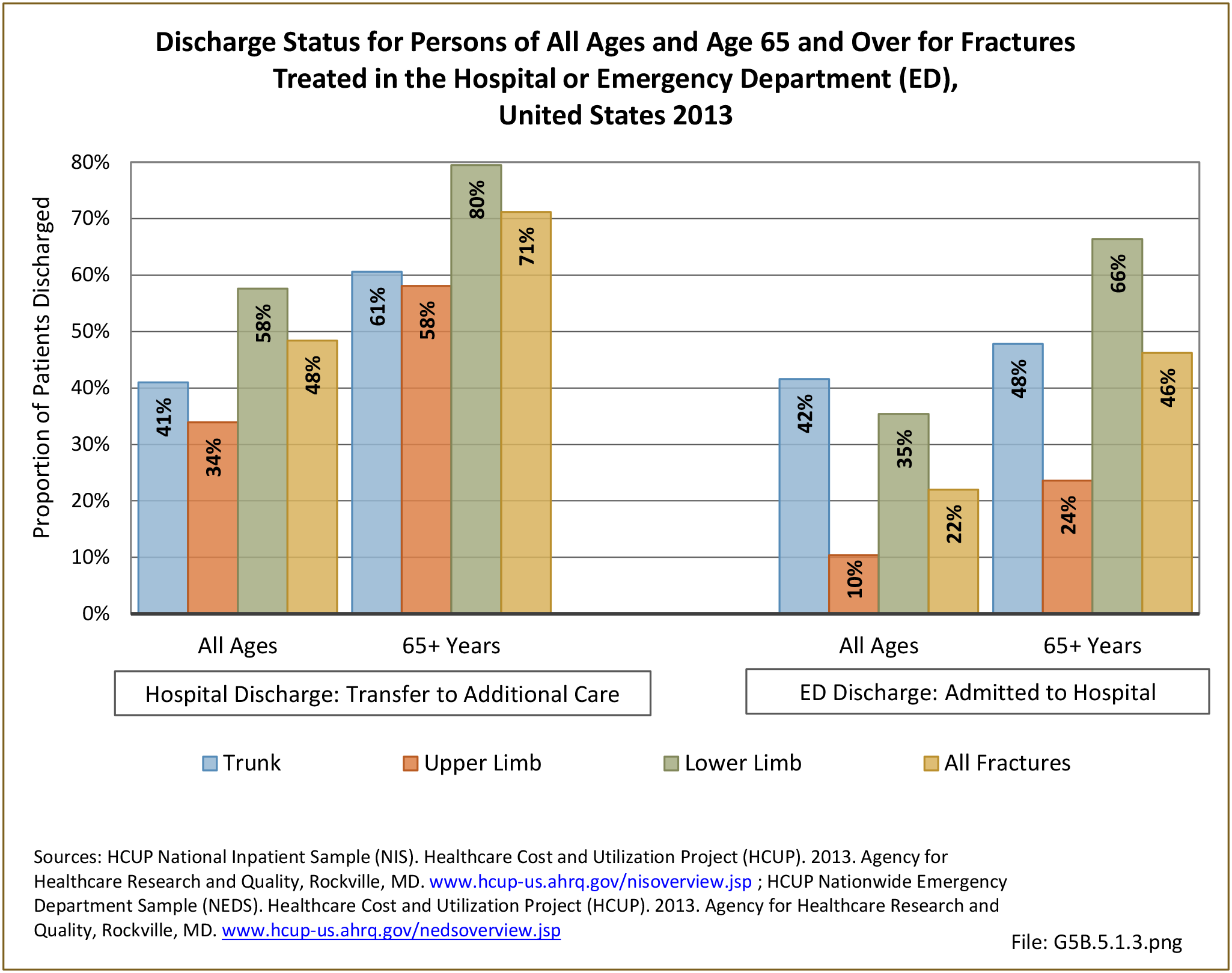
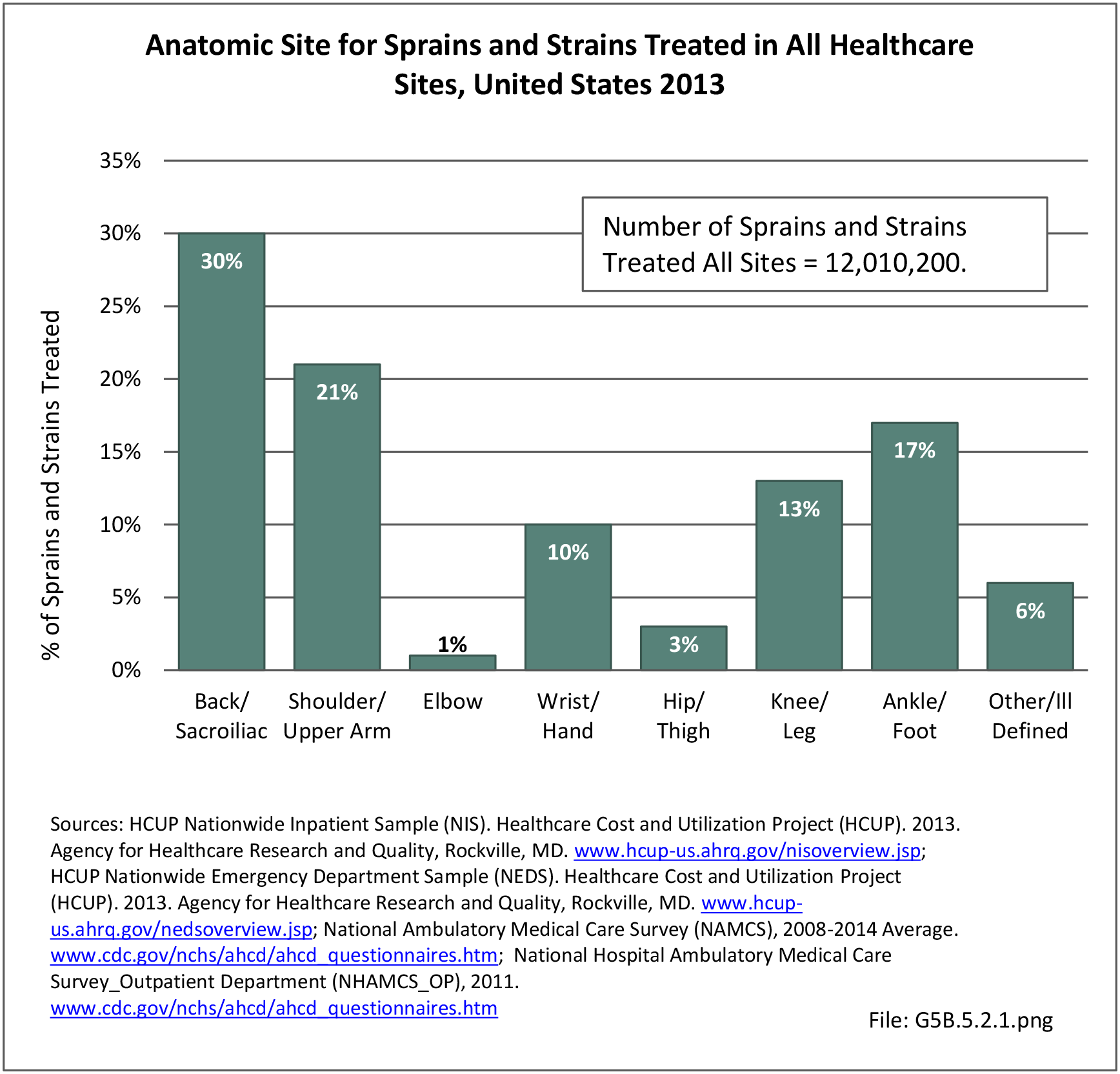
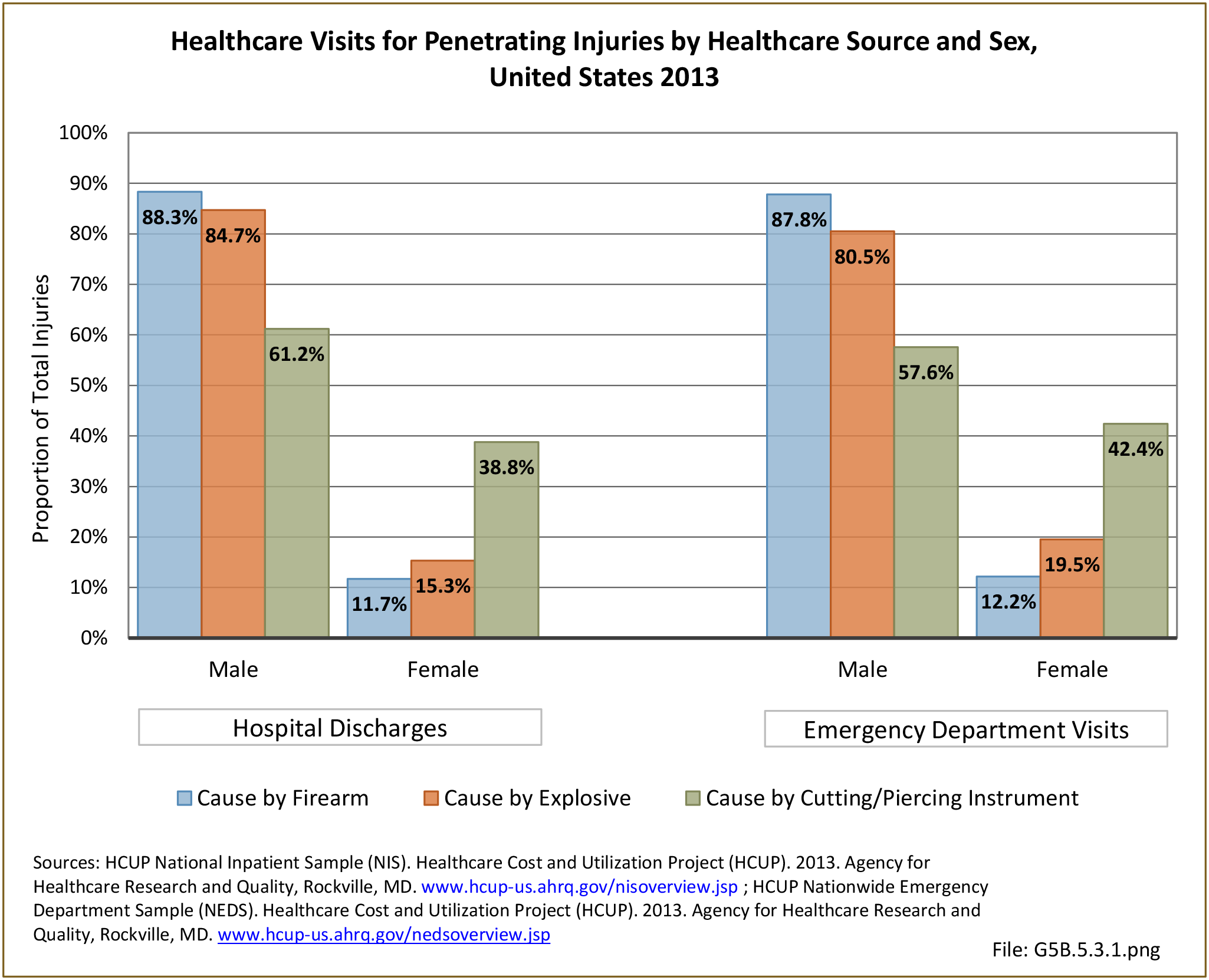
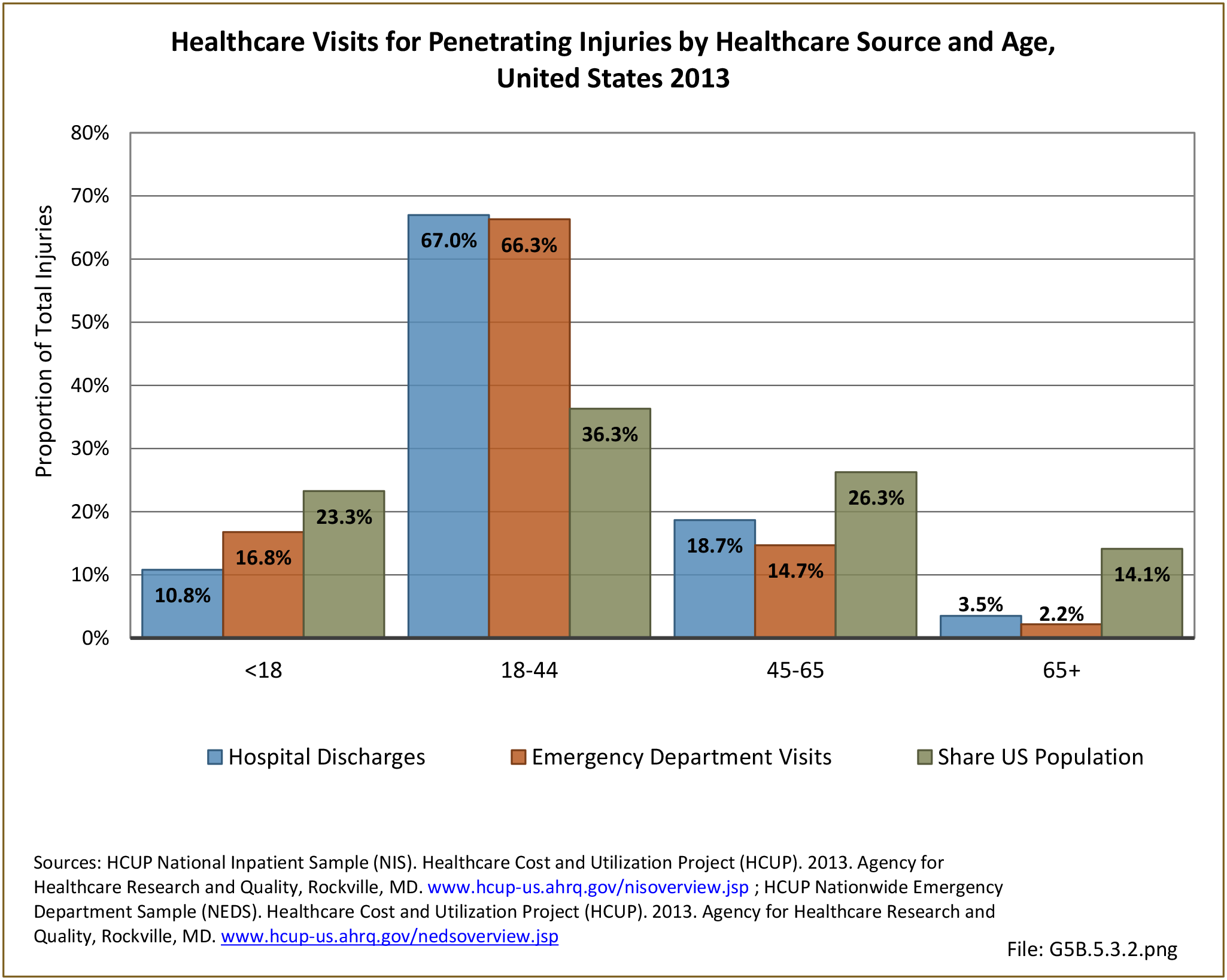
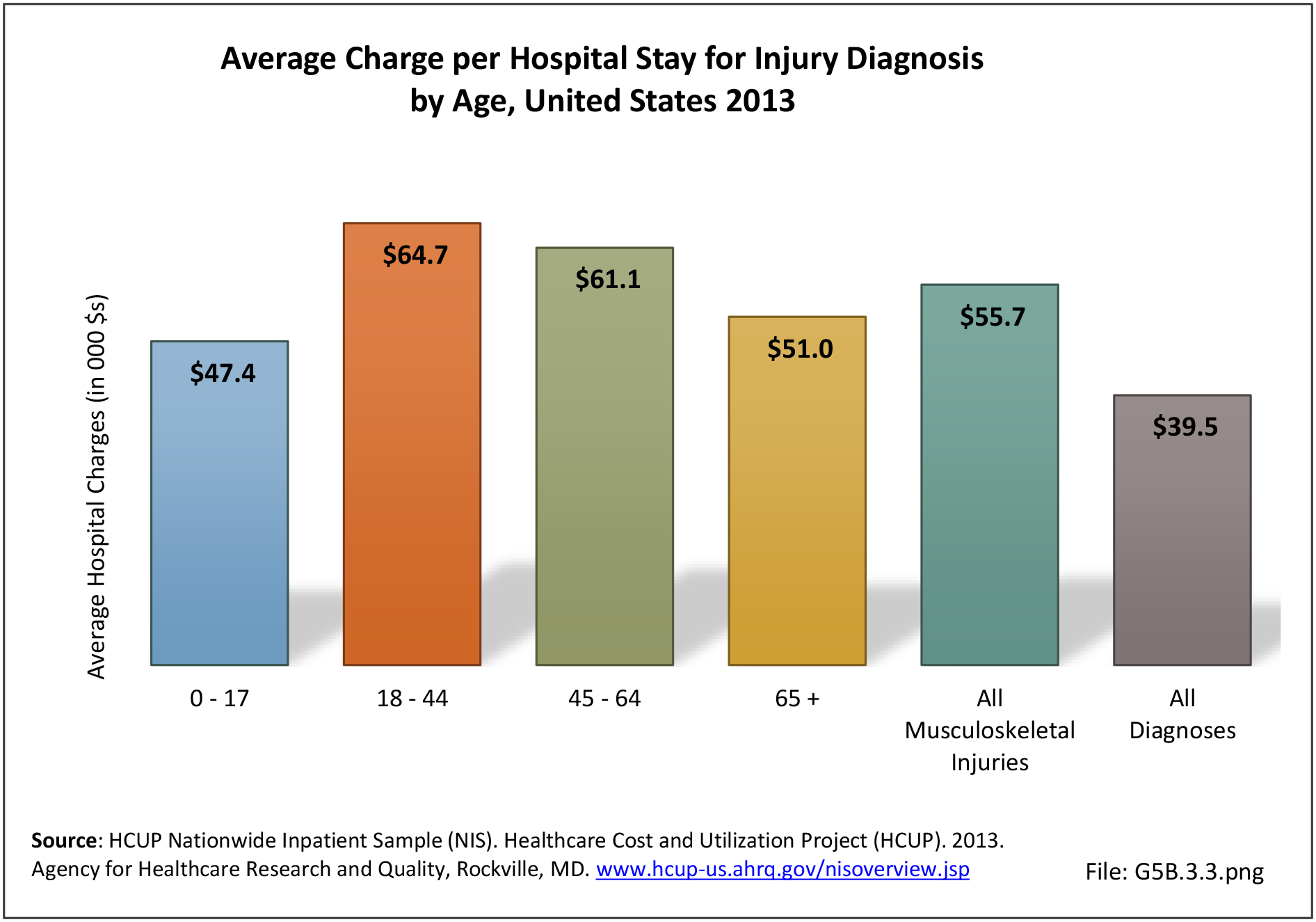
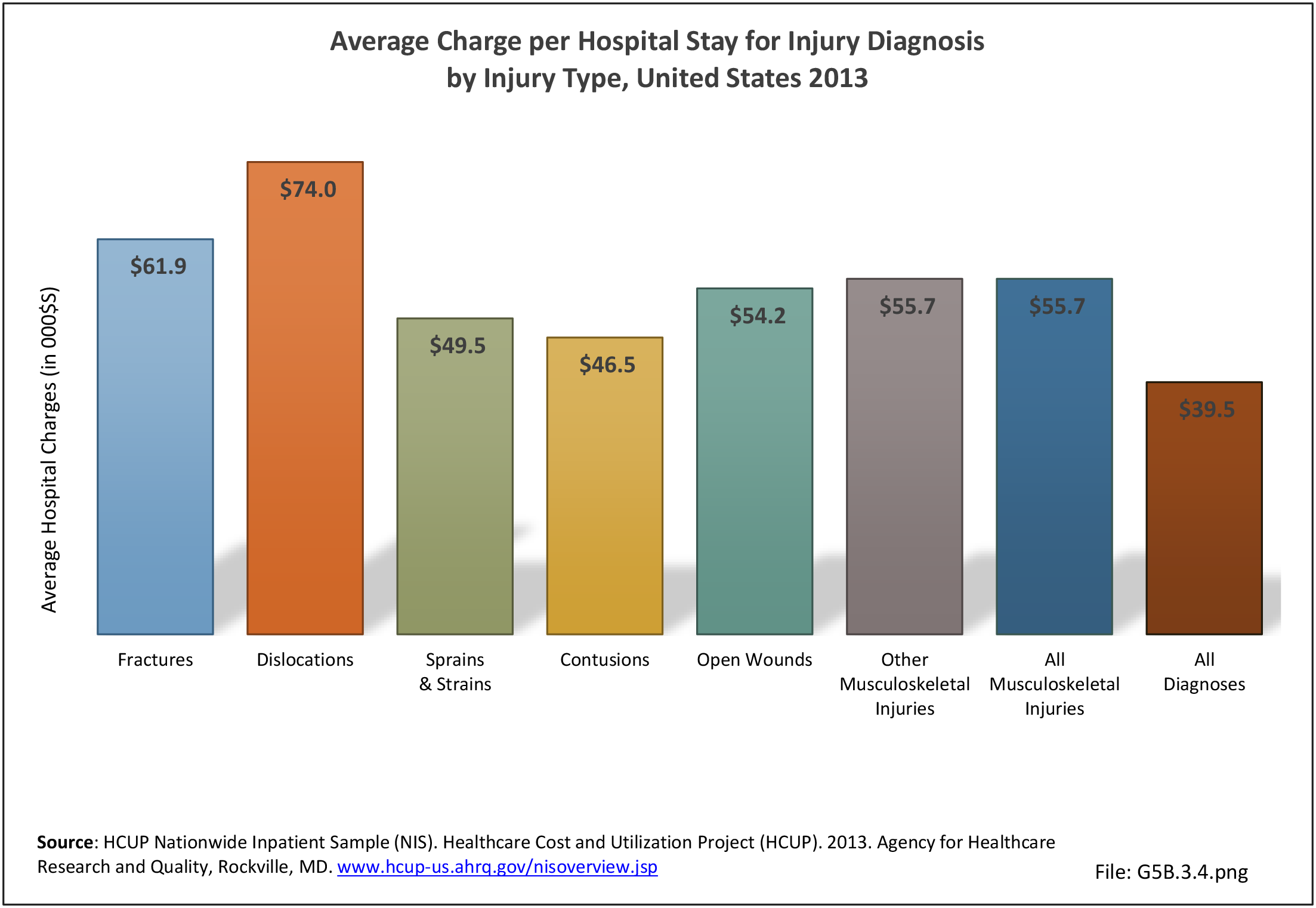
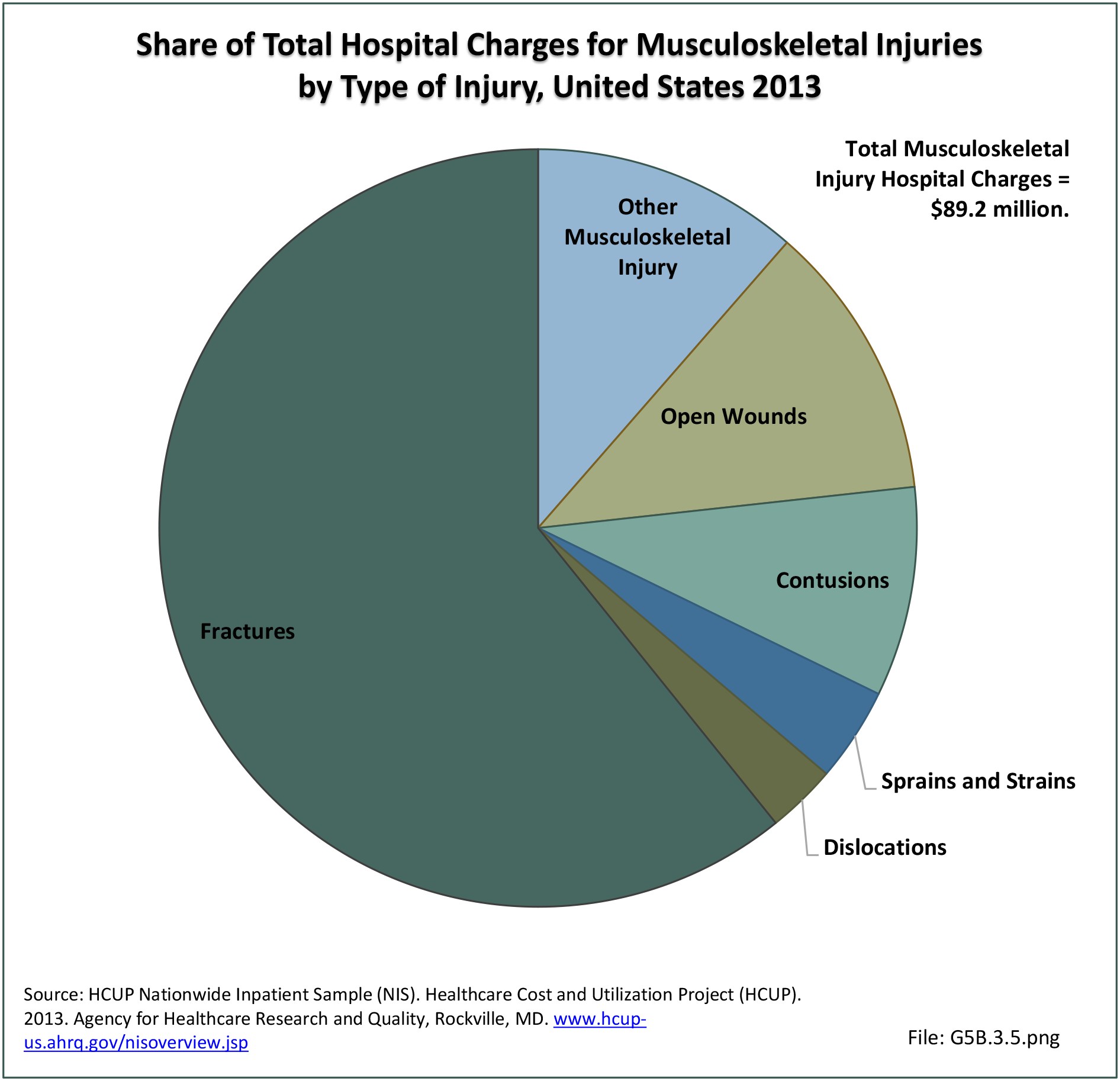
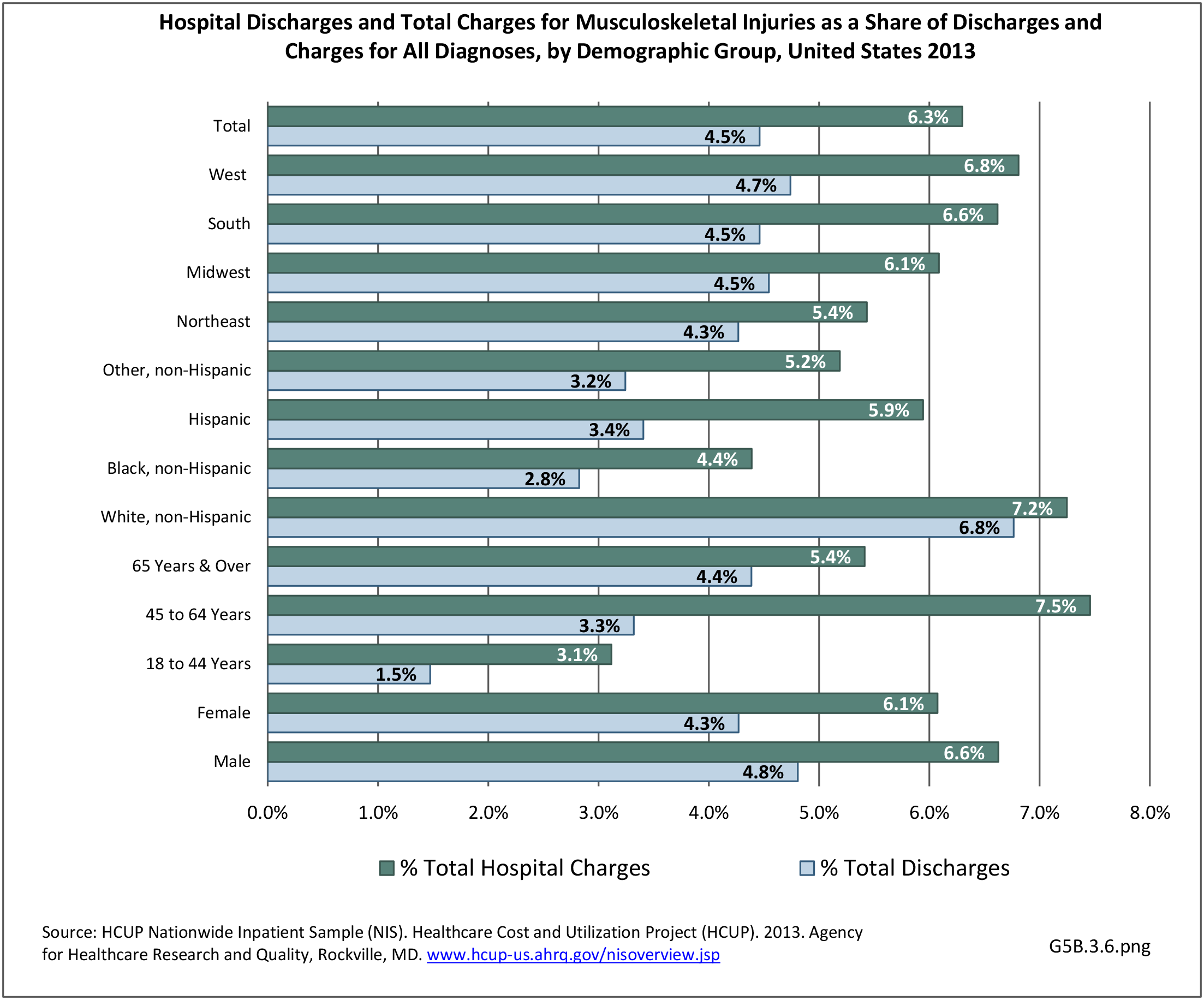
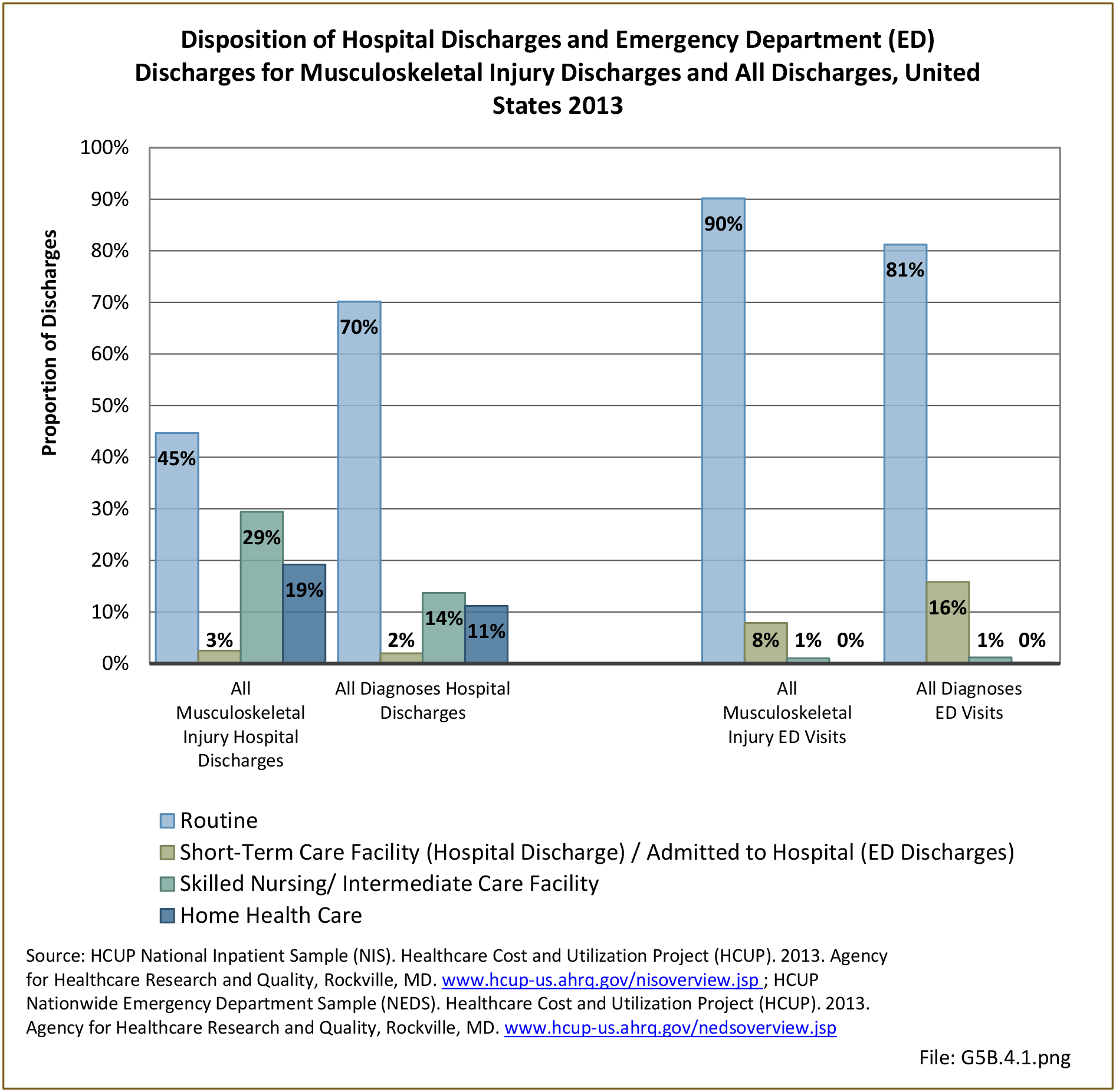
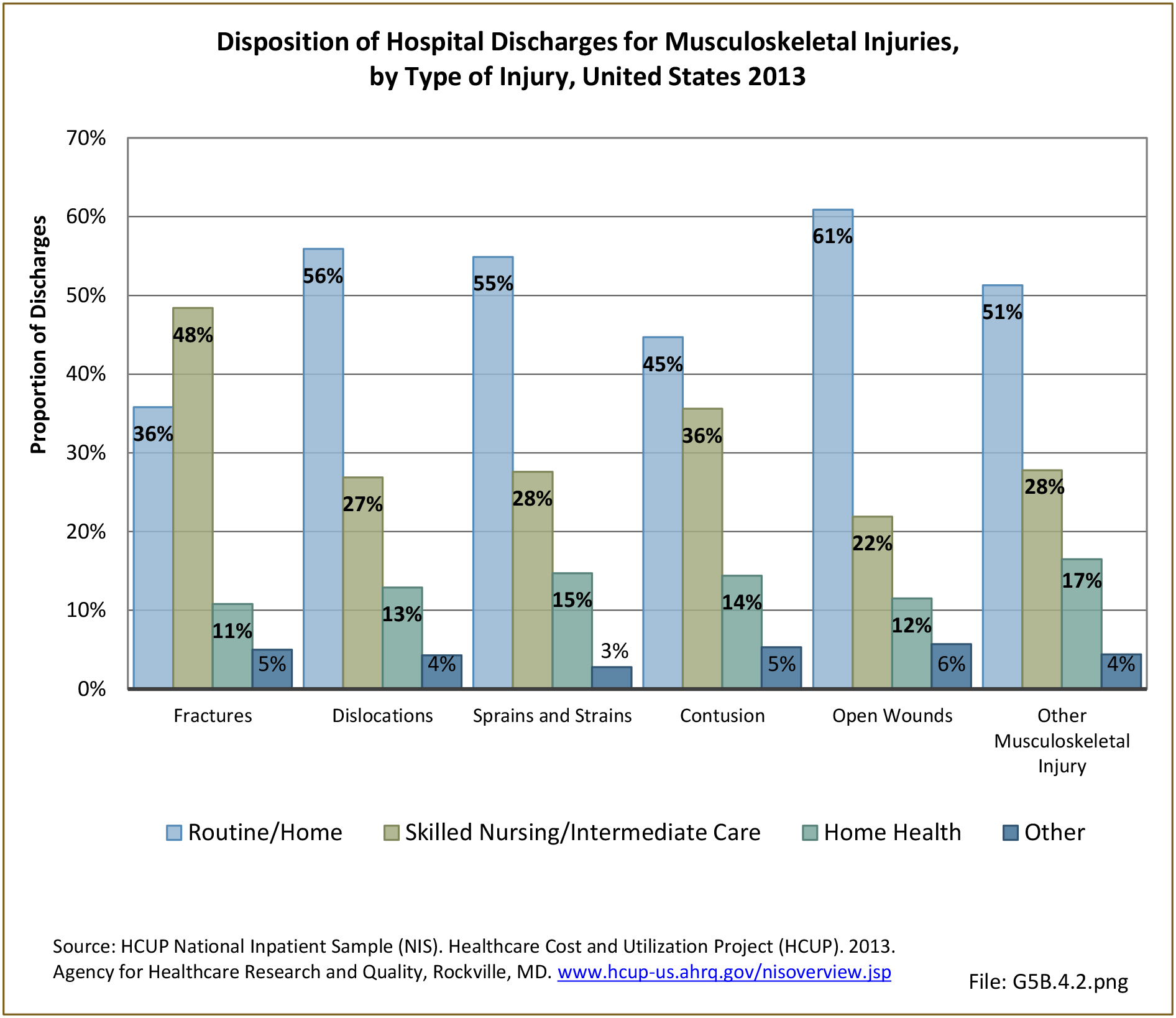
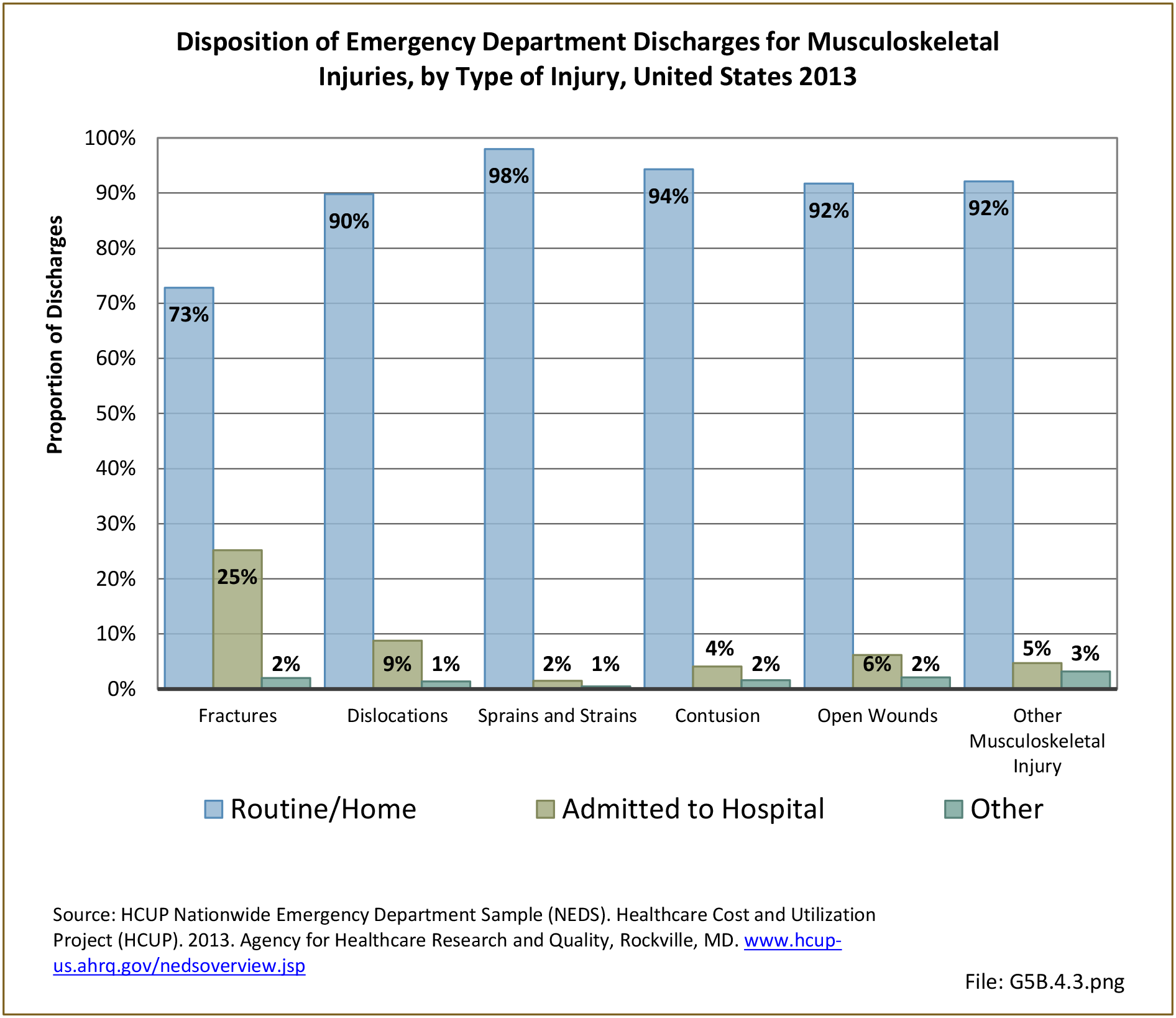
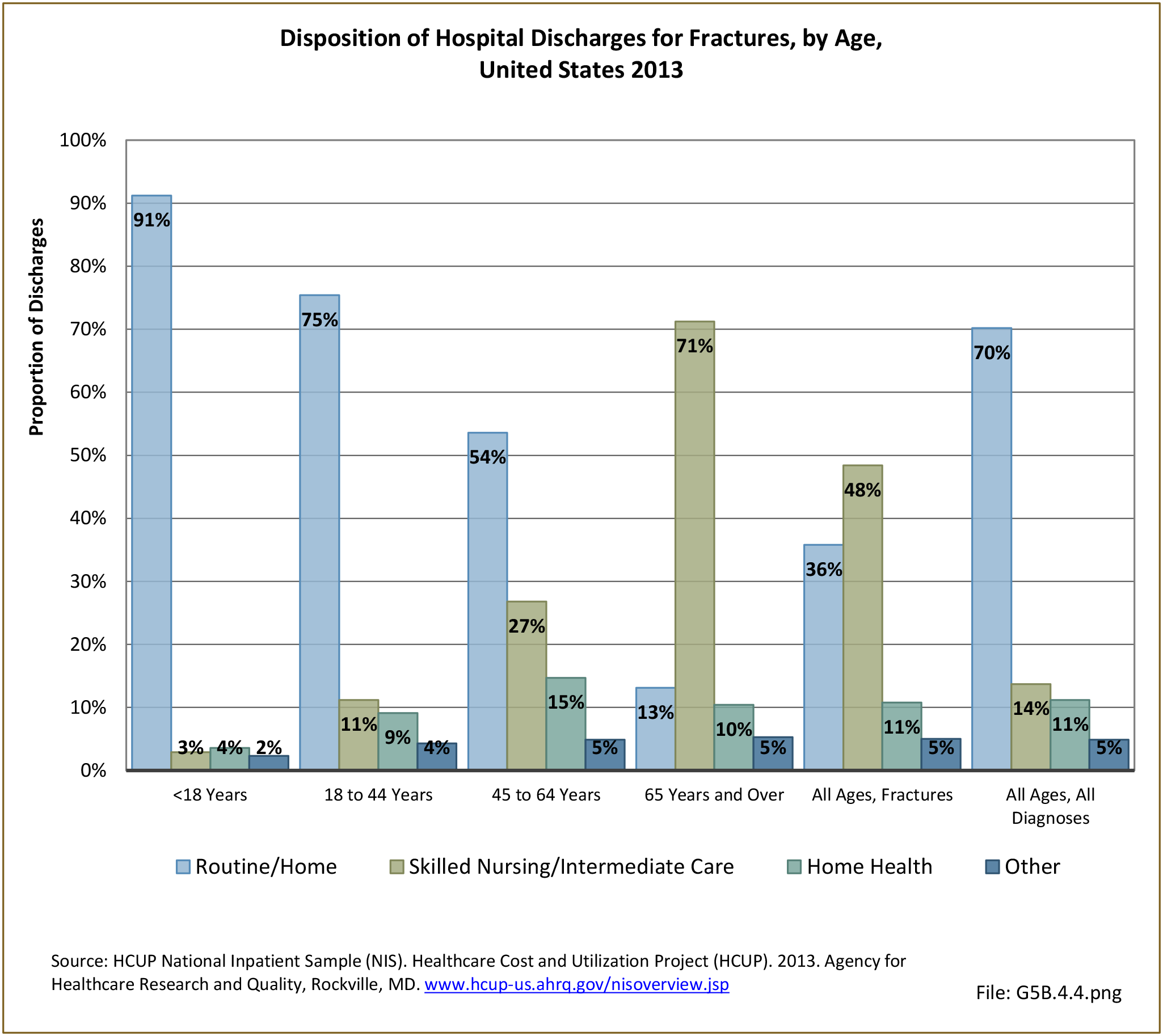
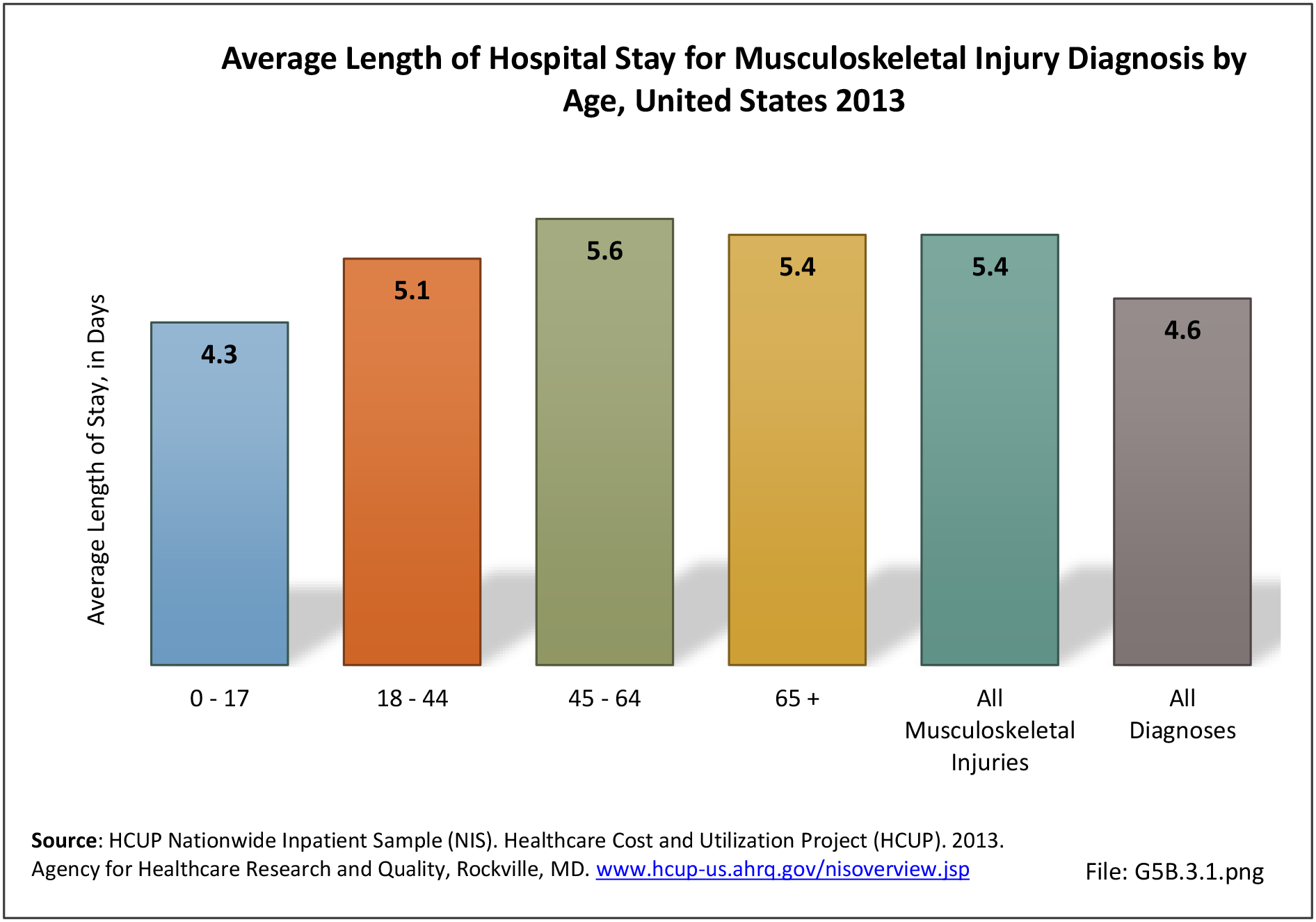
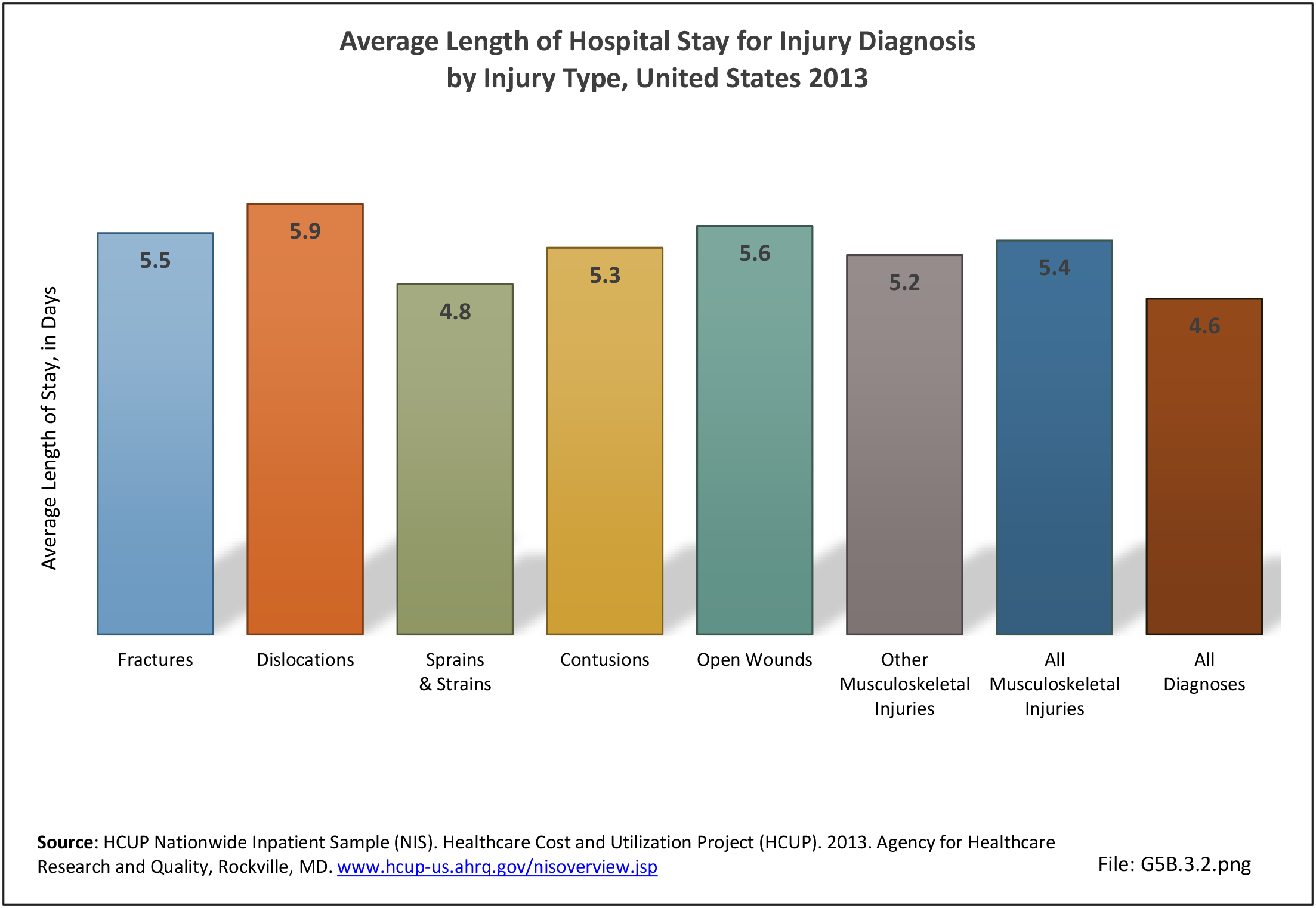
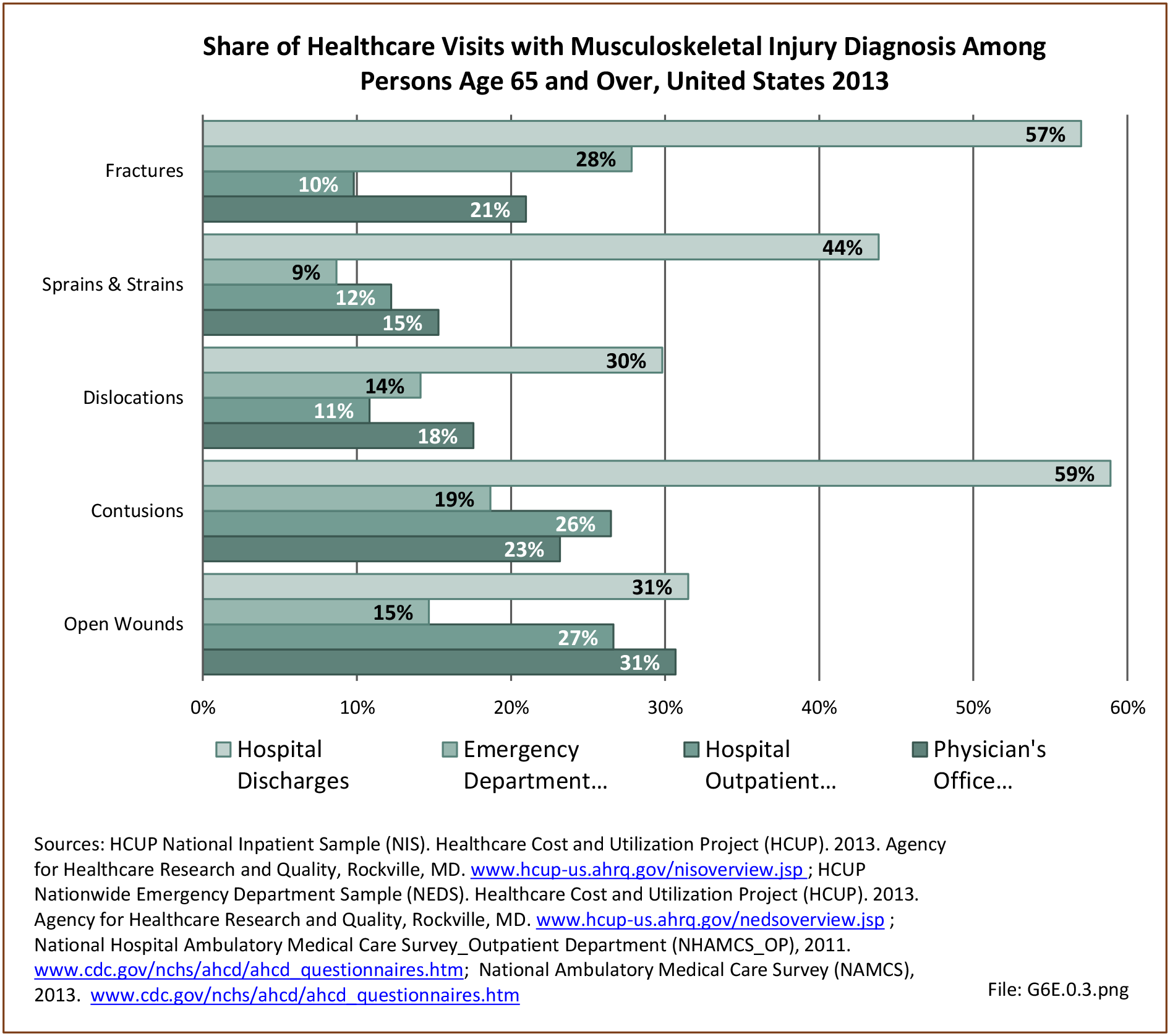
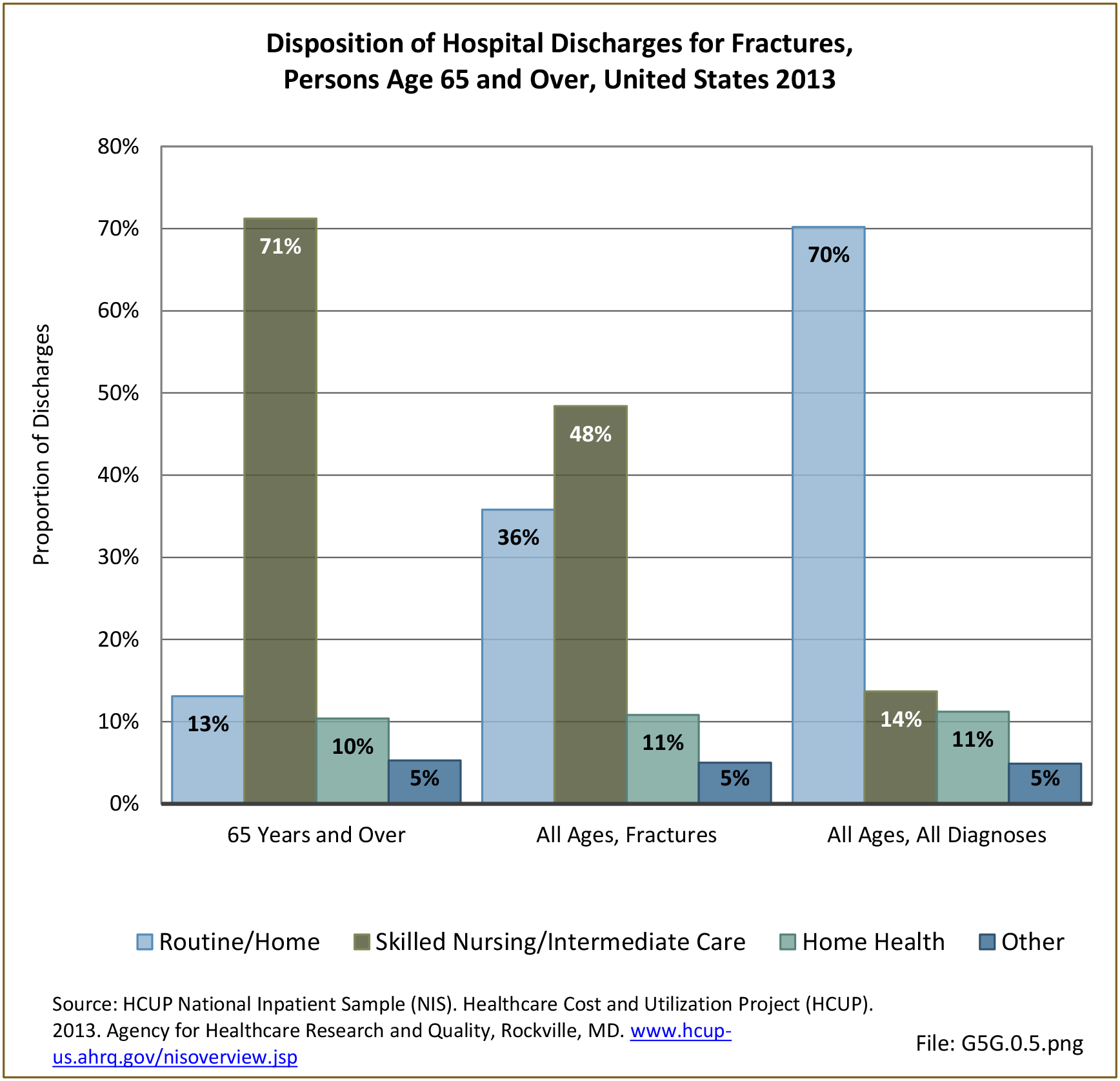
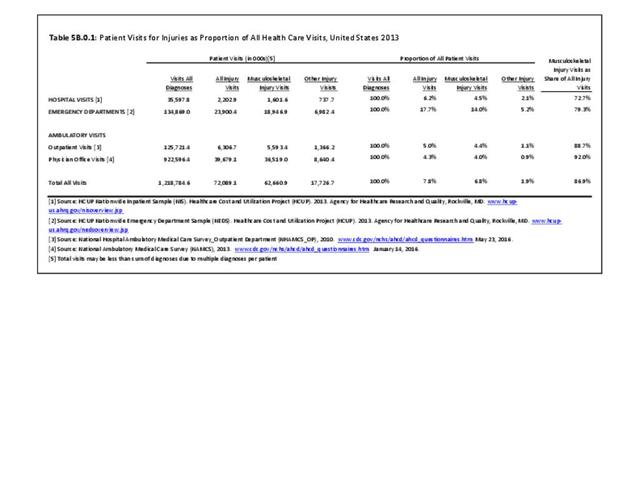
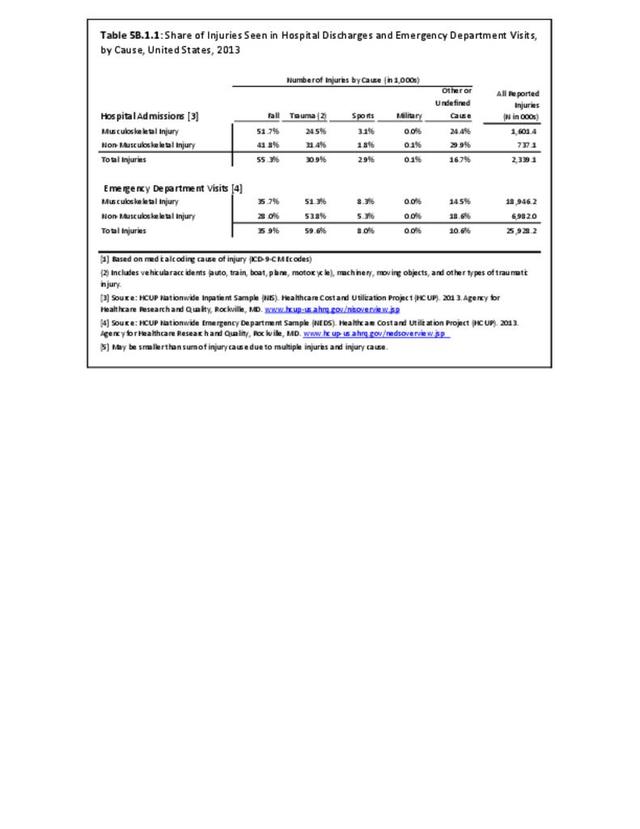
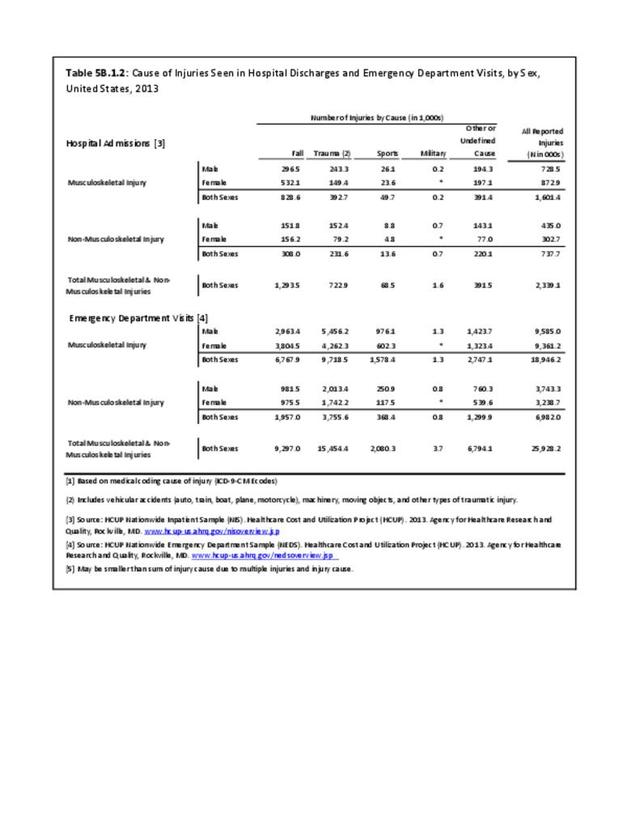
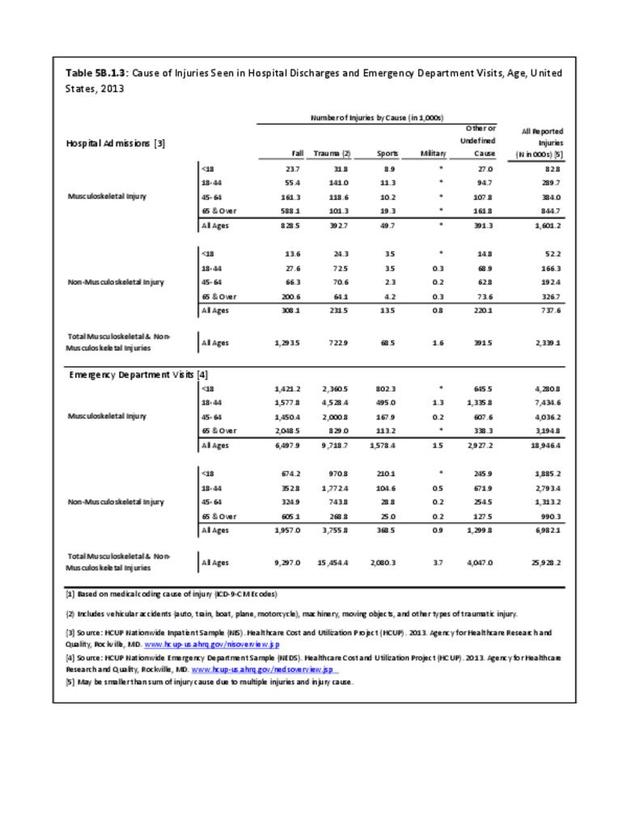
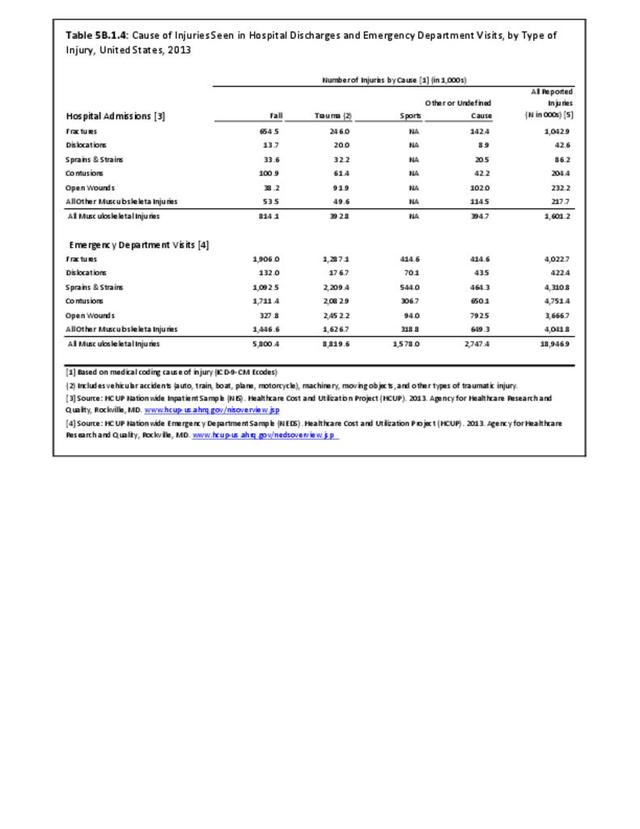
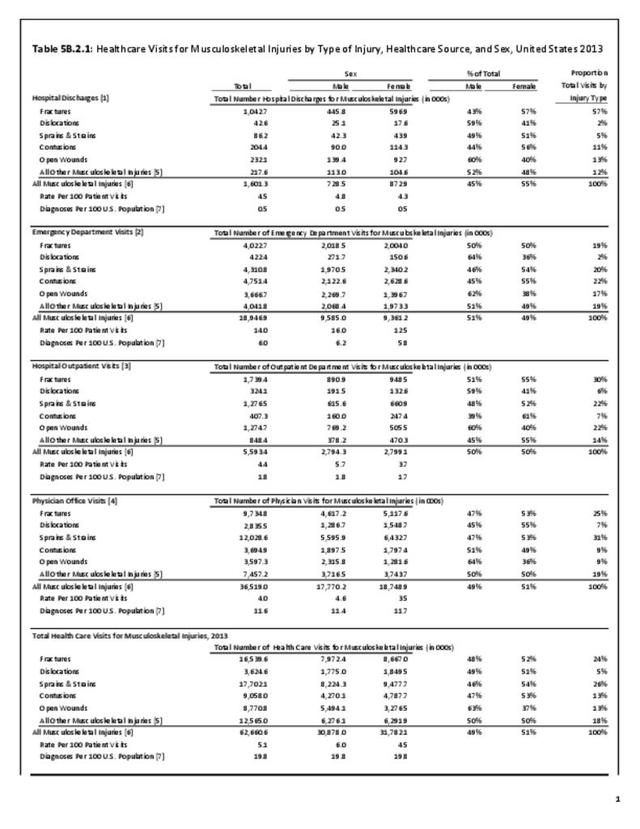
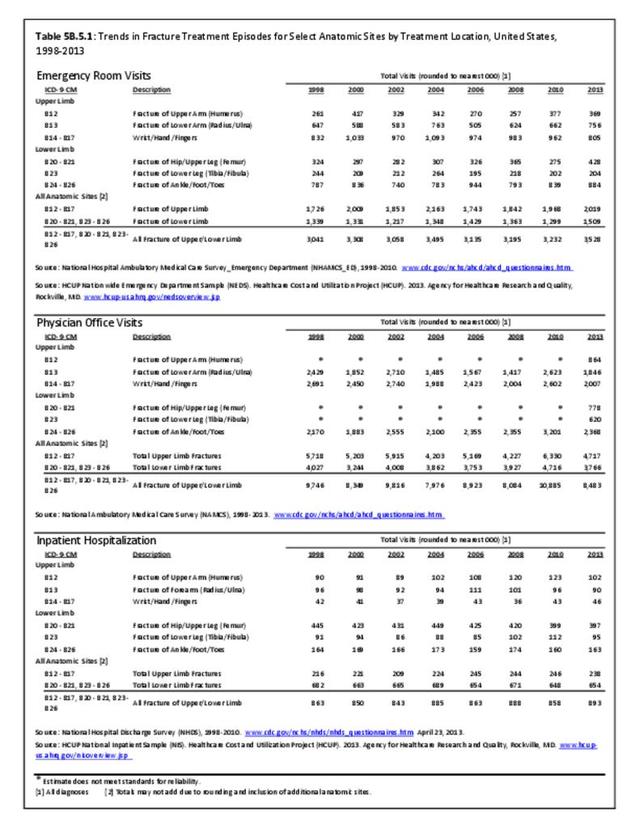
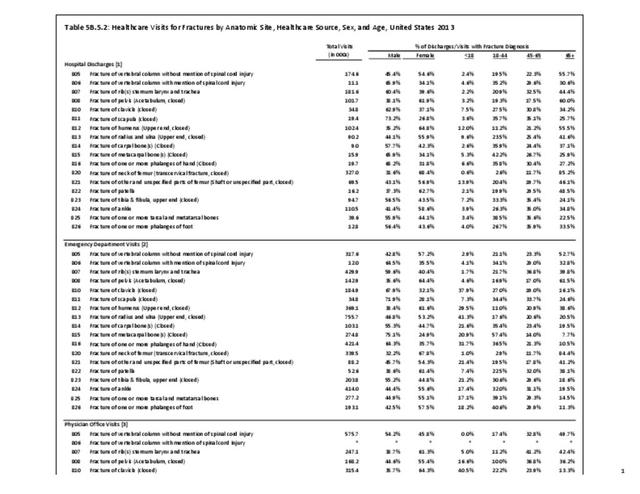
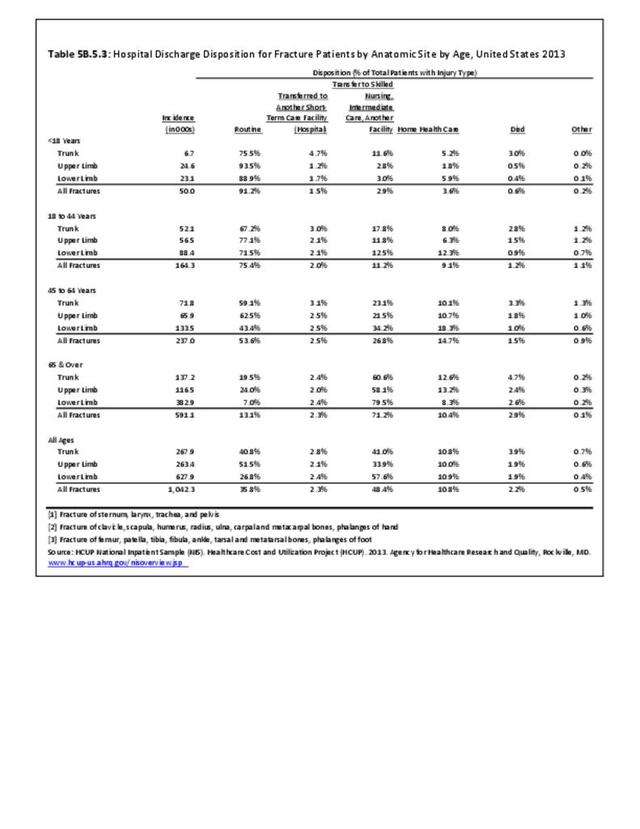
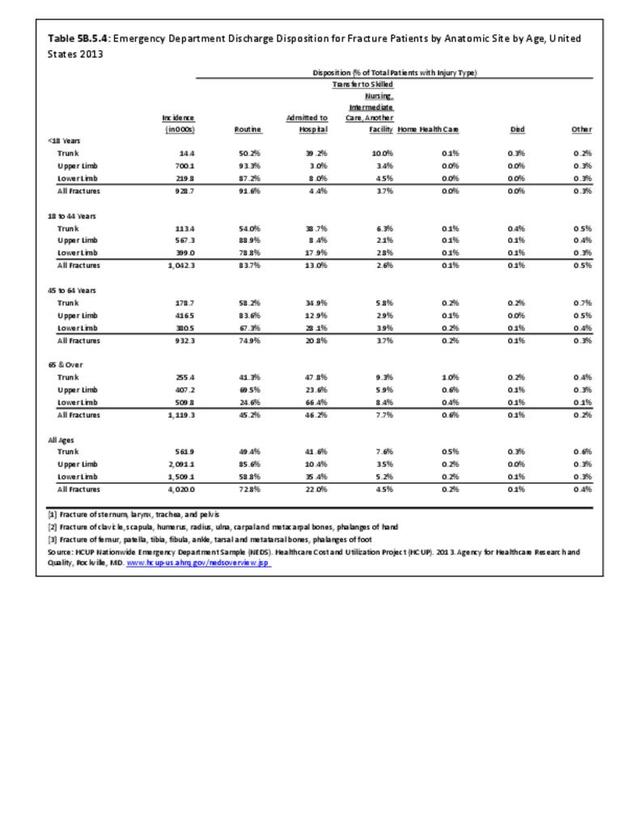
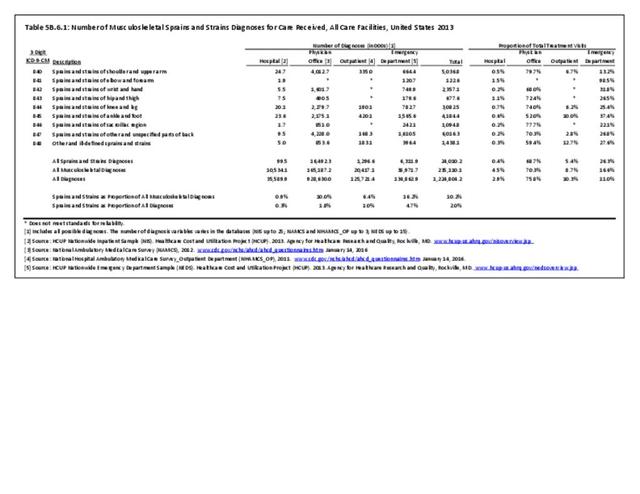
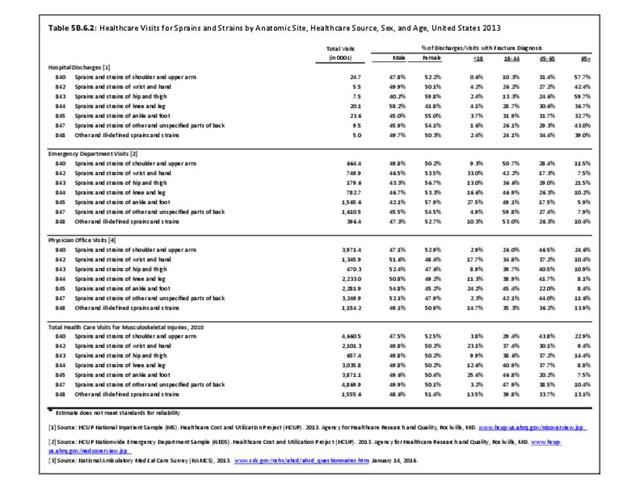
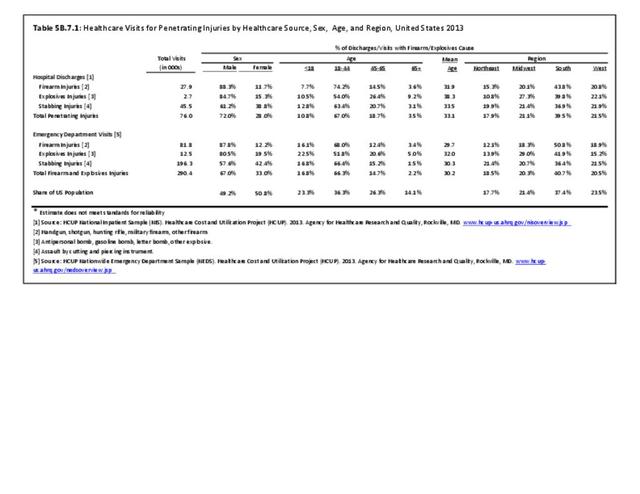
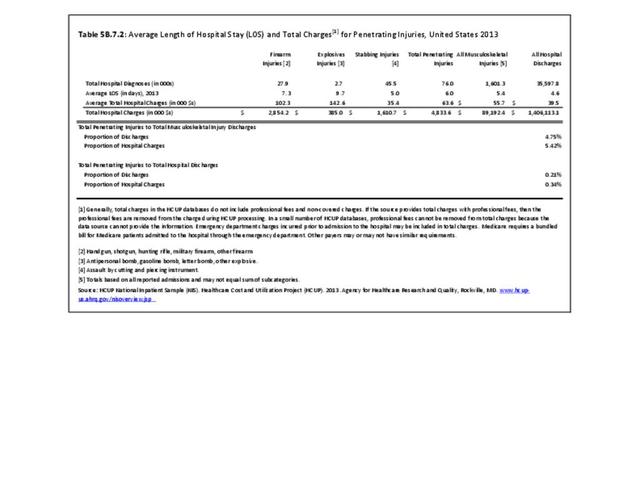
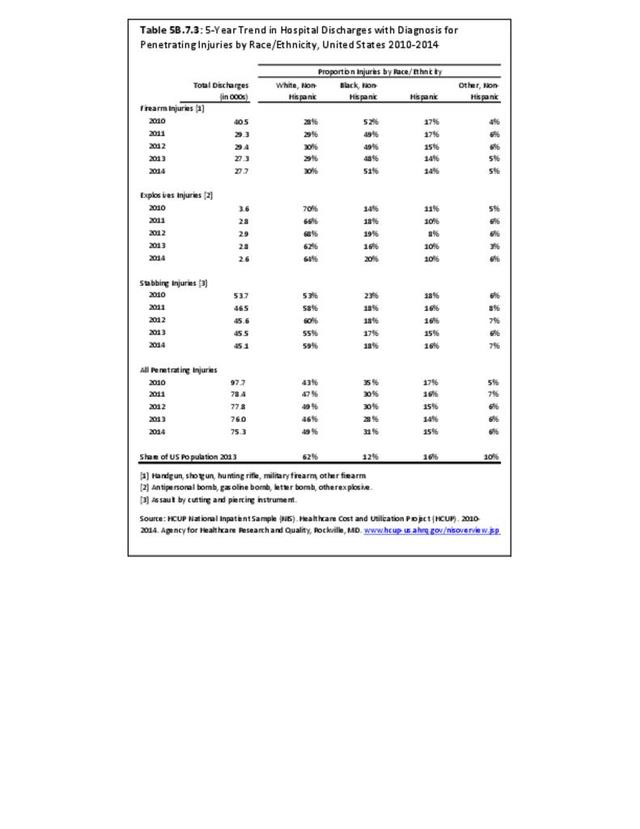
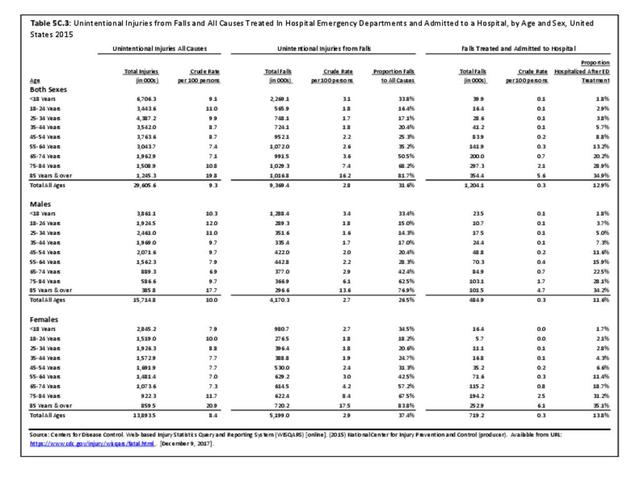
Traumatic Injuries: Traumatic injuries are unintentional physical injuries of sudden onset and severe enough to require immediate medical attention. Causes of traumatic injuries include moving vehicle accidents (i.e., car, bicycle, motorcycle), gunshot injuries, sports, and falls. A major trauma is an injury that has the potential to cause prolonged disability or death. Data on traumatic injuries is based on national health care databases compiled annually by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) and the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) of discharges and visits to hospitals, emergency rooms, outpatient clinics, and physician offices.
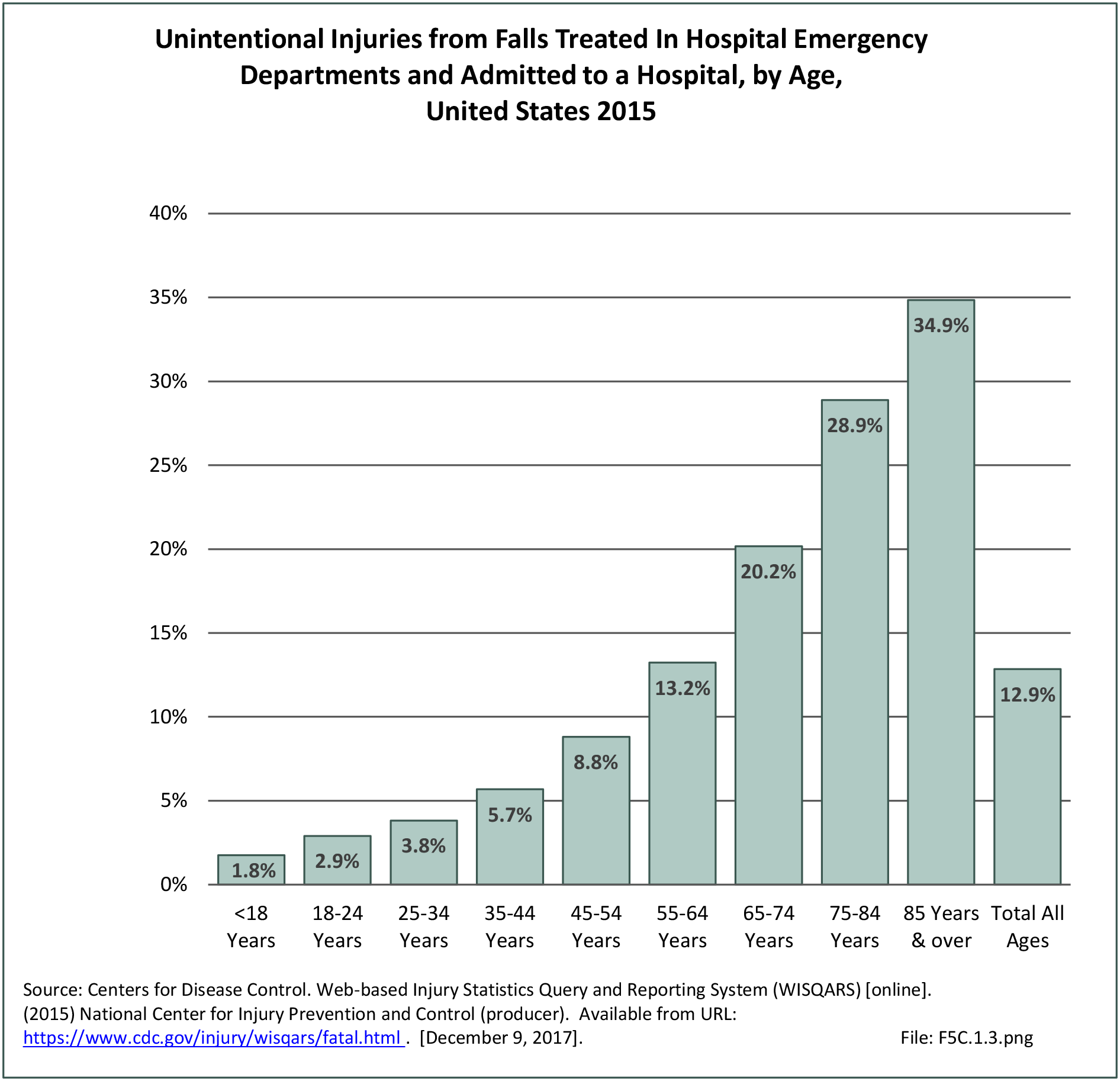
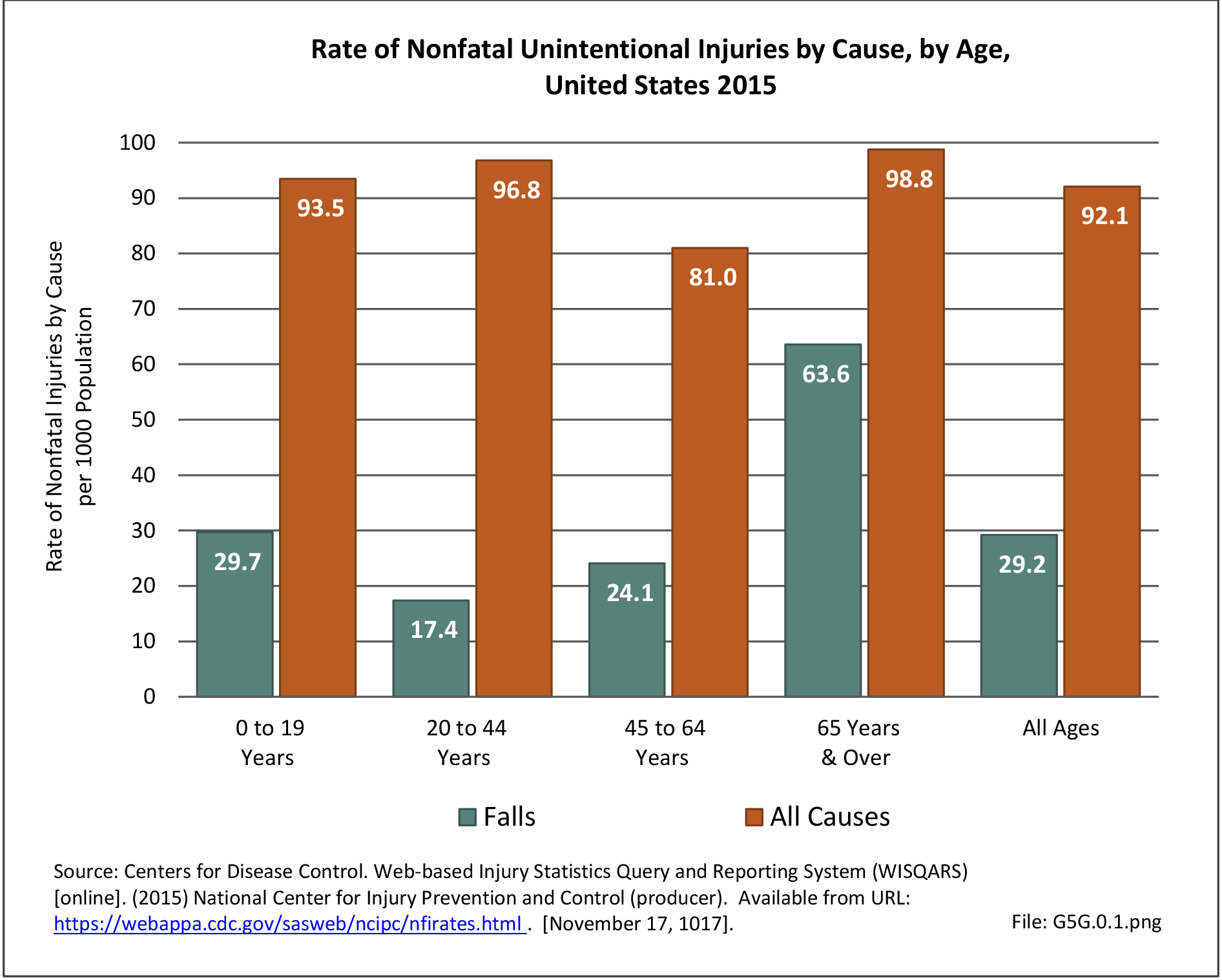
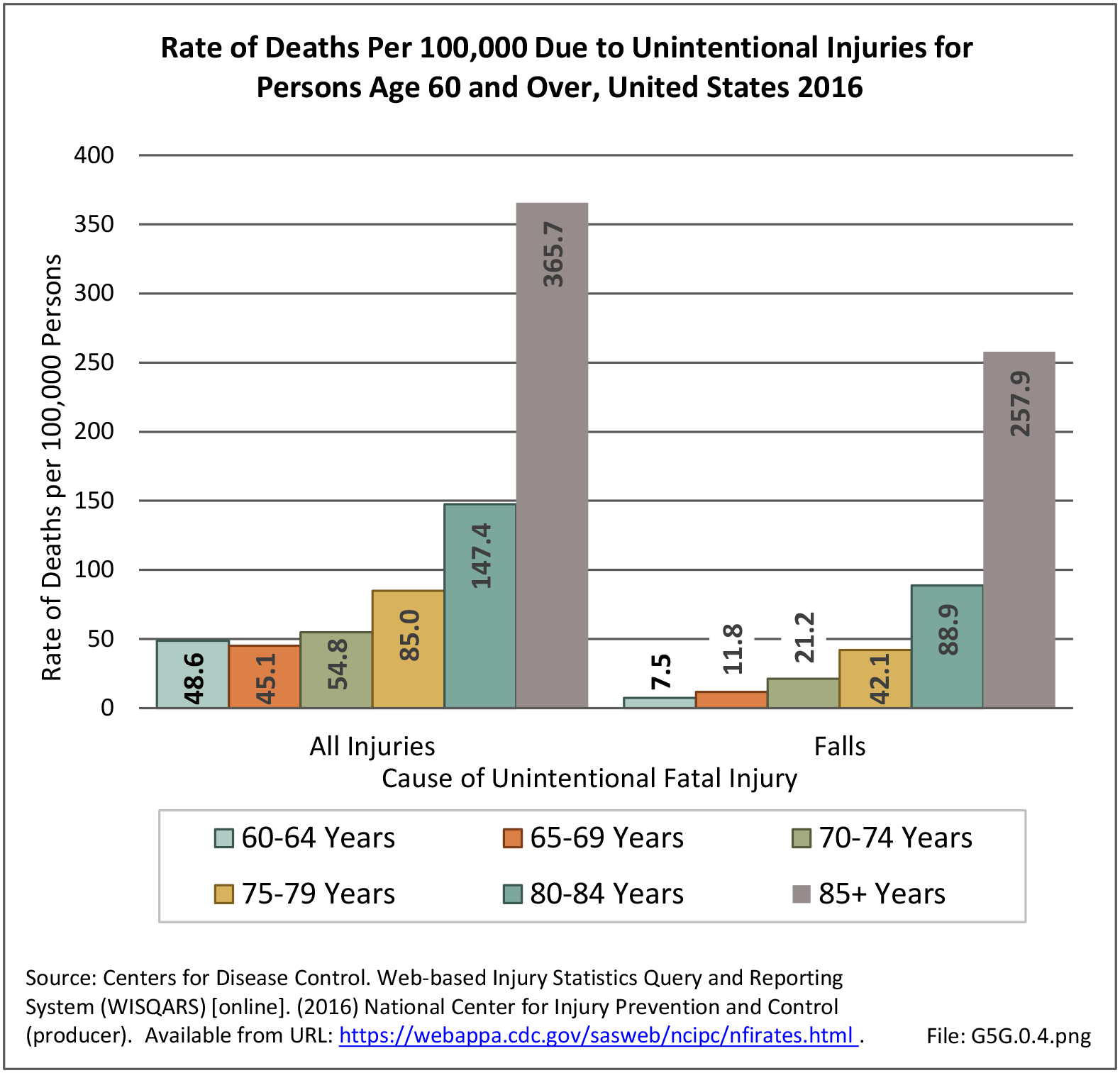
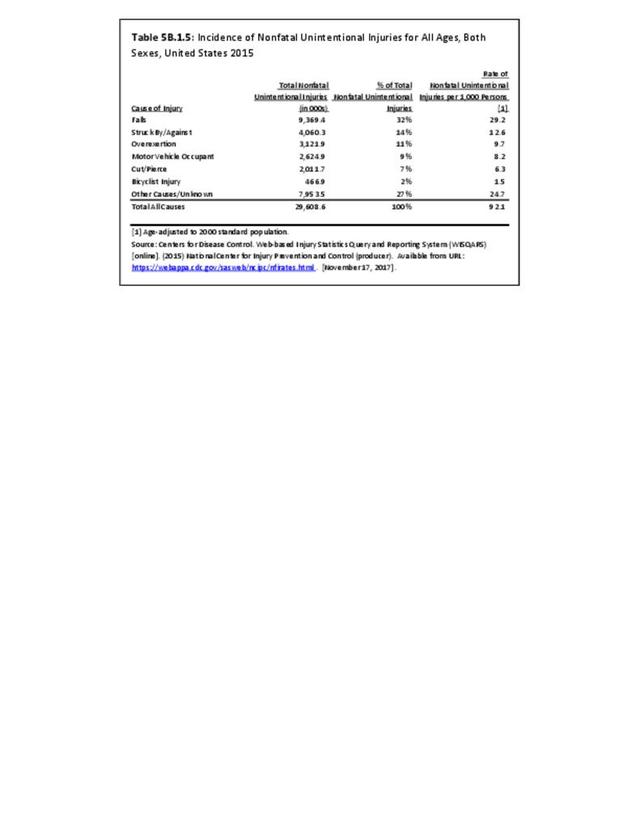
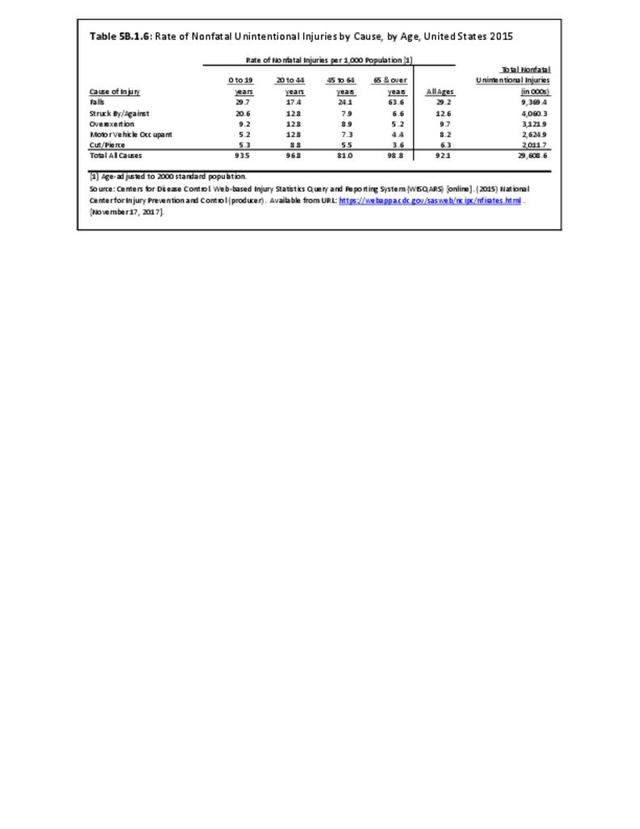
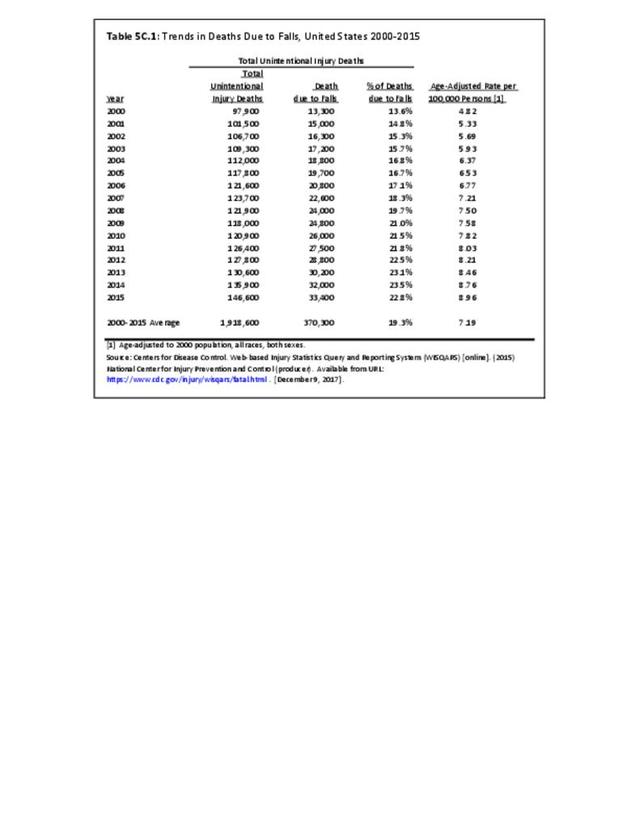
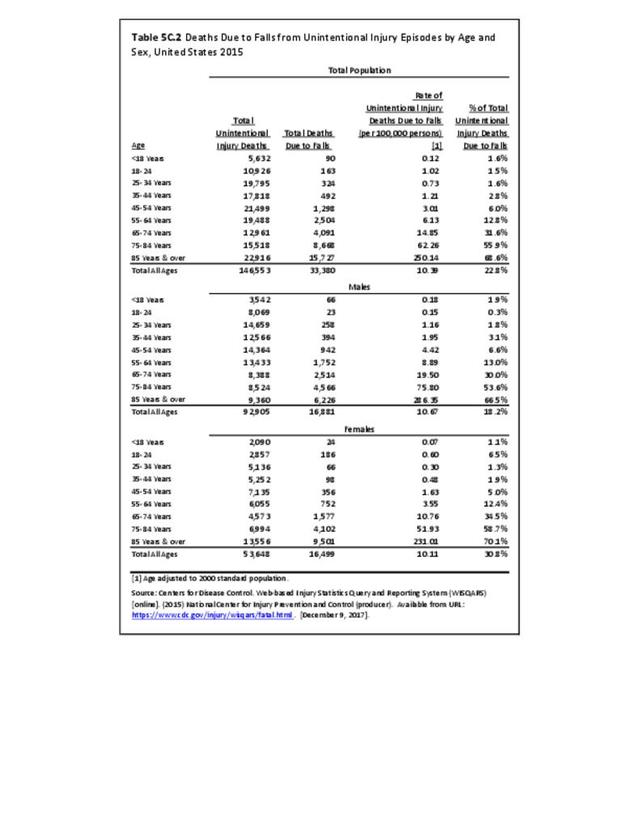
Falls: Unintentional injury deaths and deaths due to falls are tracked by the Centers for Disease Control (CDC). Falls are a major cause of traumatic injury and death to the aging population.
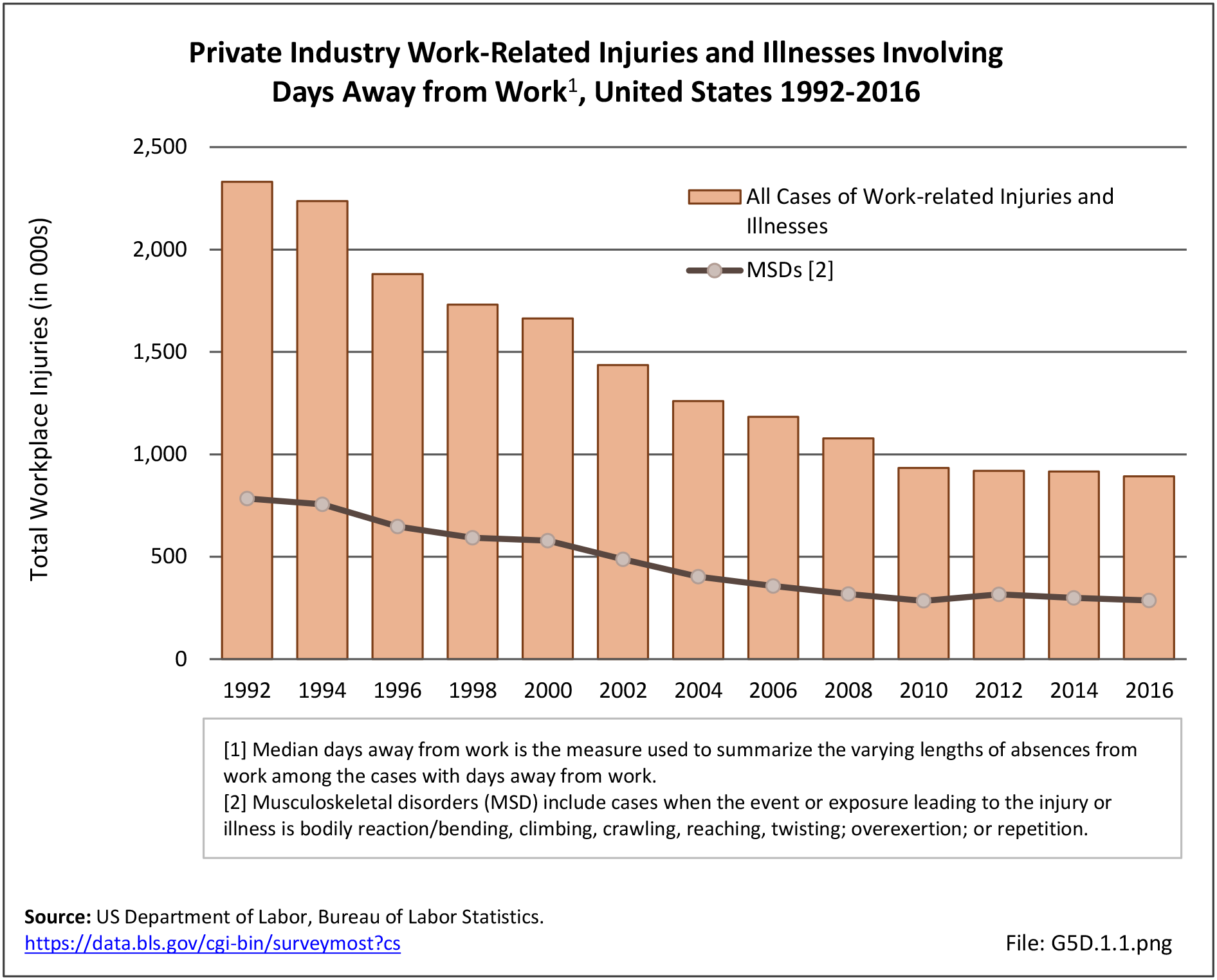
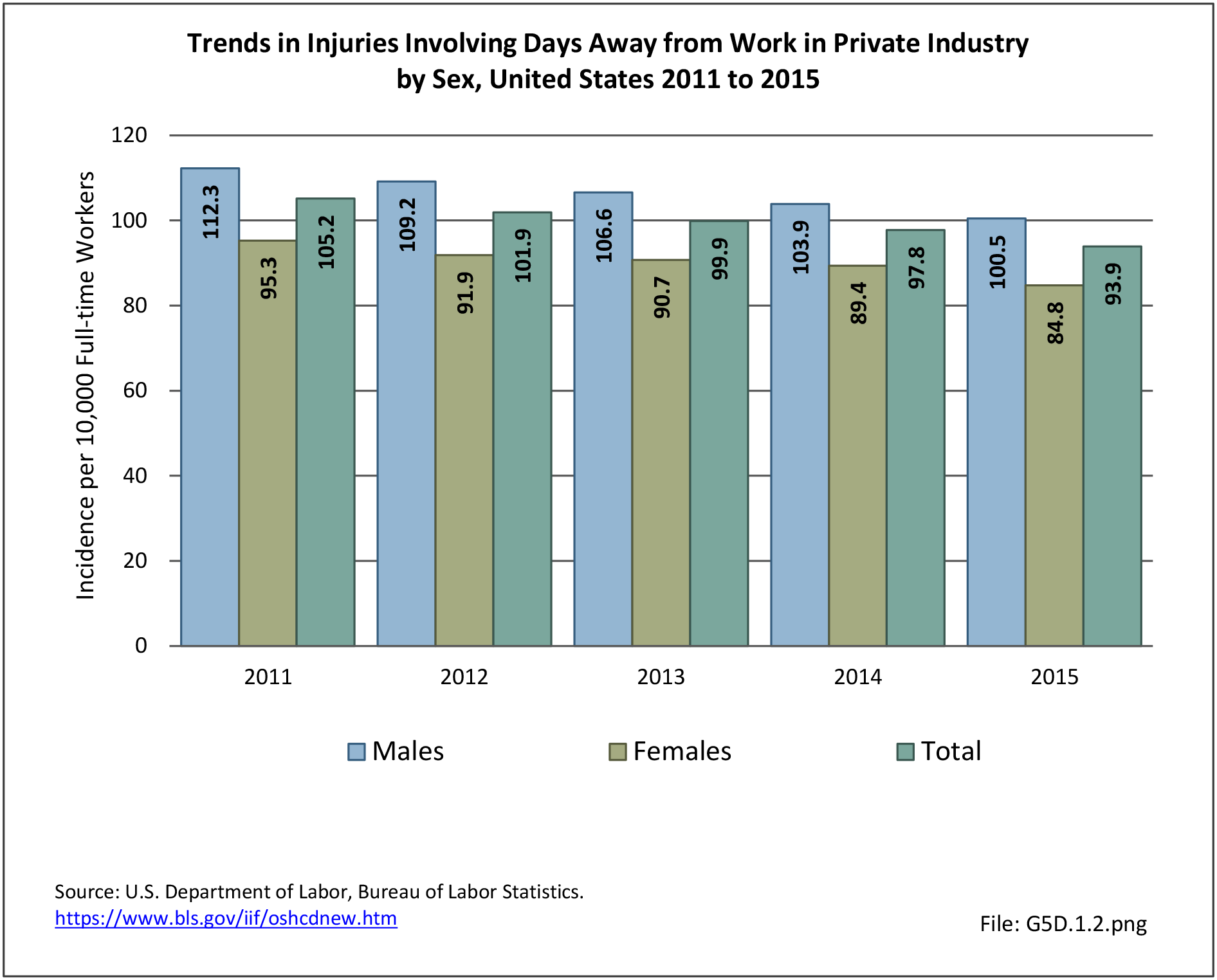
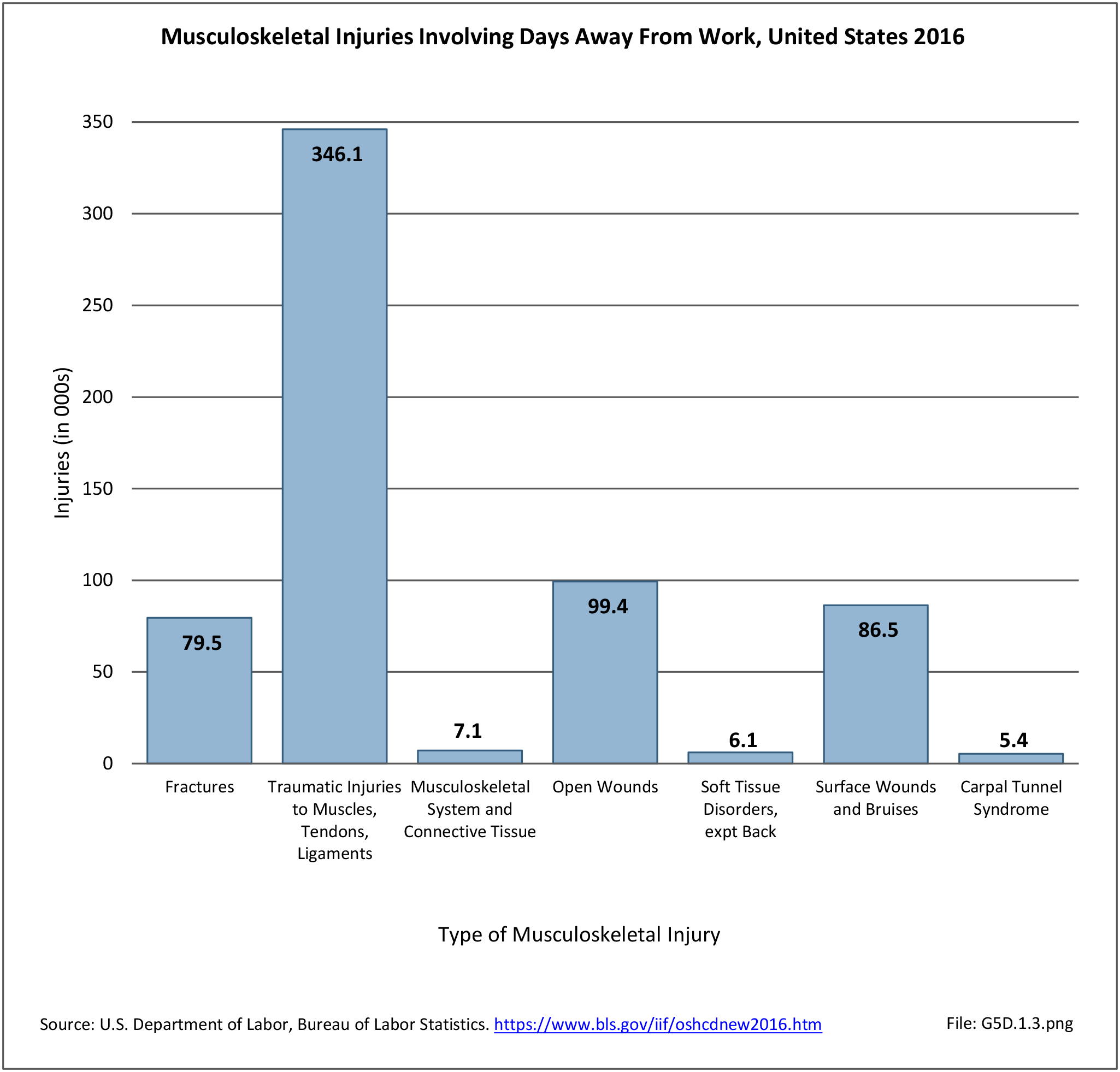
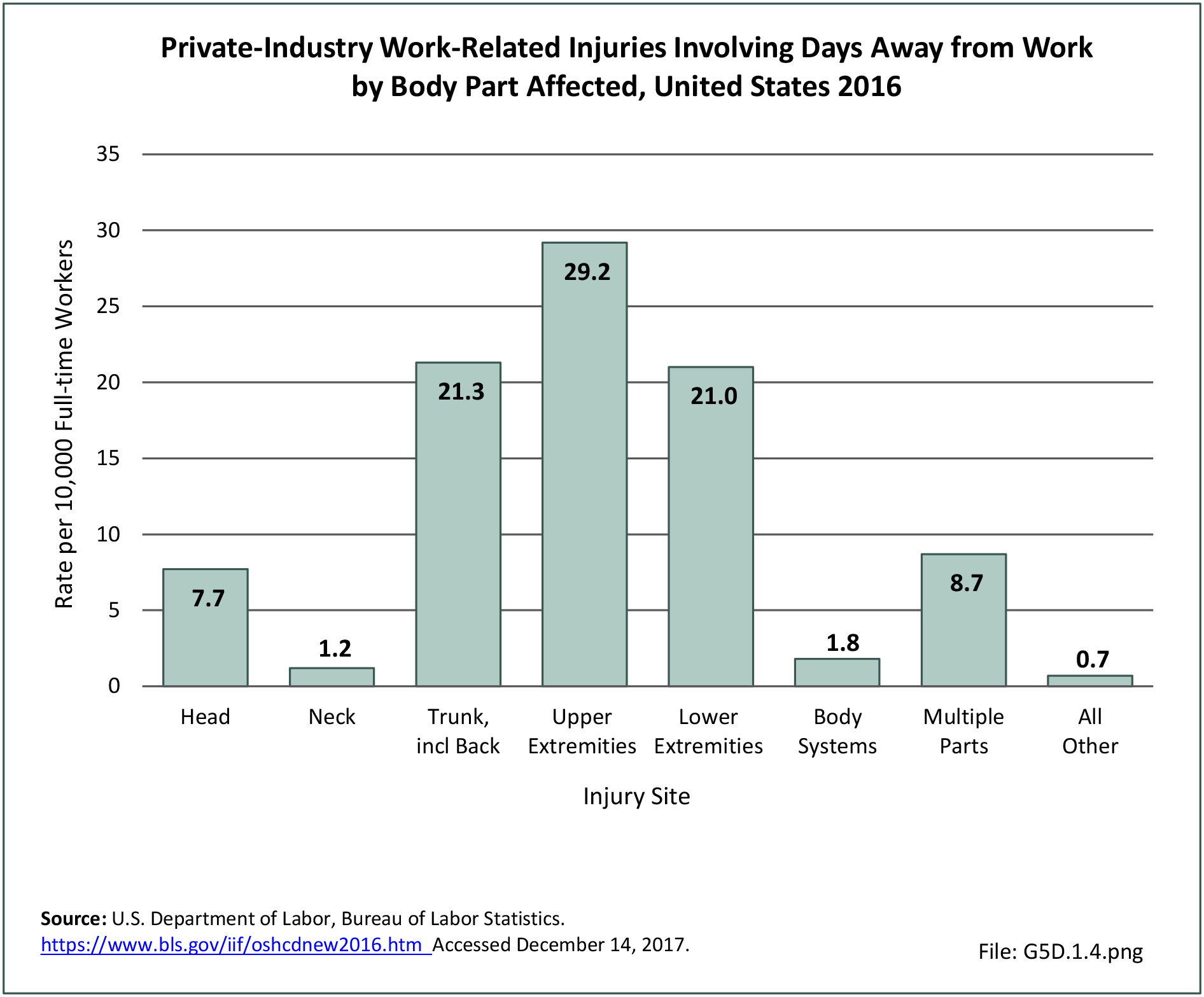
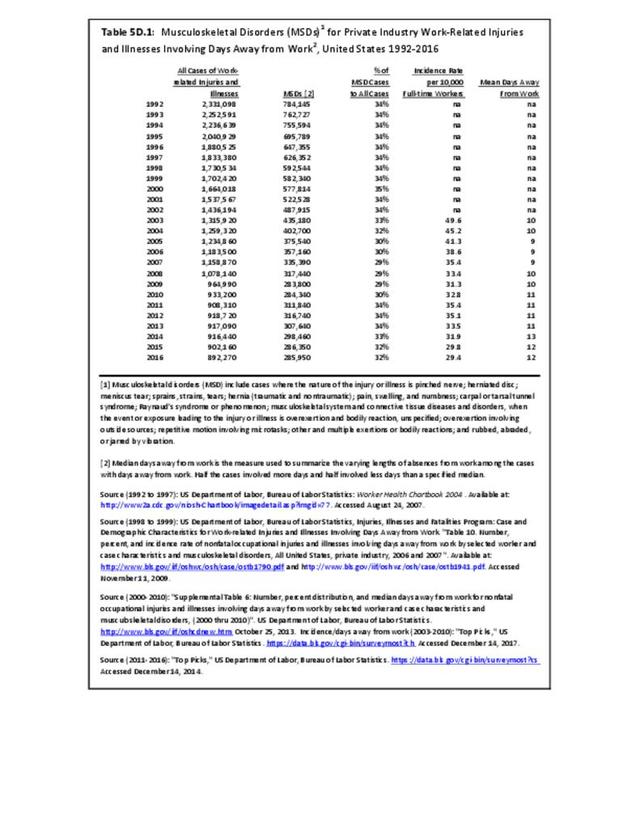
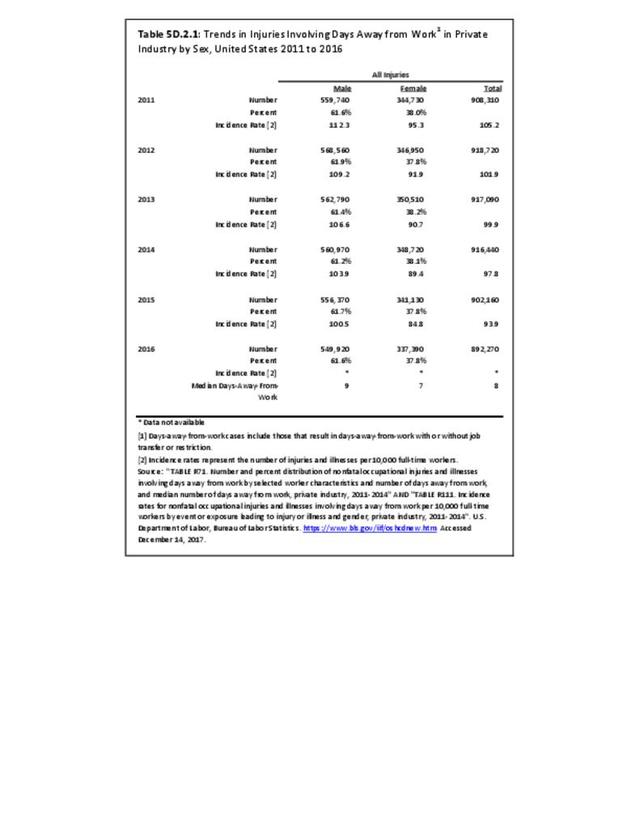
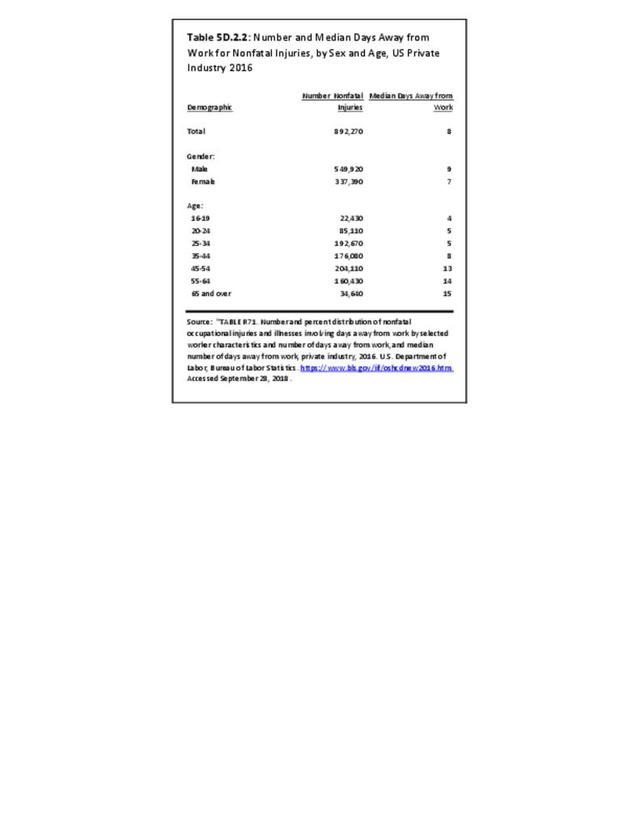
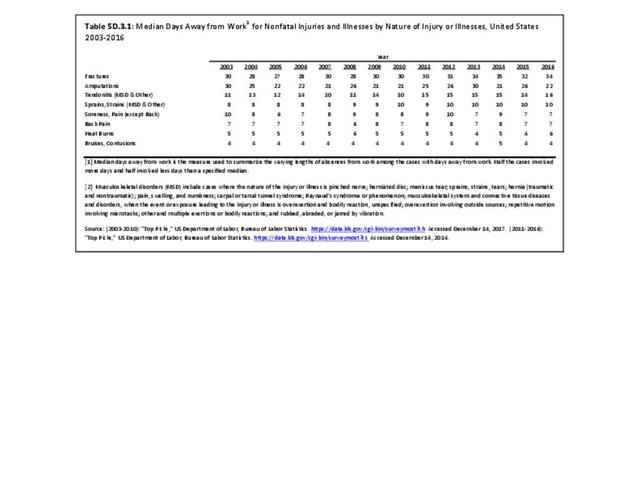
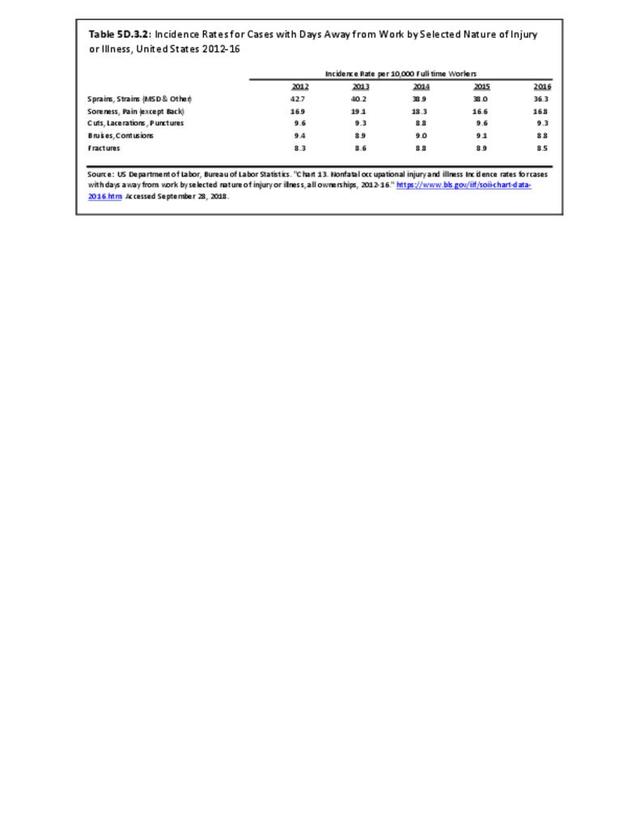
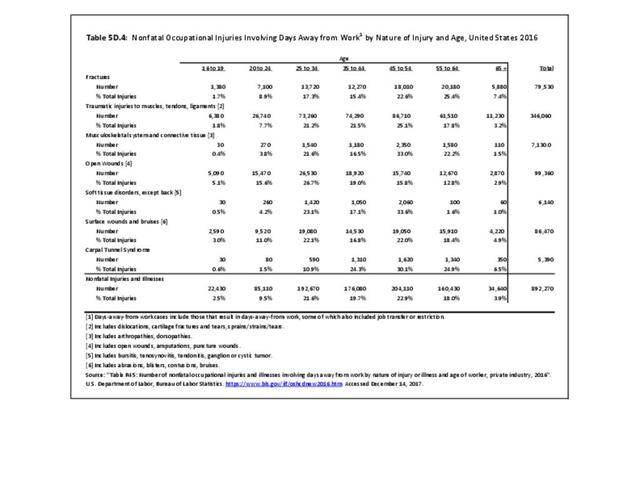
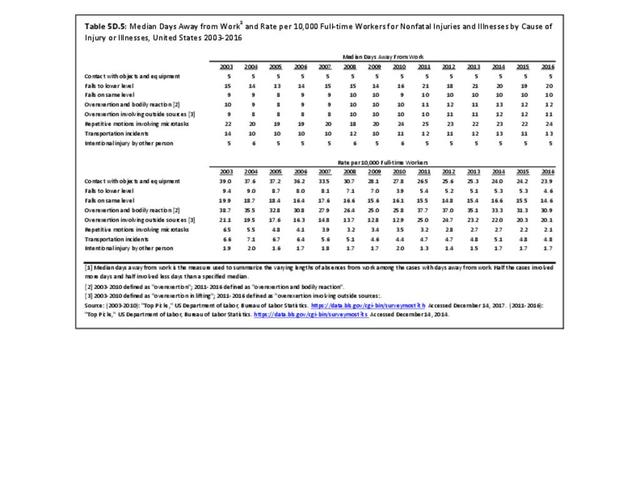
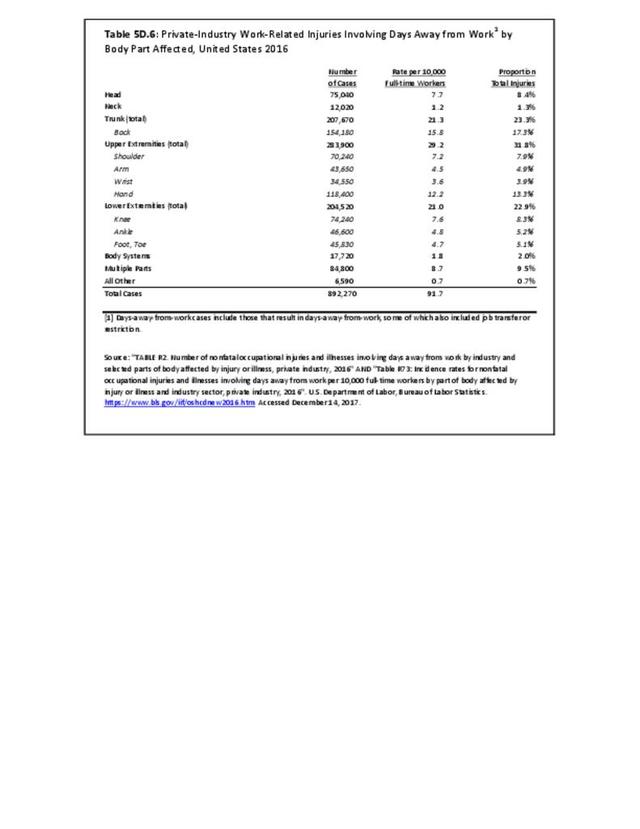
Workplace Injuries: Workplace injuries are compiled annually by the US Department of Labor, Bureau of Labor Statistics, Injuries, Illnesses and Fatalities Program. Musculoskeletal injuries are classified as musculoskeletal disorders (MSD) that affect muscles, tendons and connective tissue, and comprise a substantial portion of all workplace injuries.
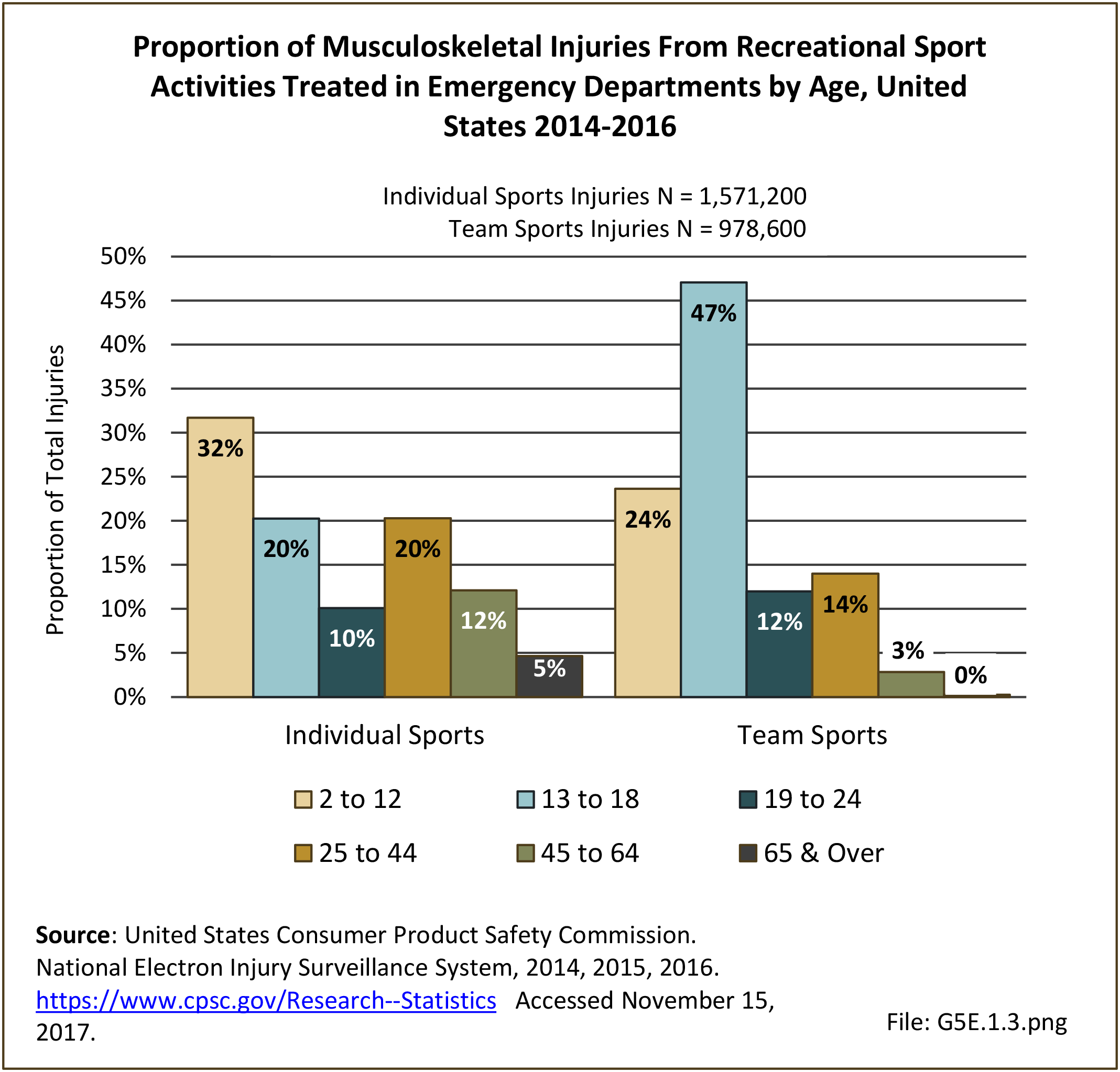
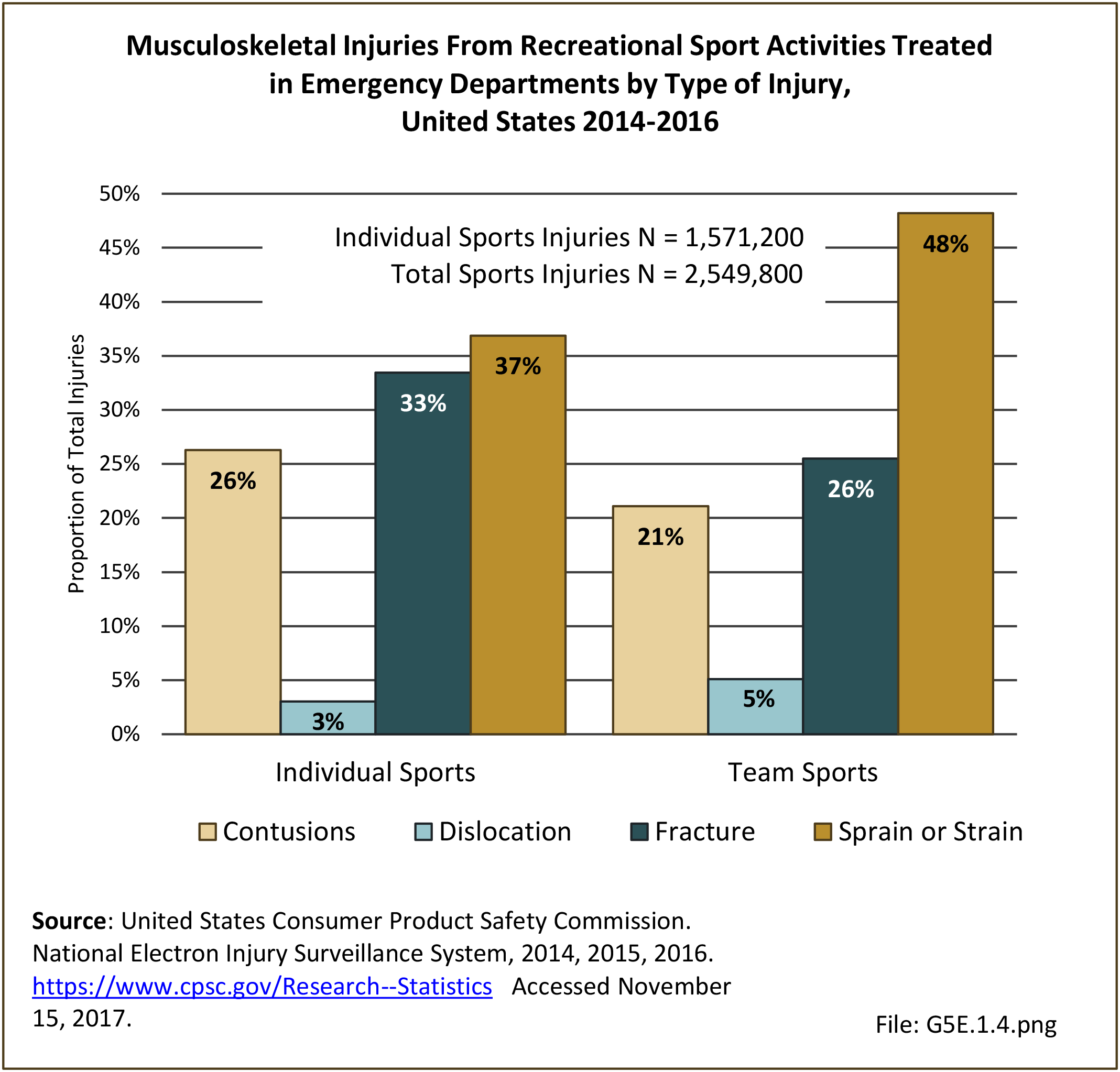
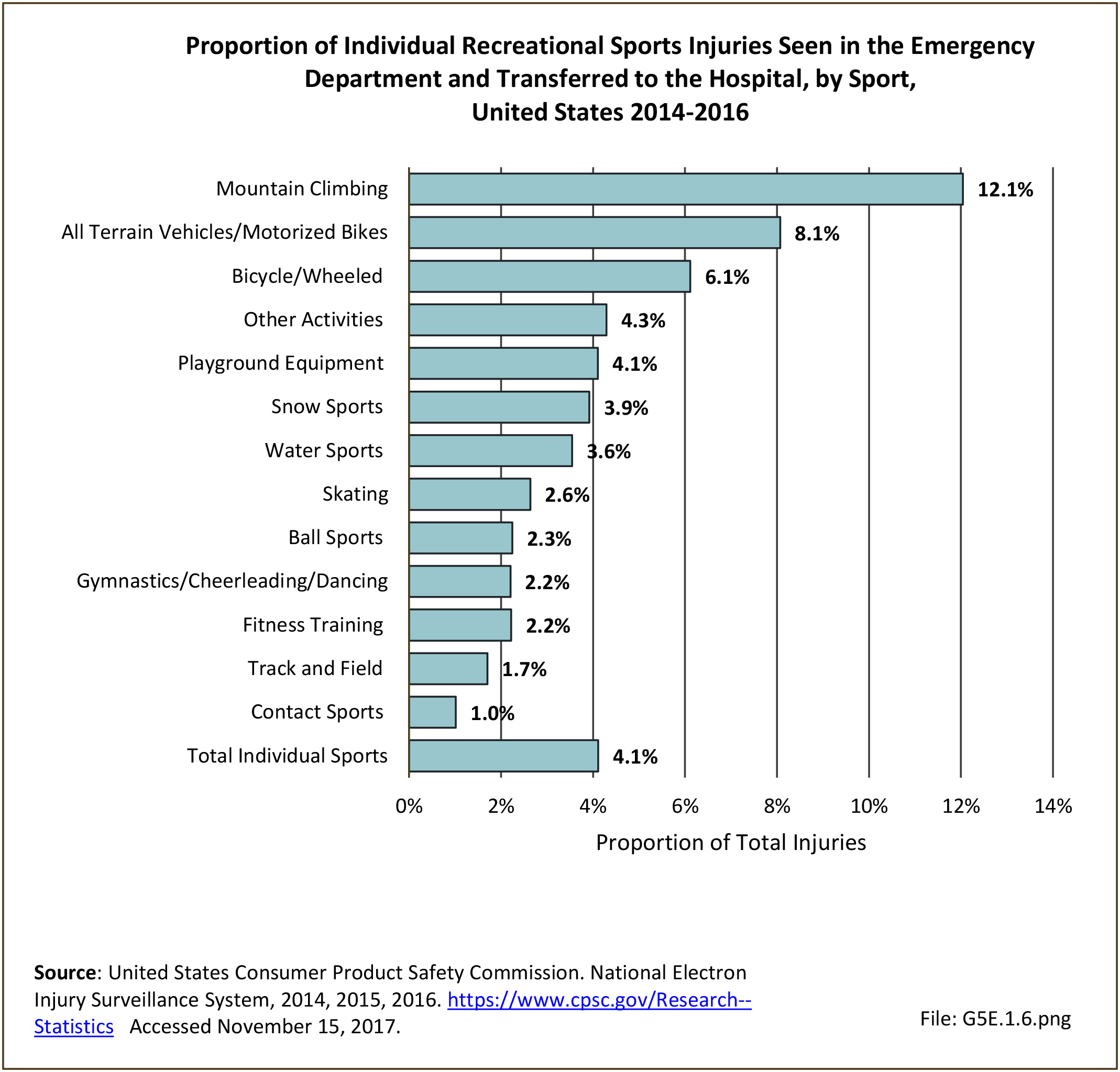
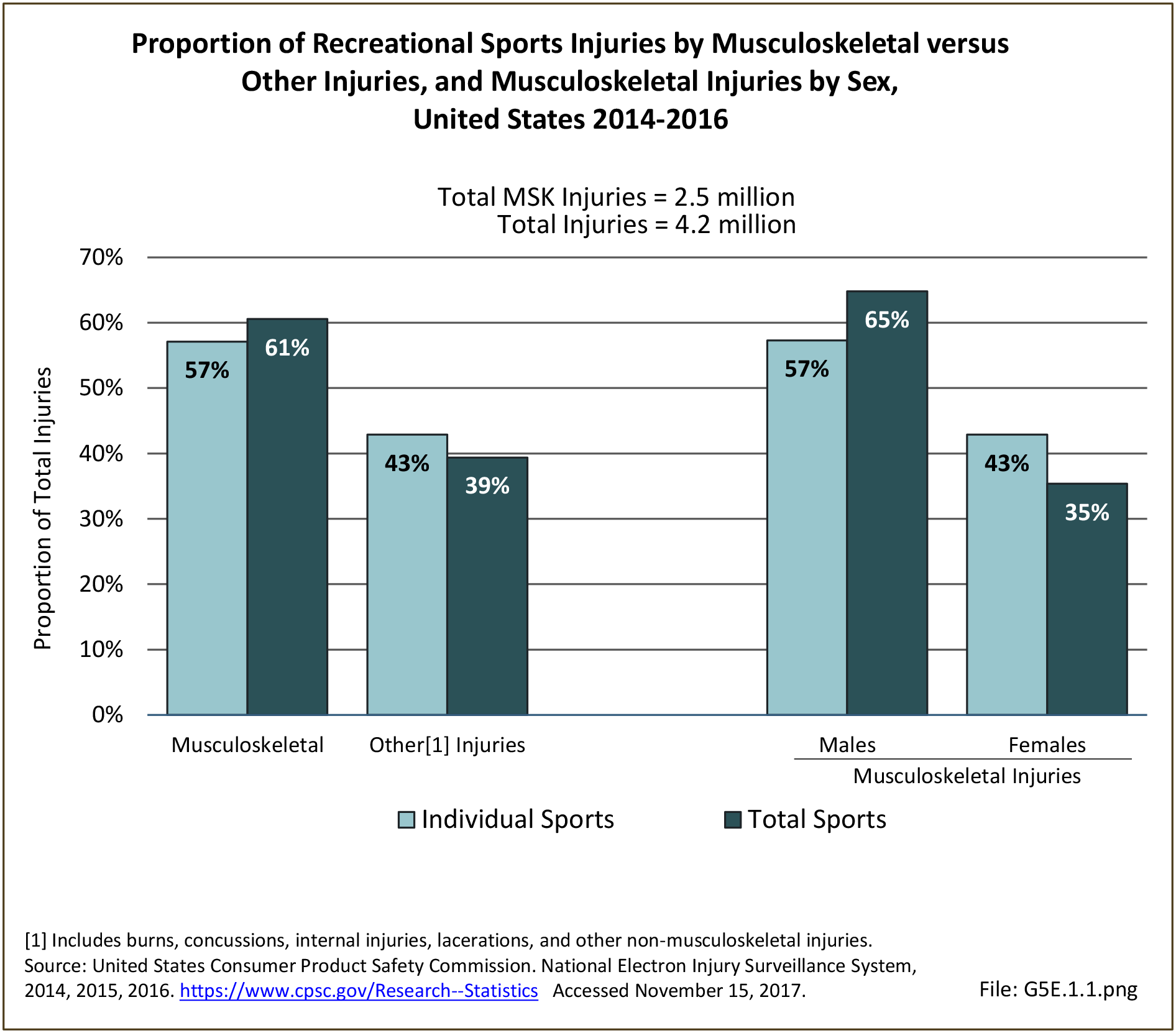
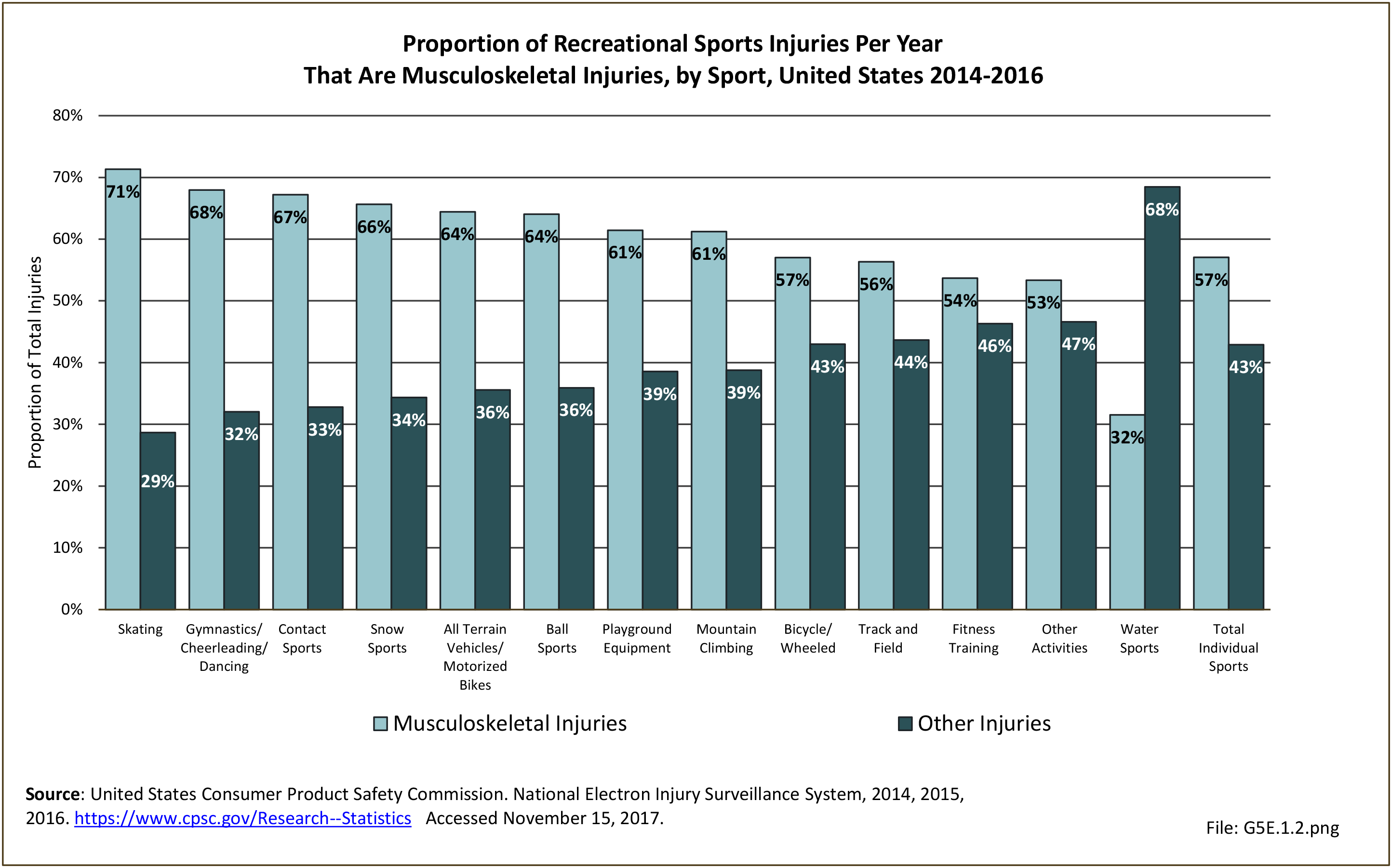
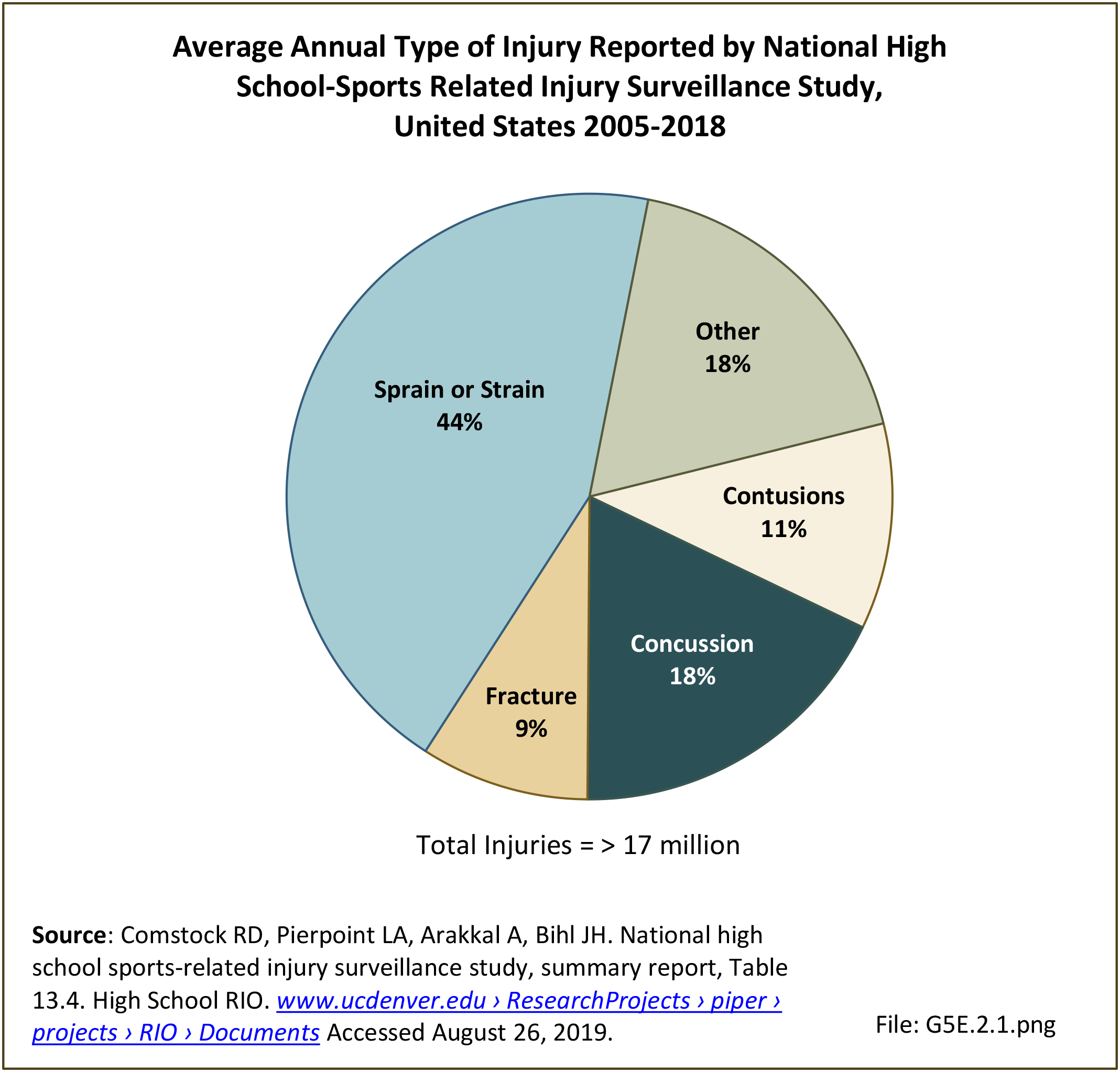
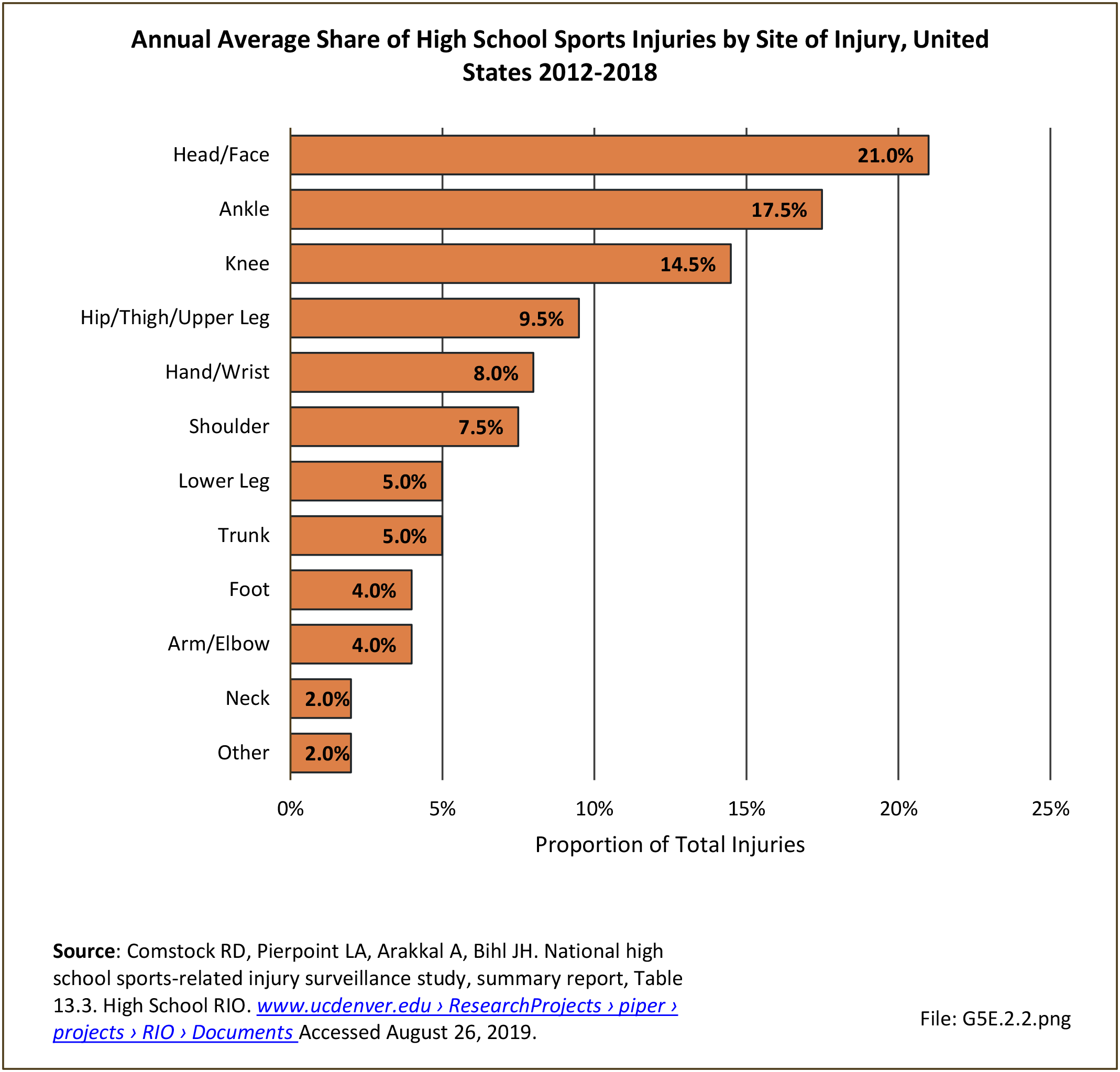
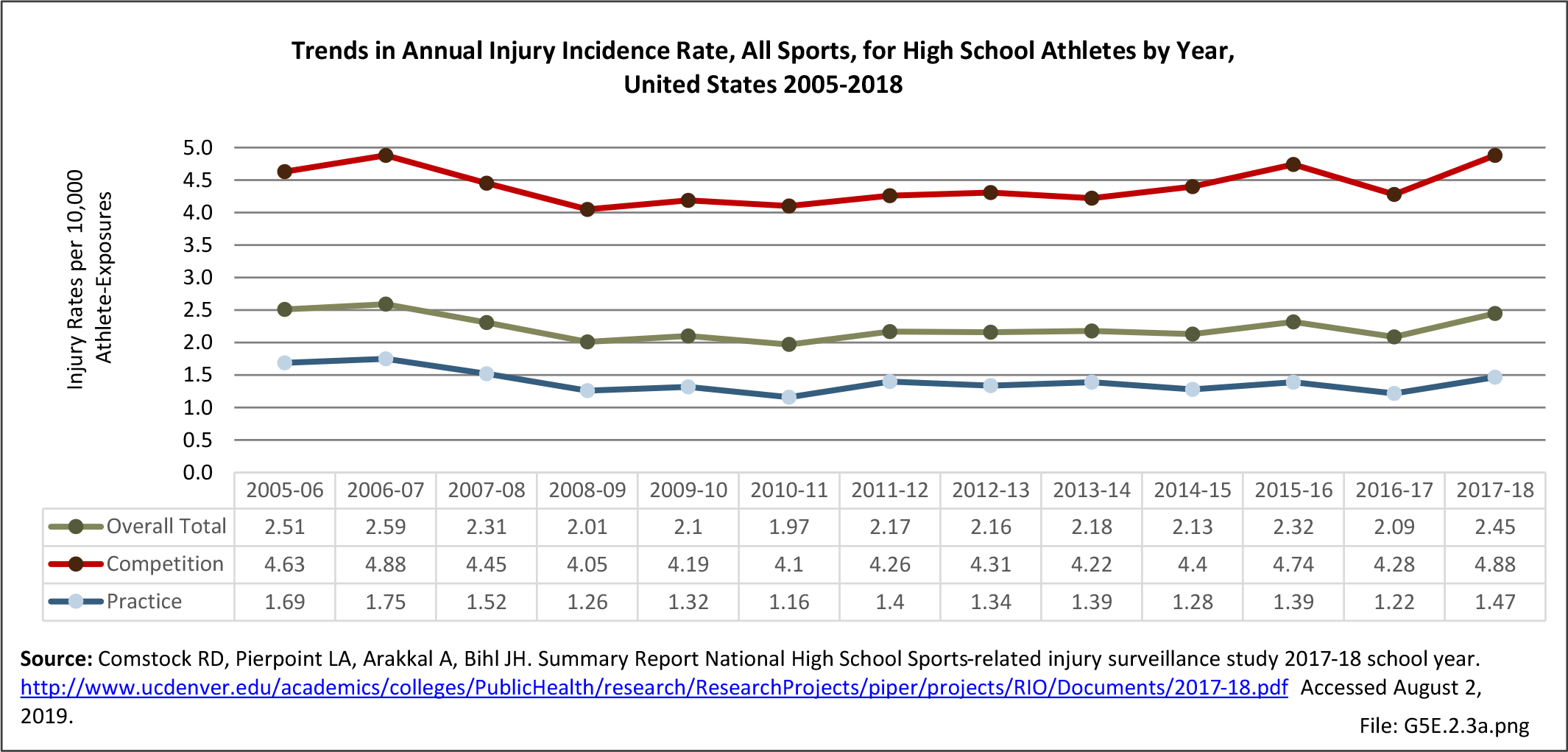
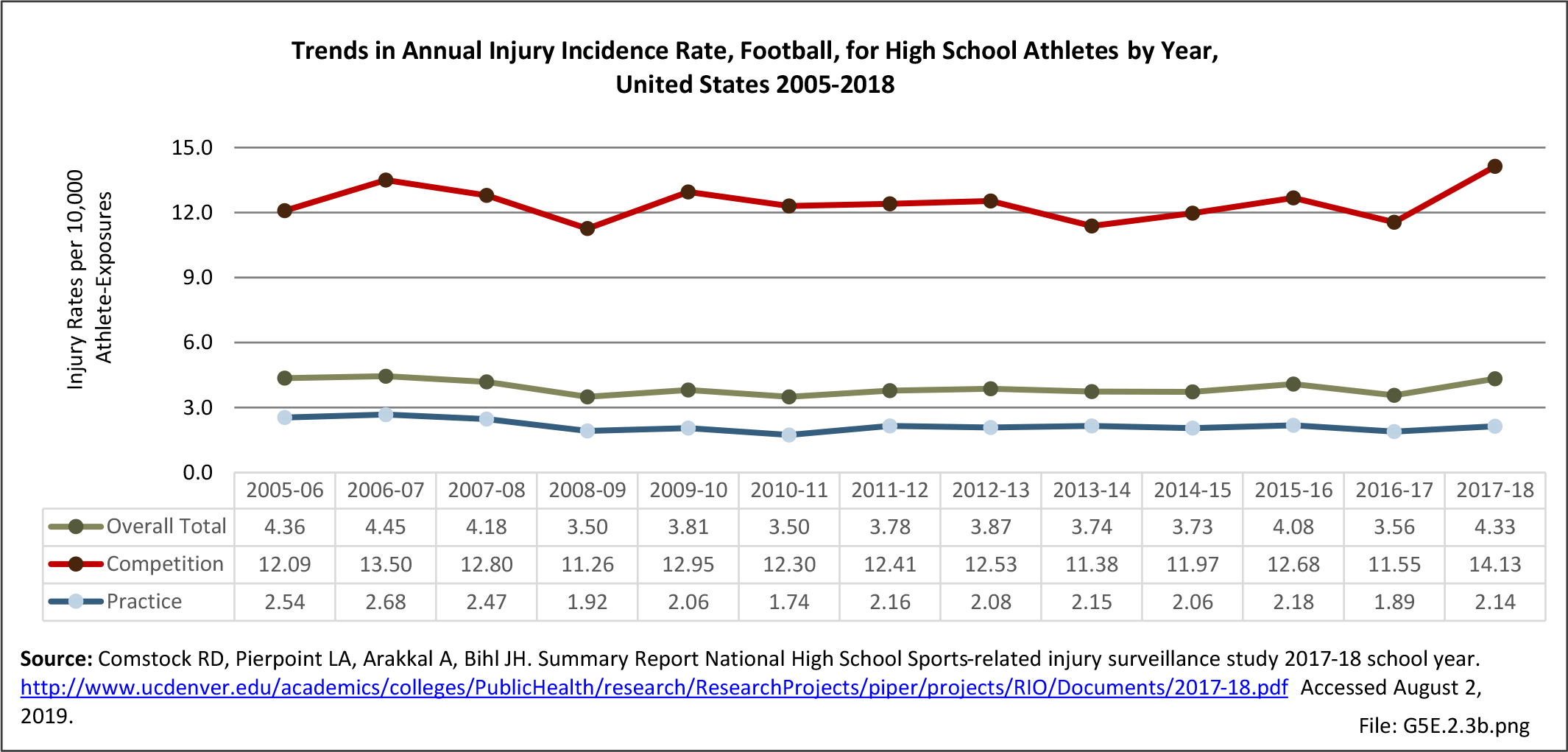
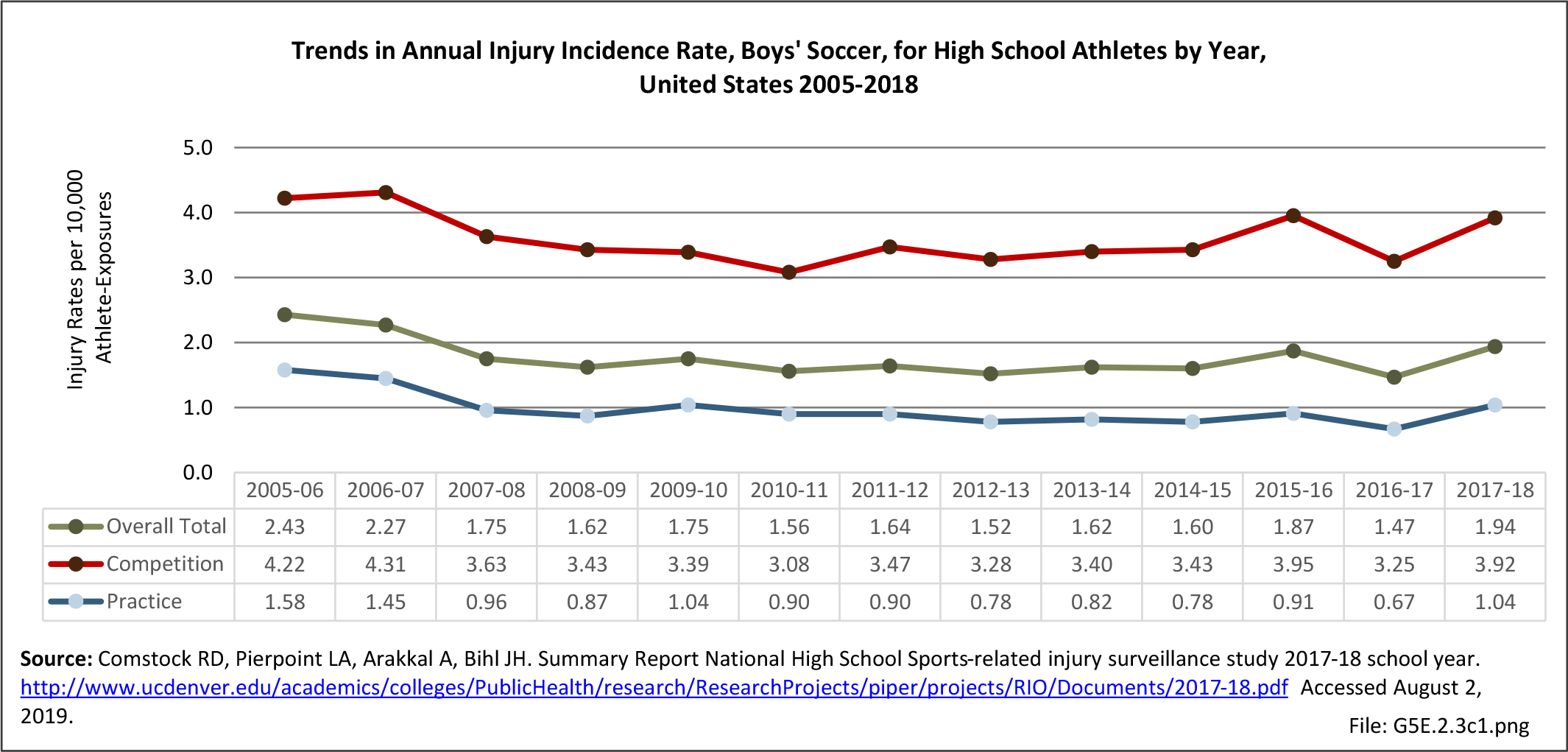
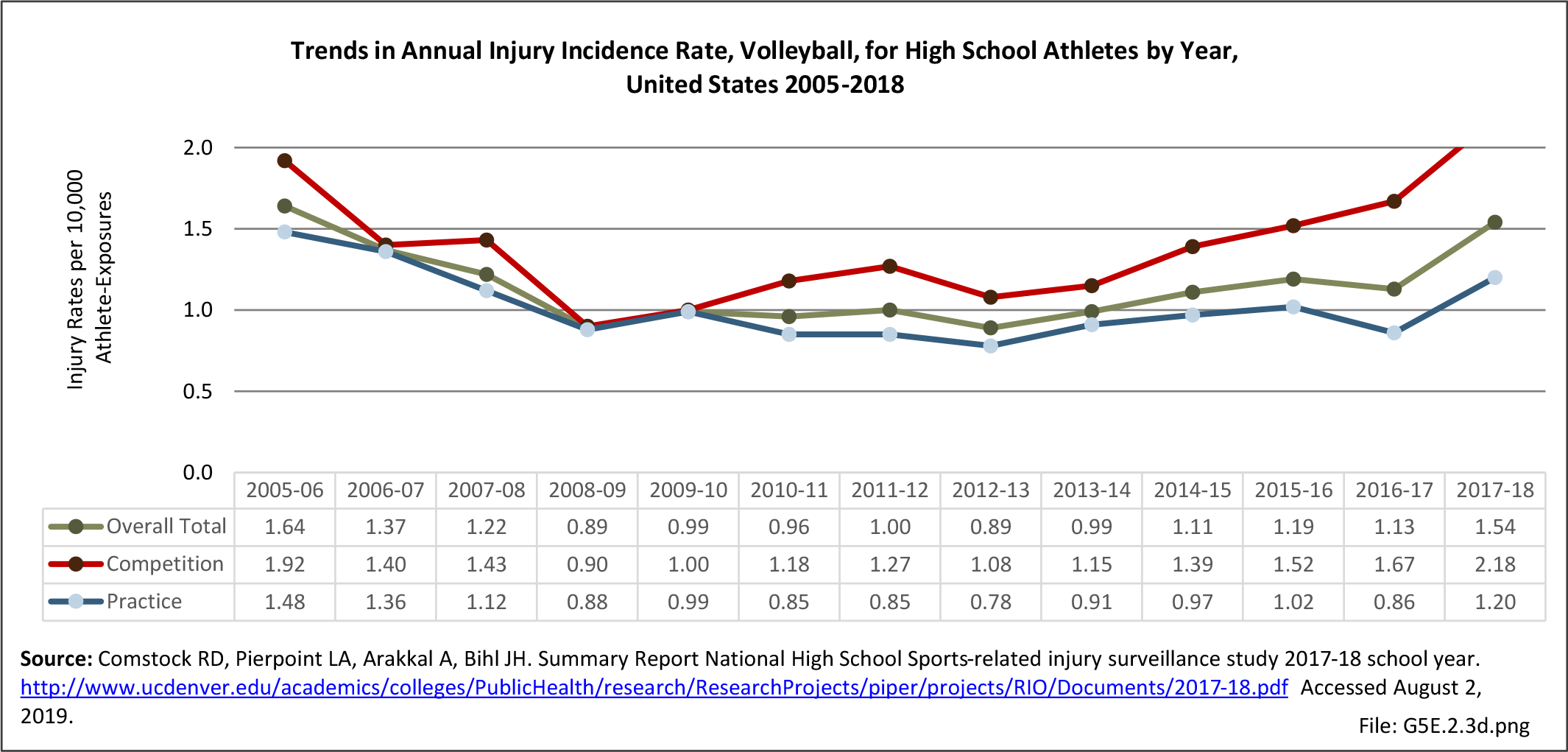
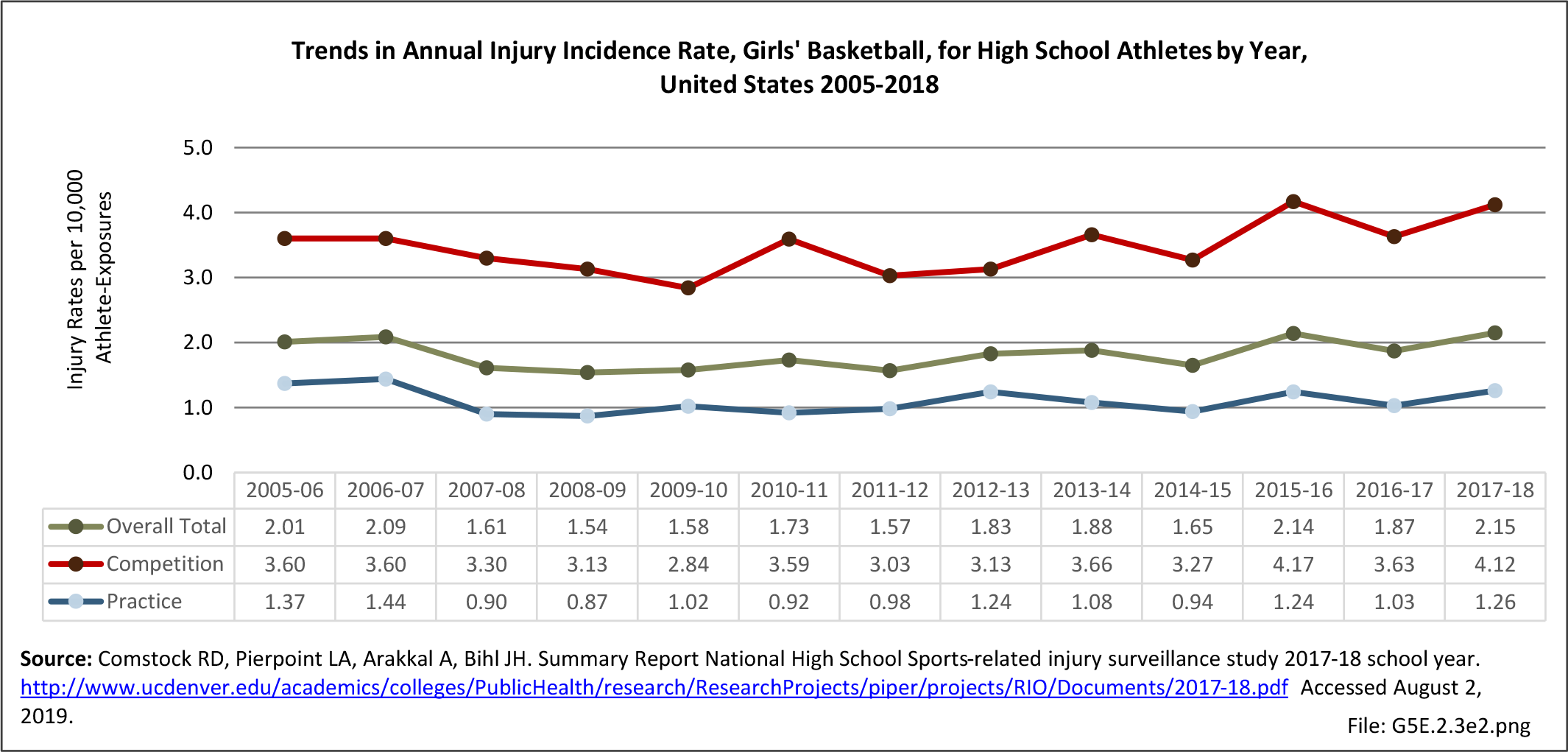
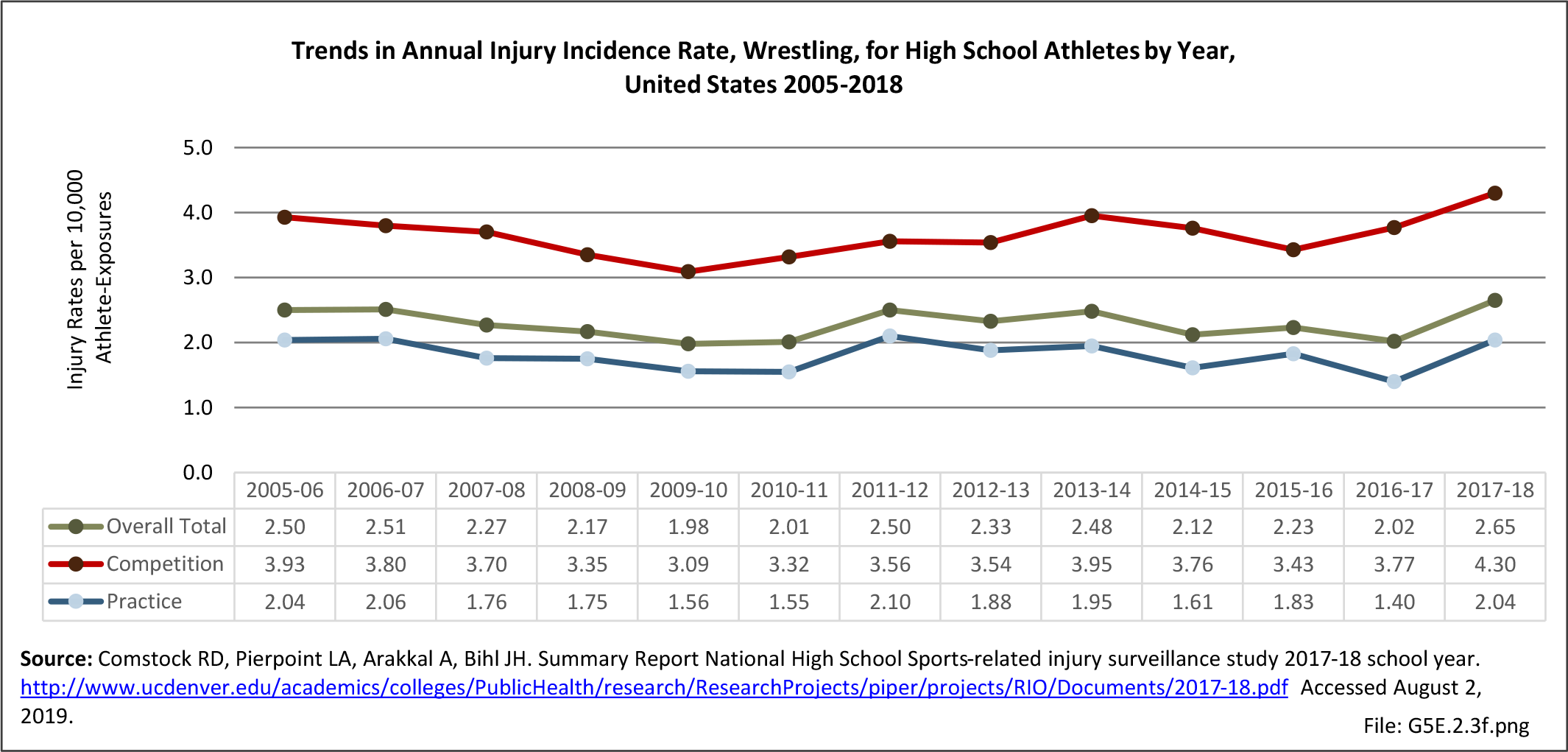
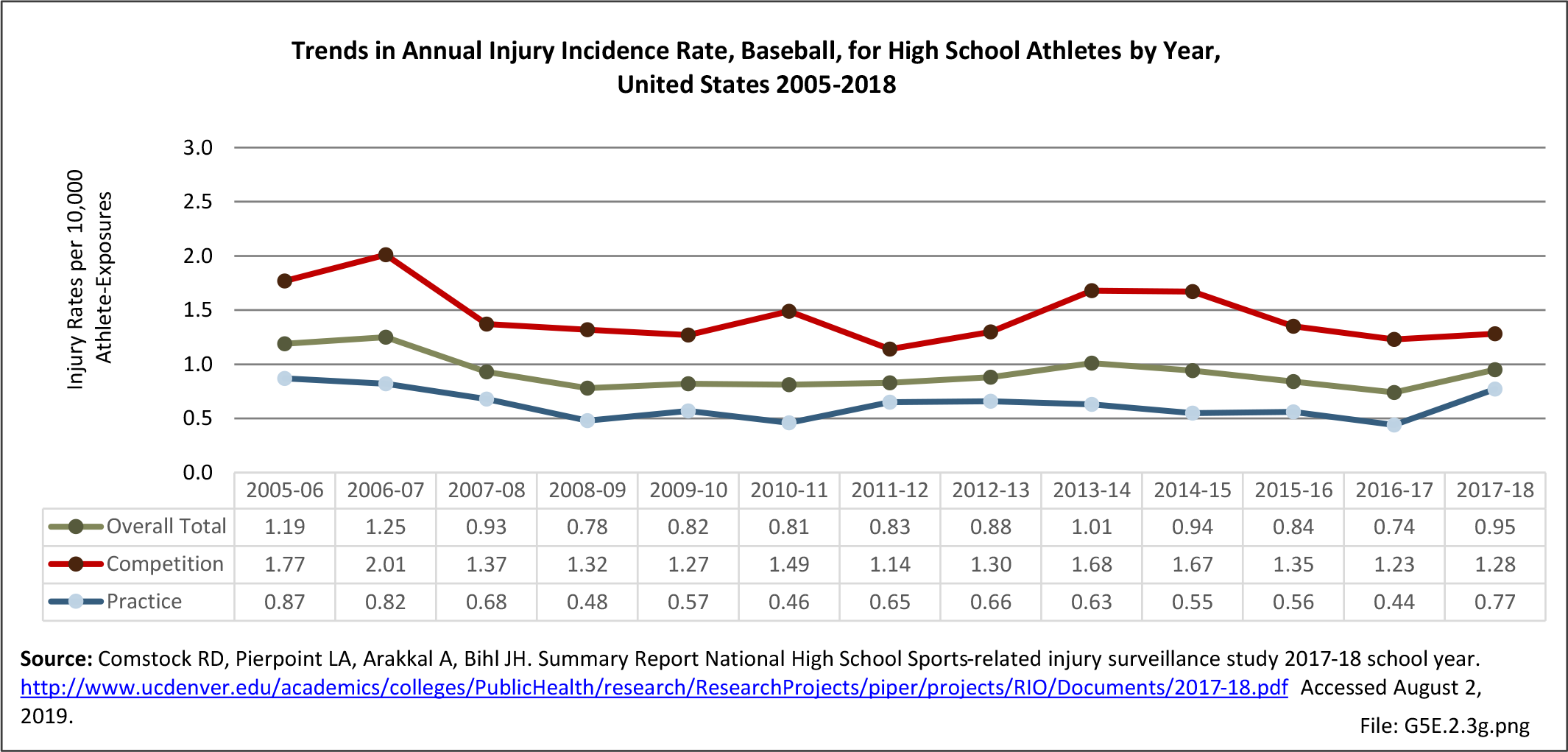
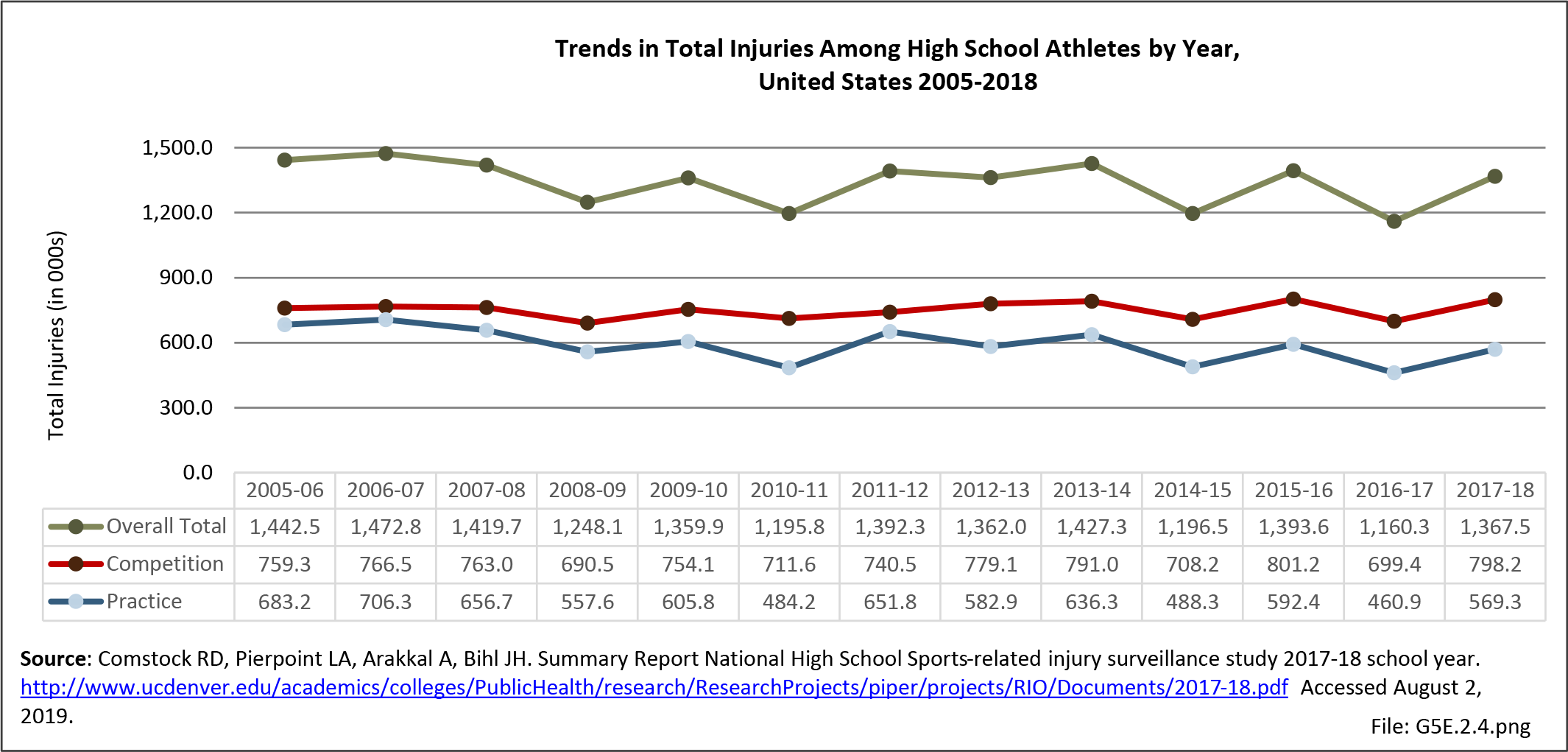
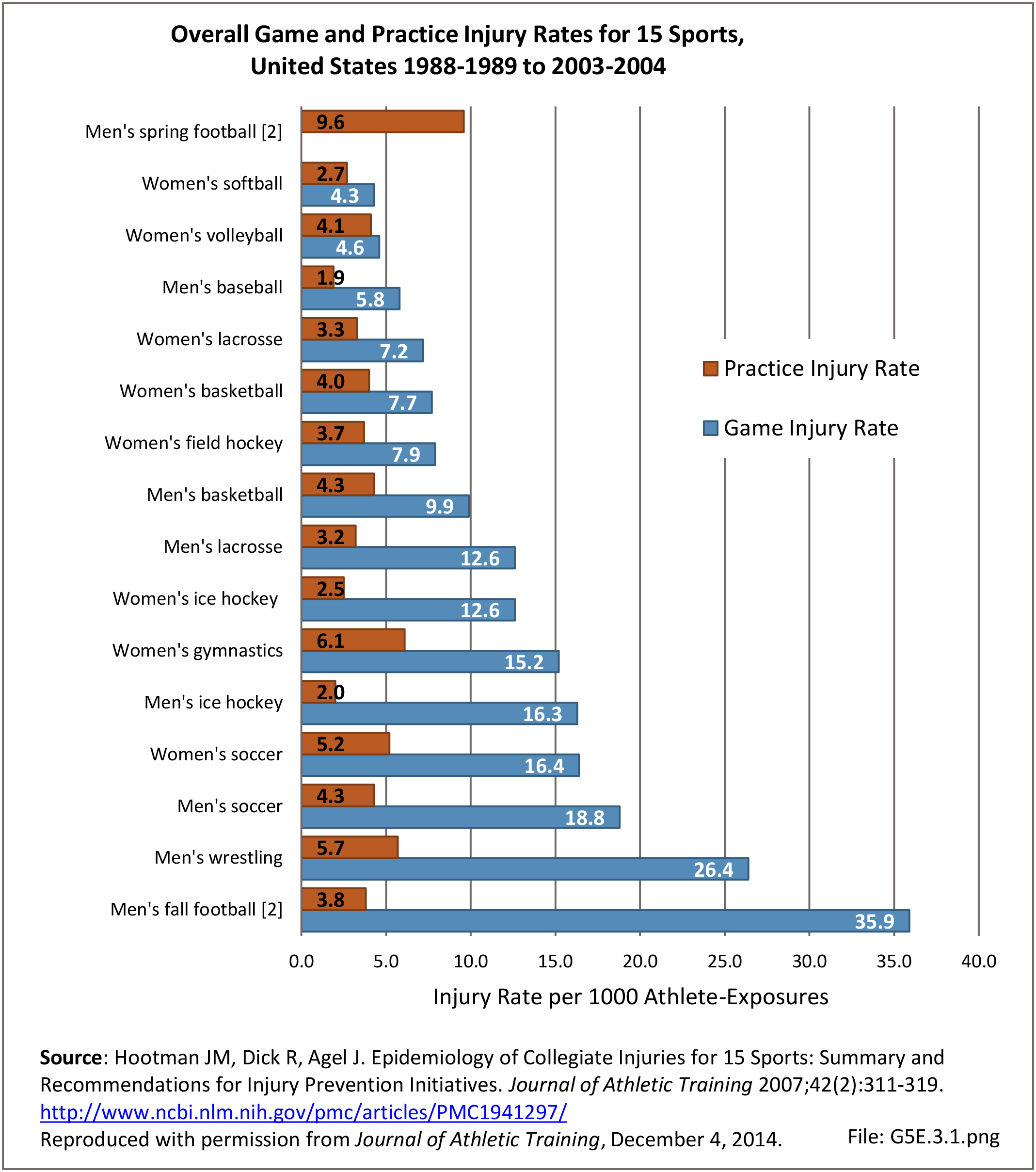
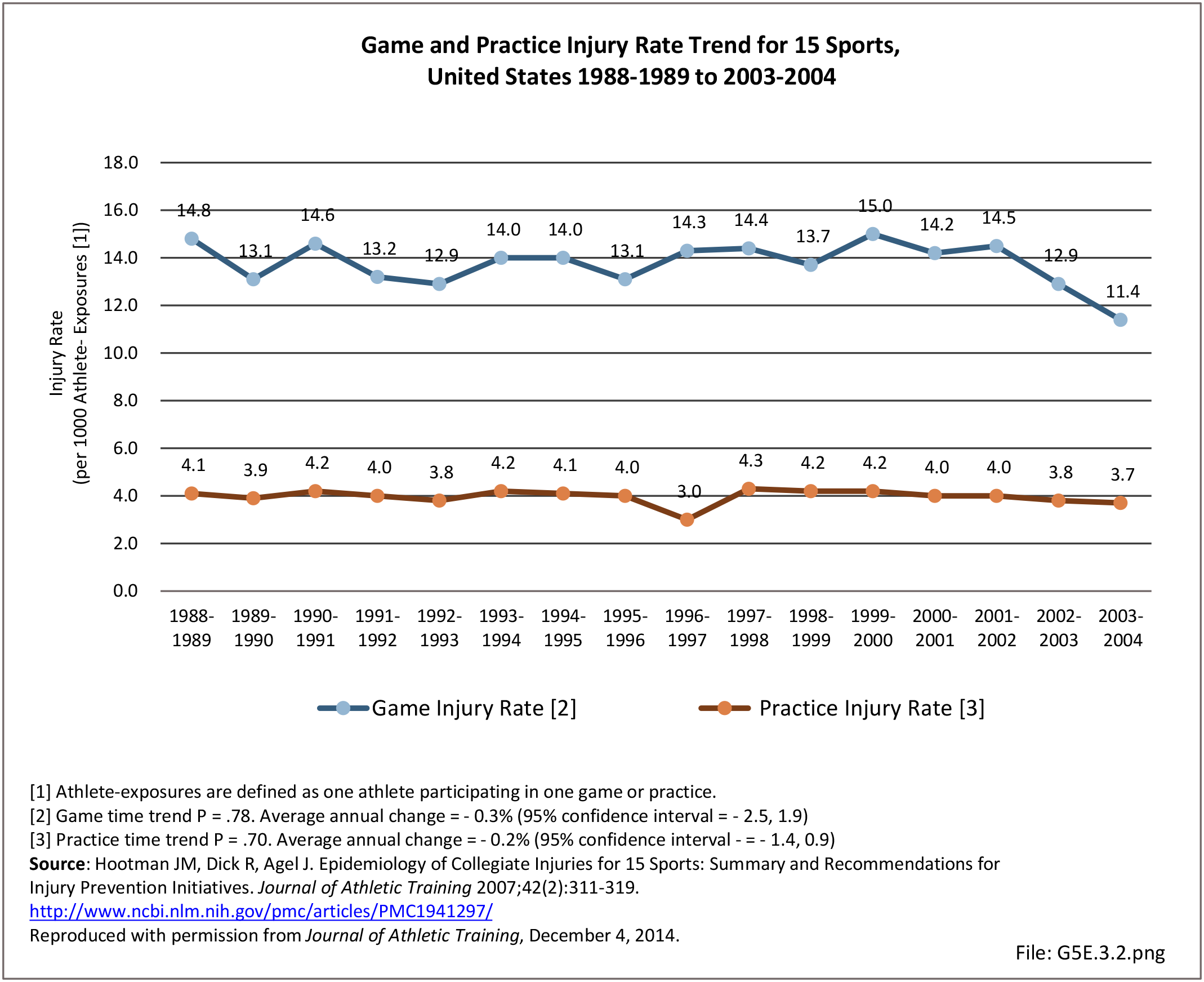
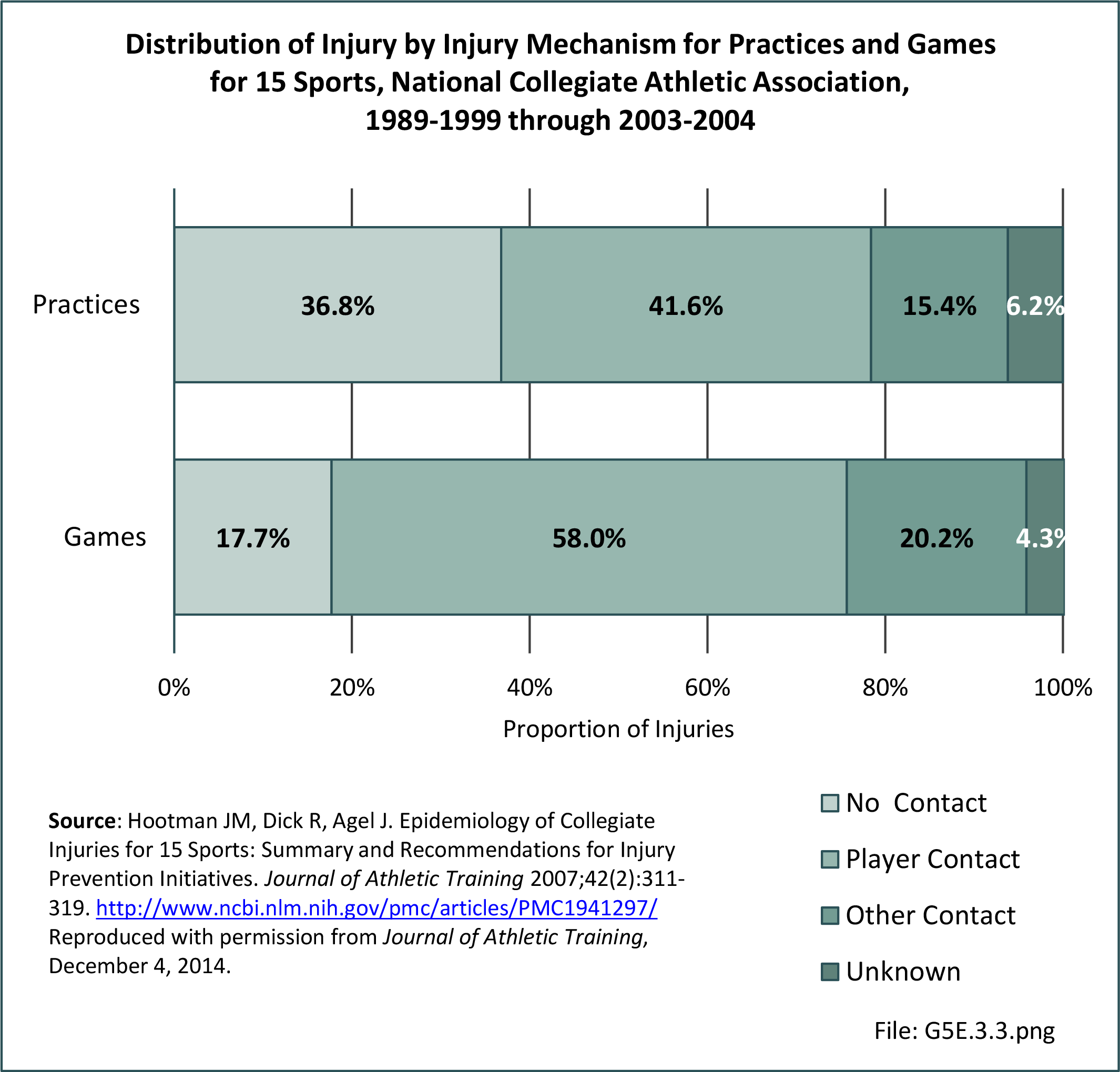
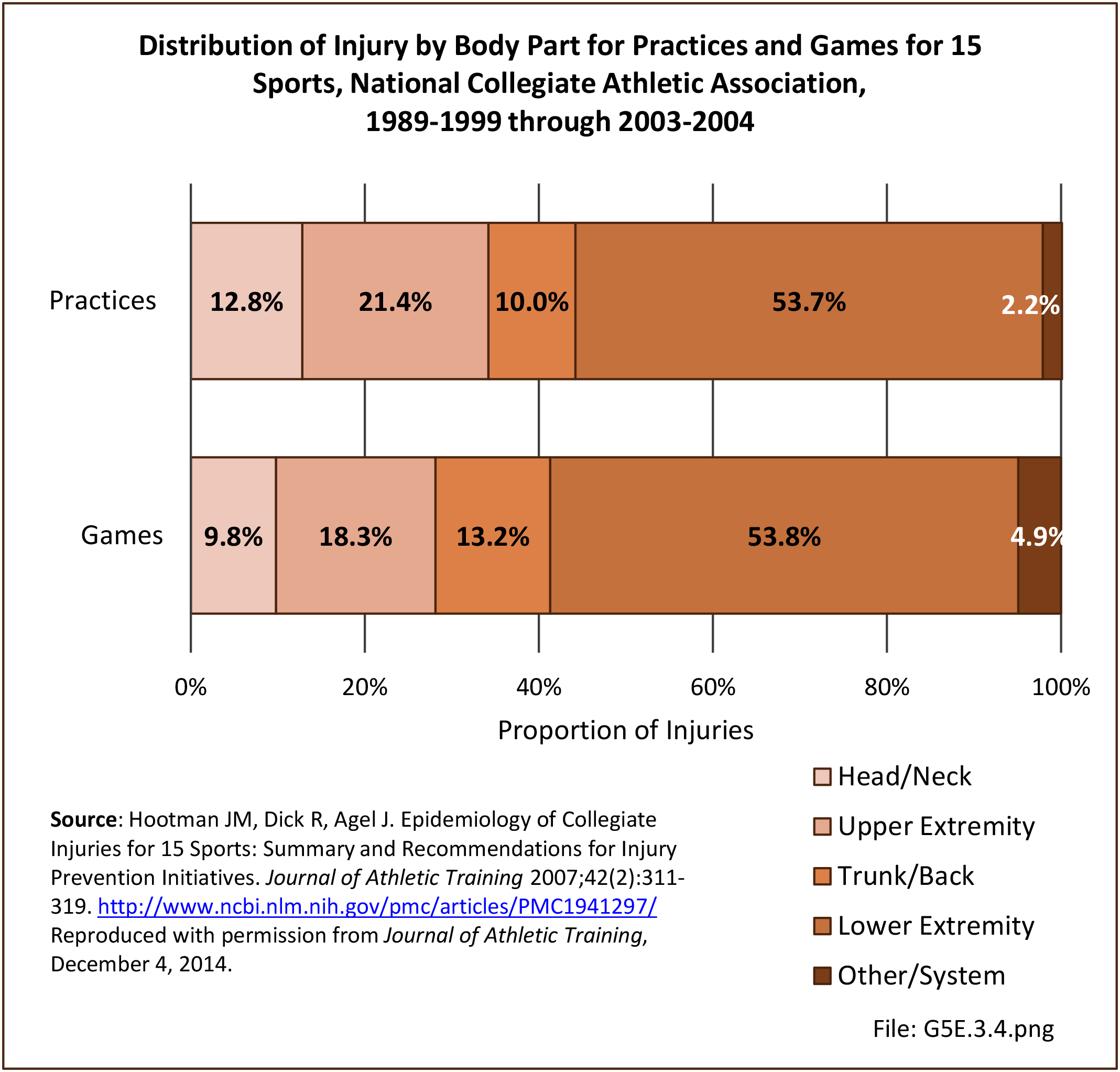
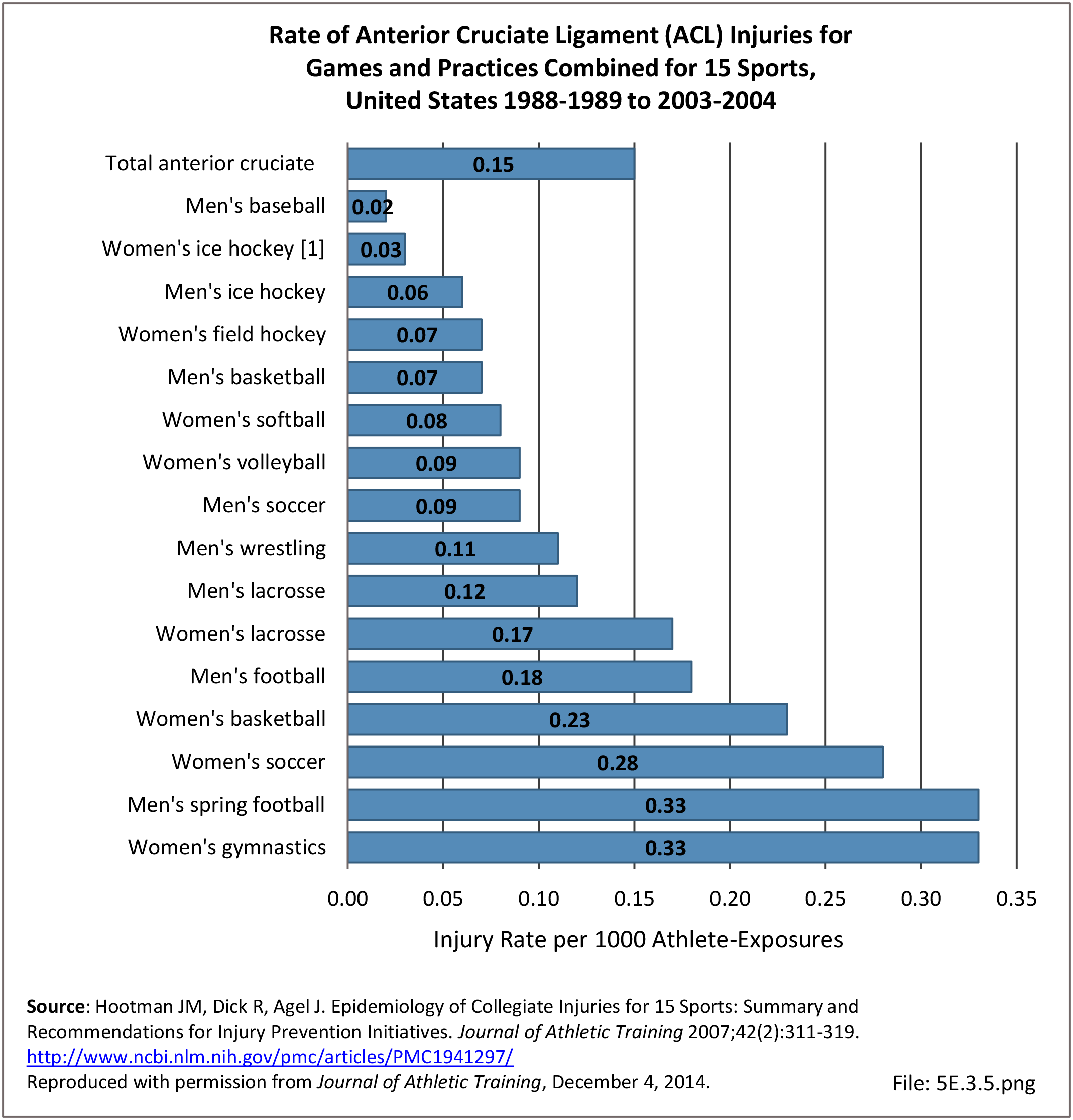
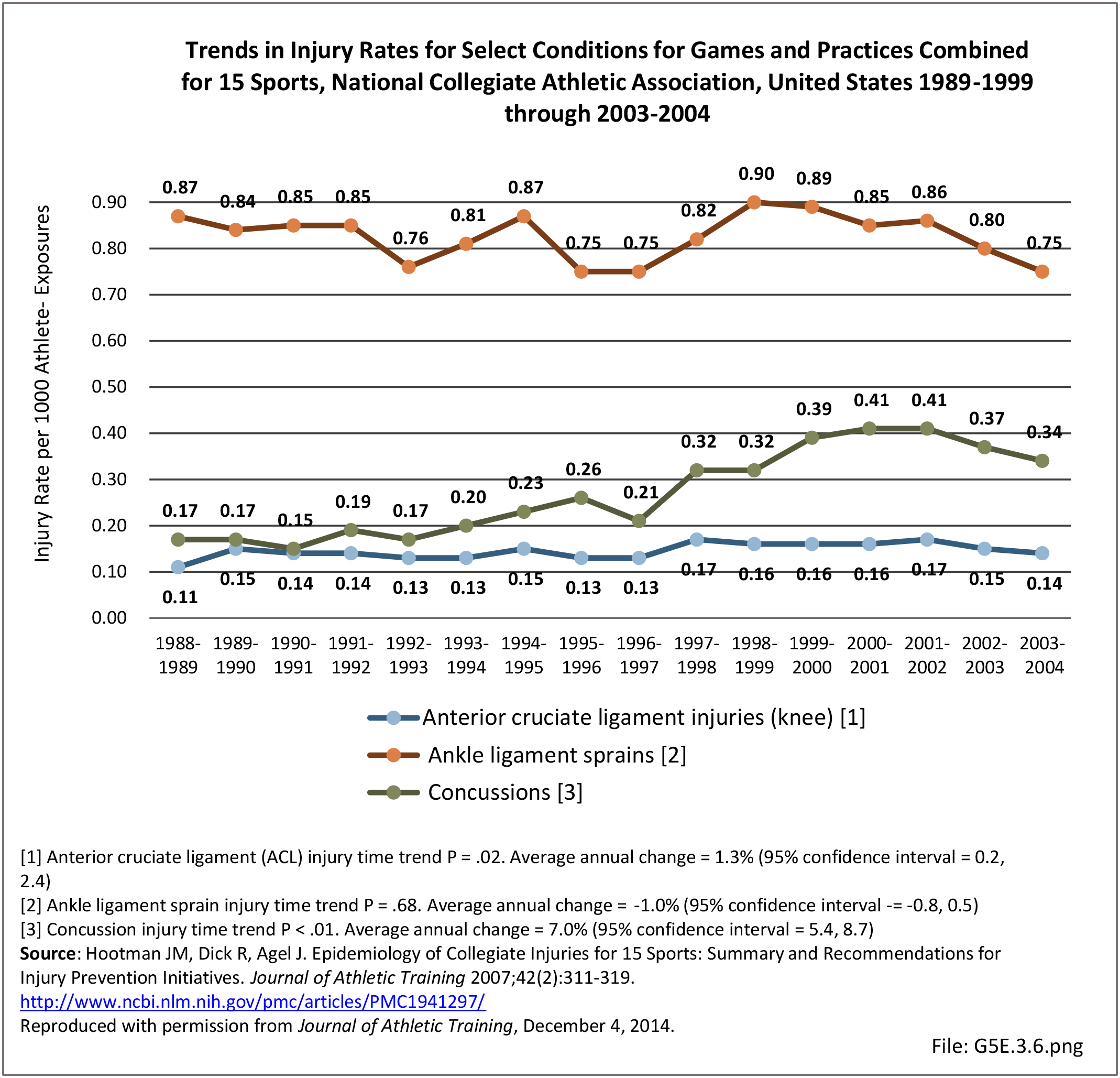
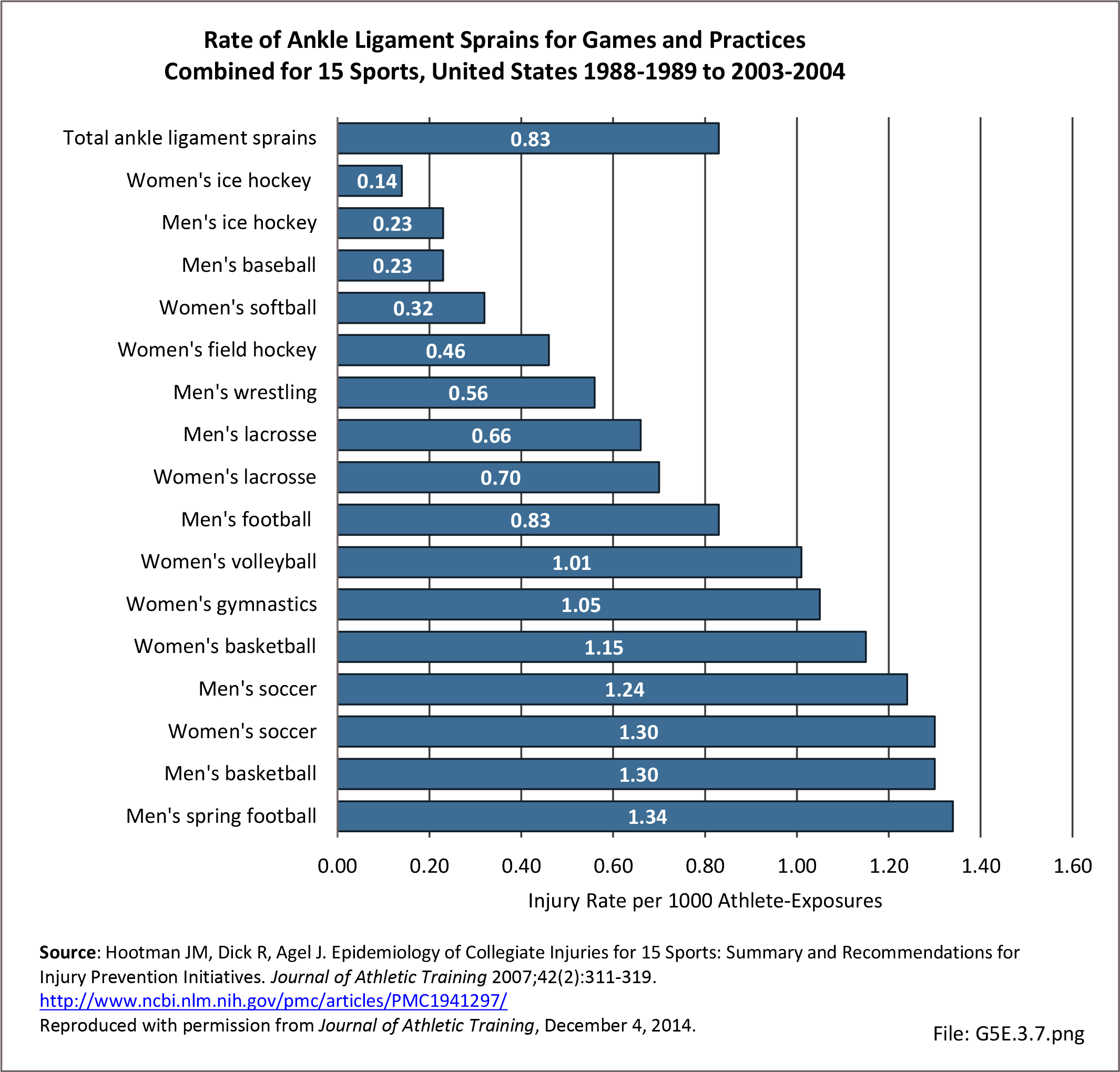
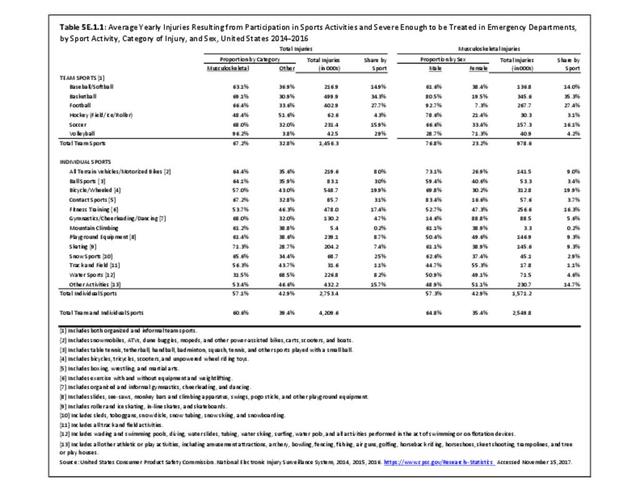
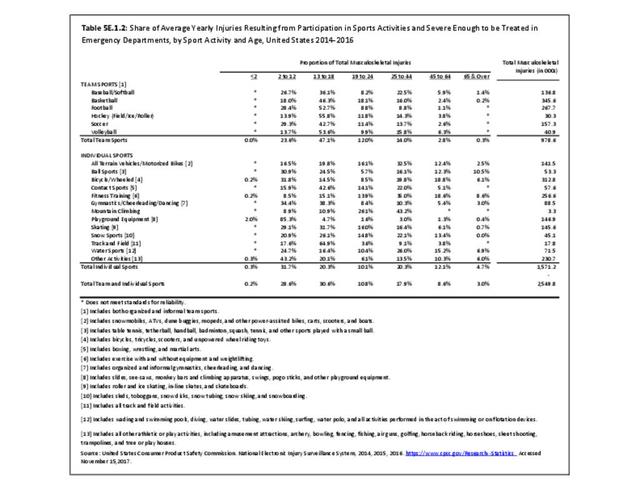
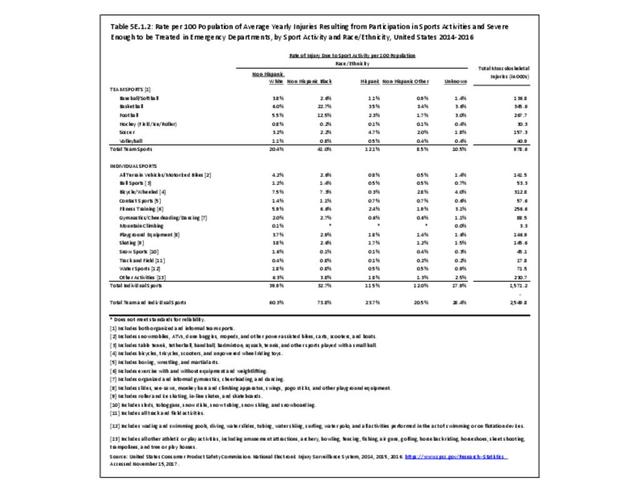
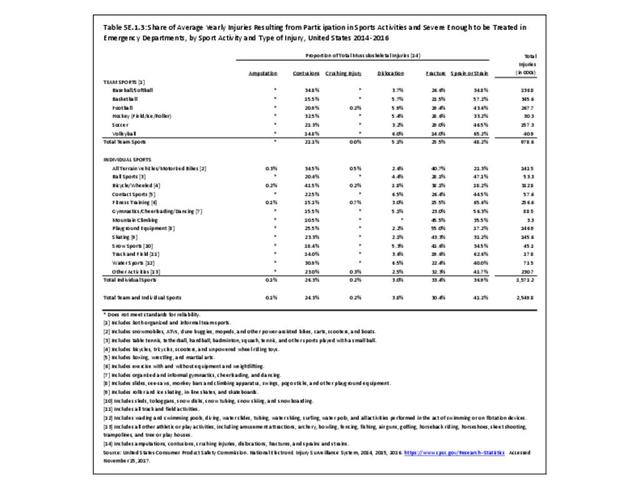
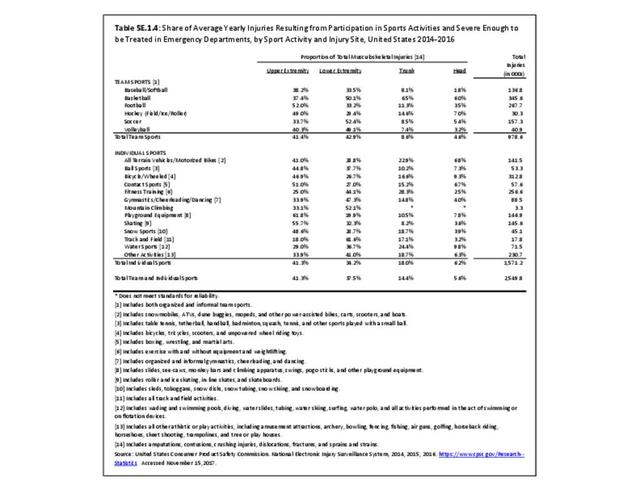
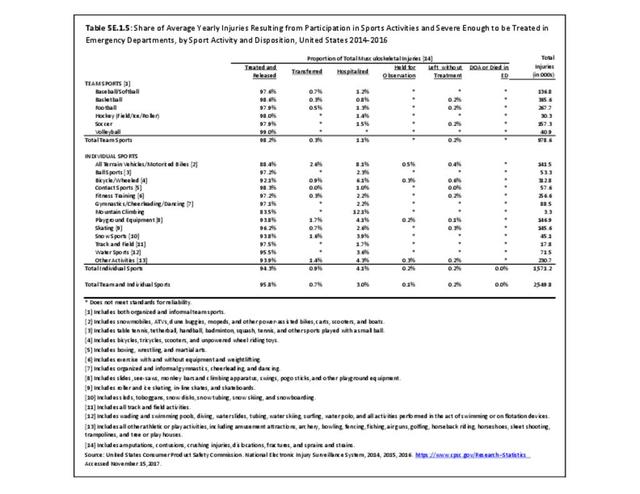
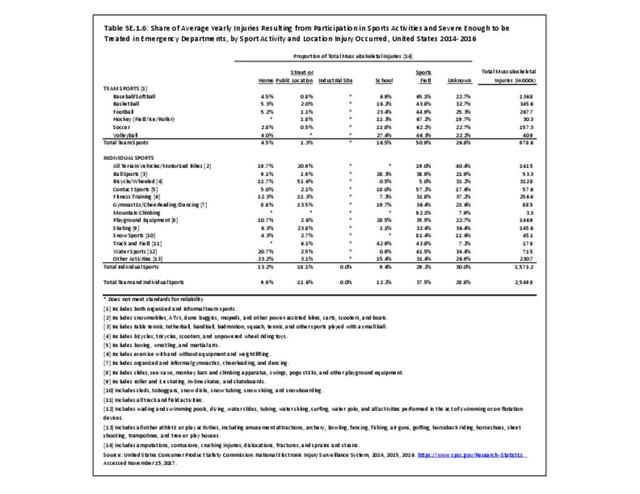
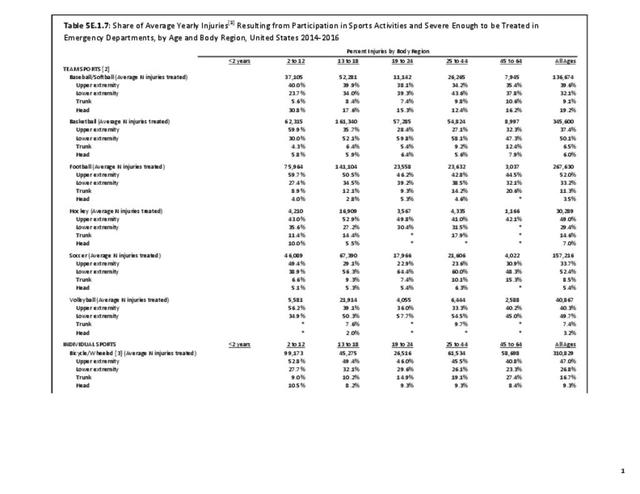
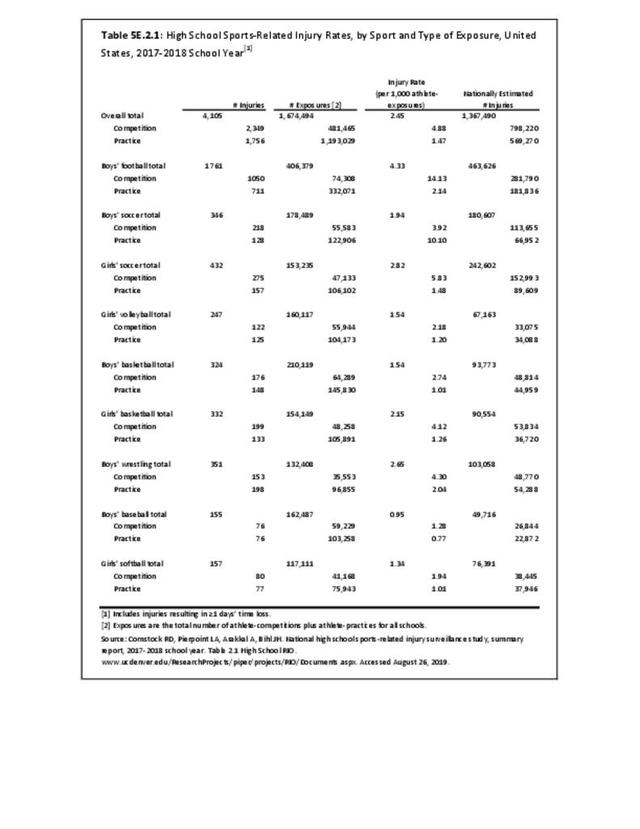
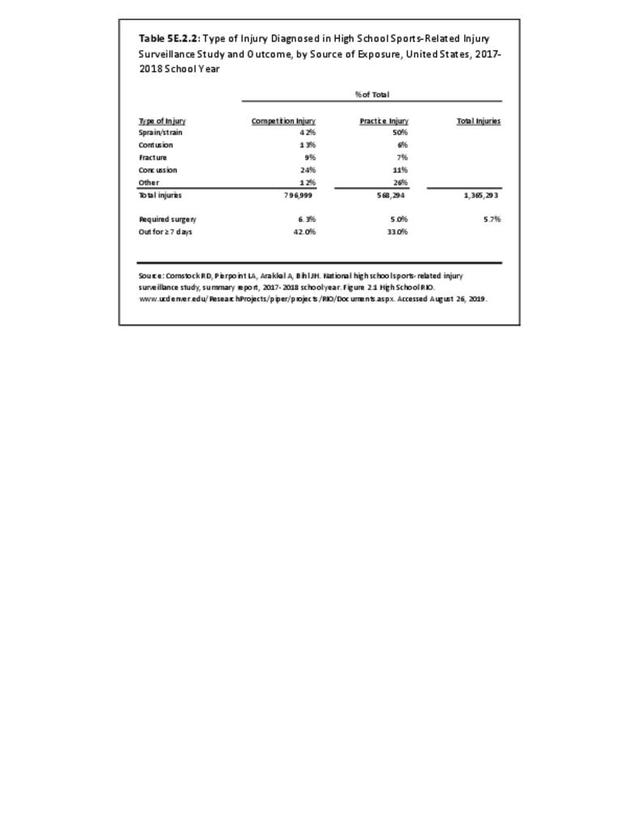
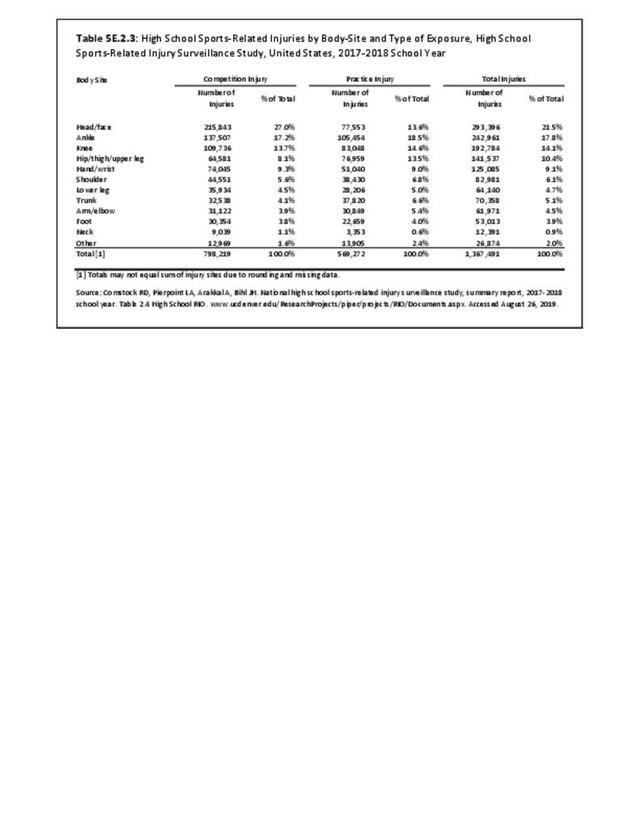
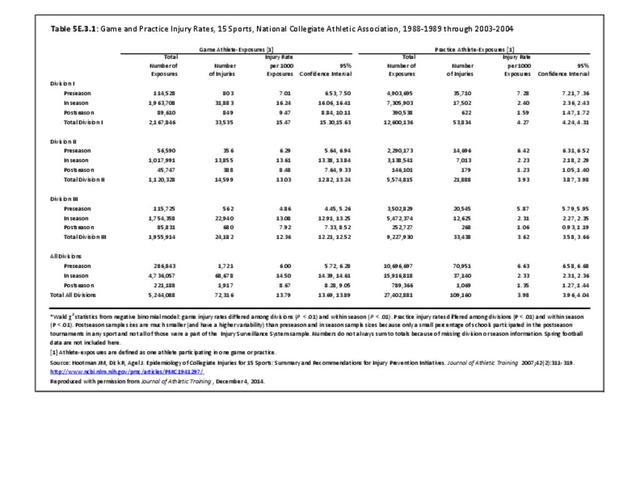
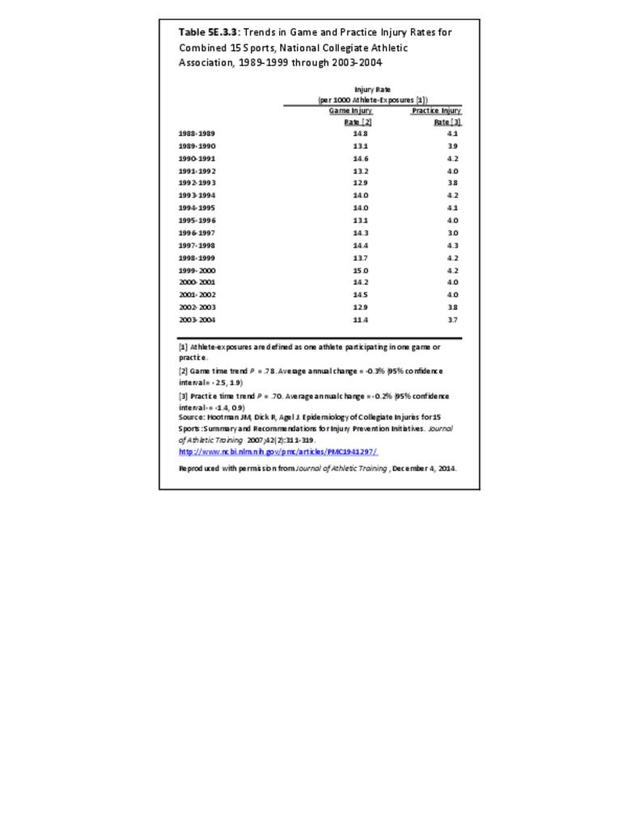
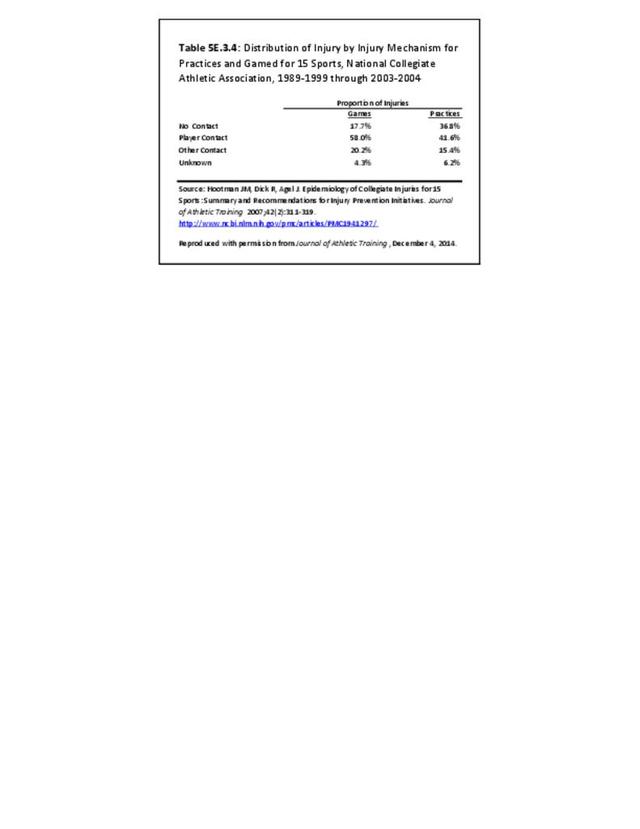
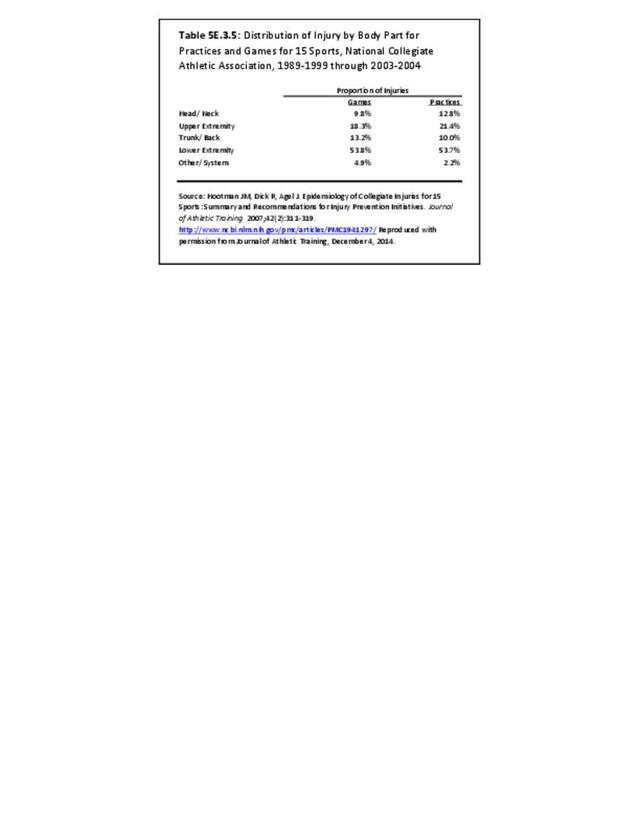
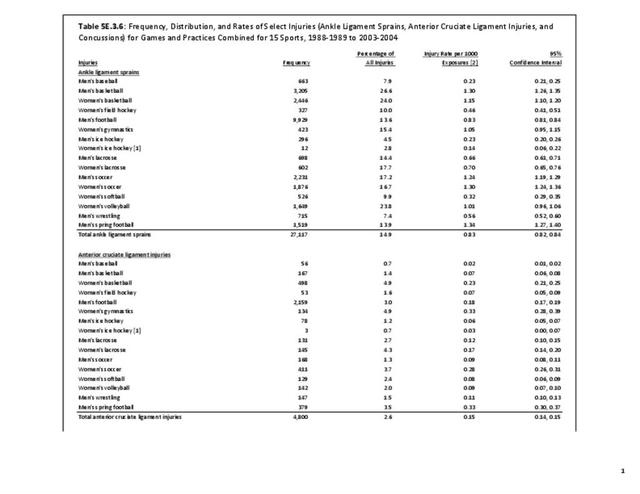
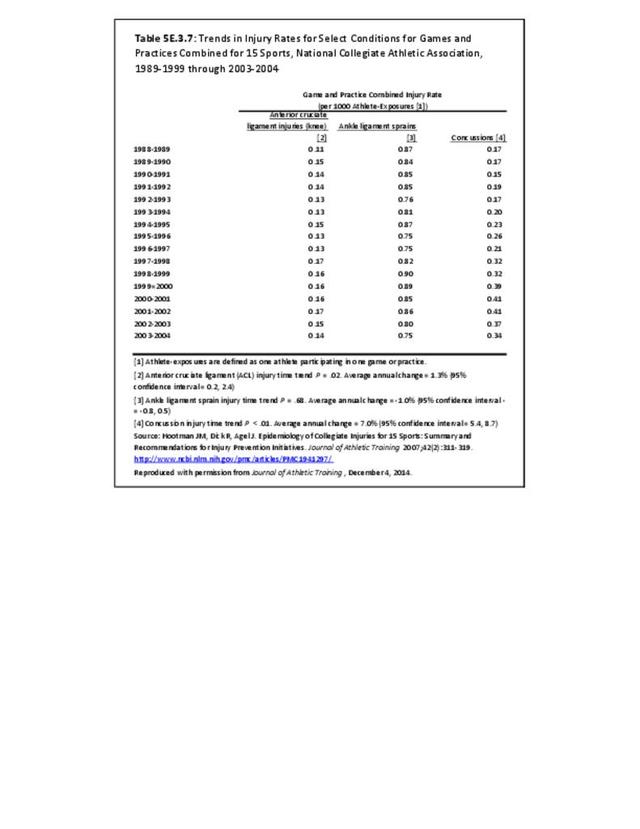
Sports Injuries: Sports injuries occur to children at playgrounds ranging all the way to professional sports. There is no single database that addresses sports injuries for all ages and activities. BMUS 4th Edition includes data from the US Consumer Product Safety Commission, National Electronic Injury Surveillance System (NEISS); the University of Colorado, Colorado School of Public Health High School Sports-Related Injury Surveillance Study (RIOTM); and data from the National Collegiate Athletic Association published in the Journal of Athletic Training. Access to raw databases used in any of these sources, as well as data from professional sports injuries, is not available.
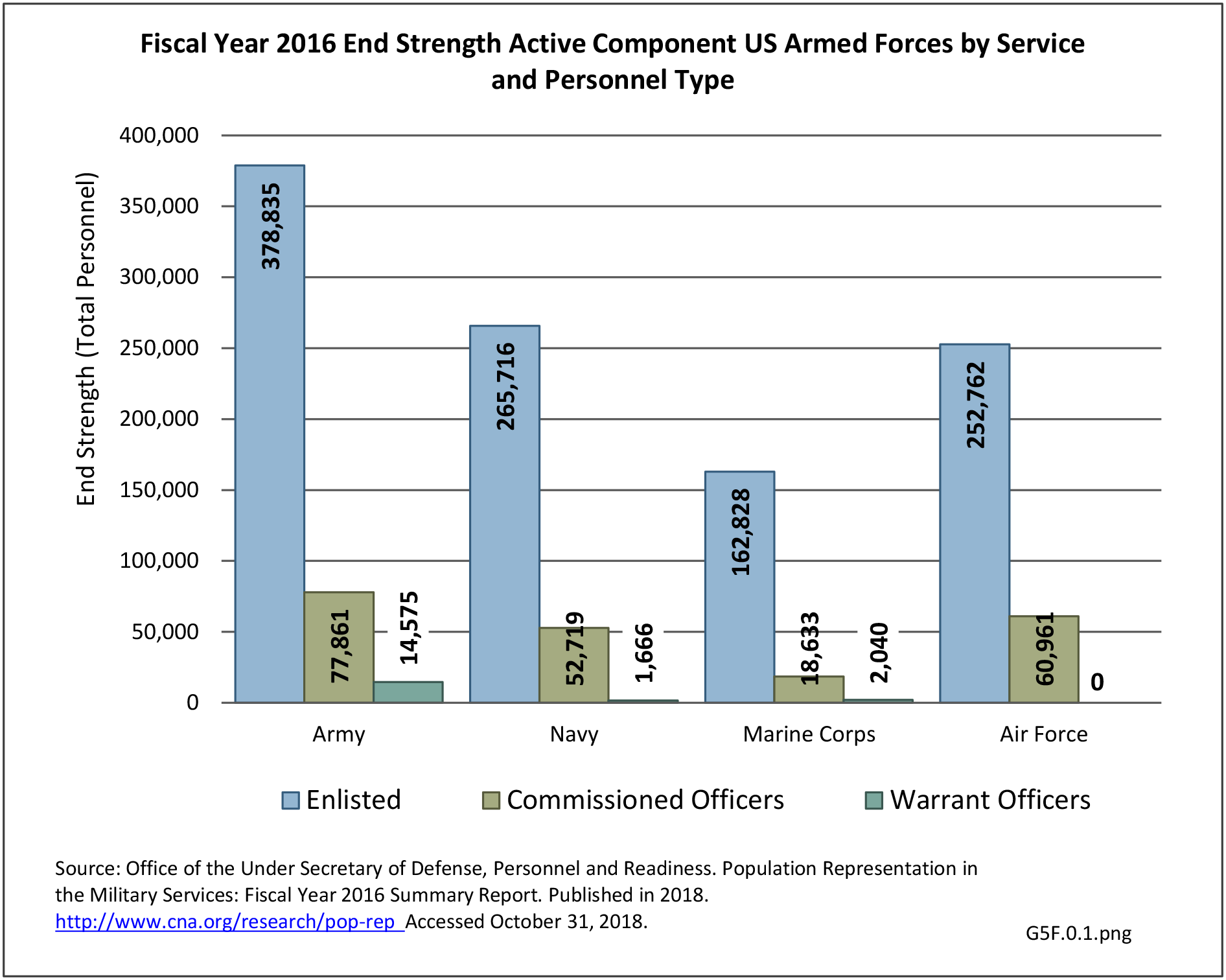
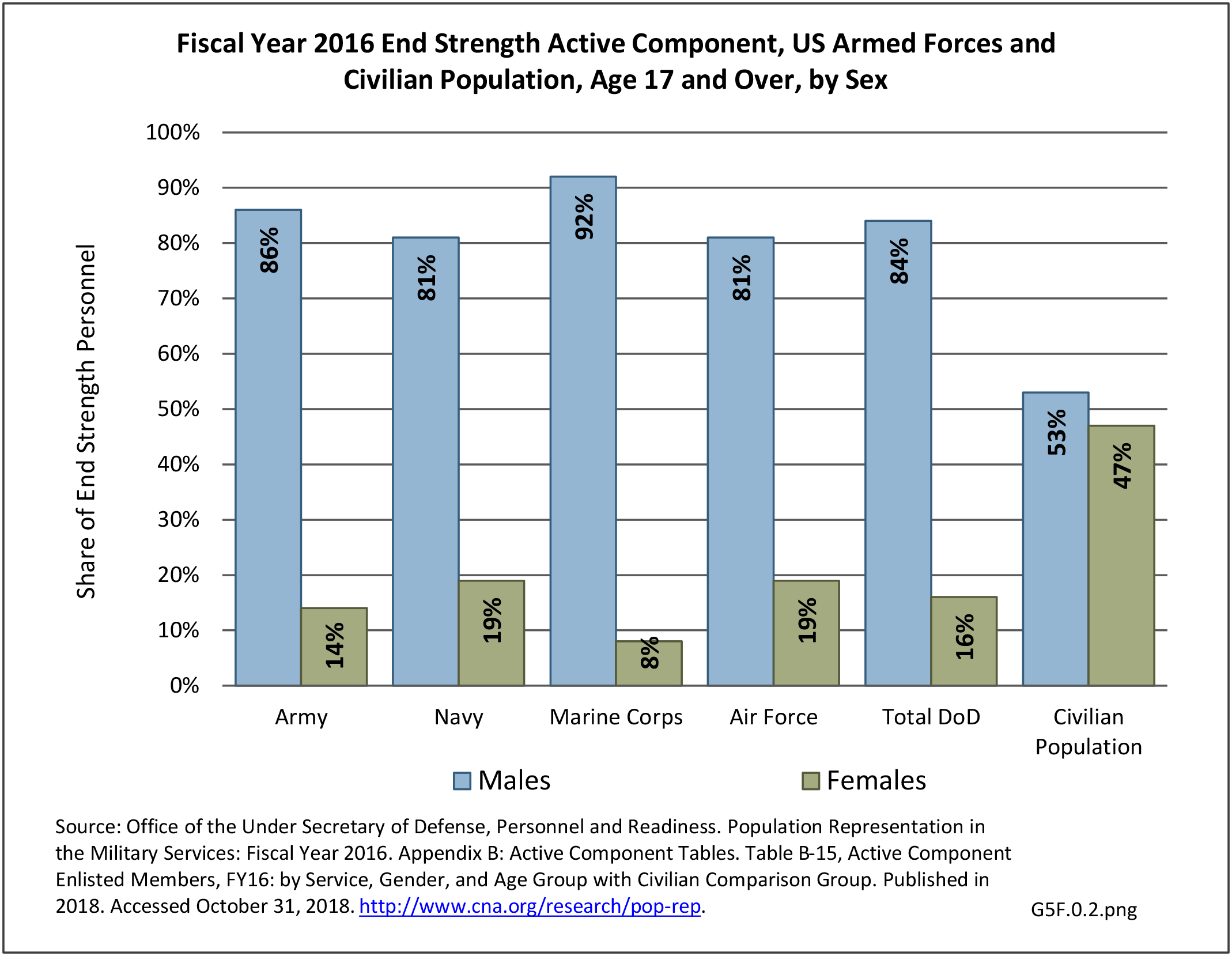
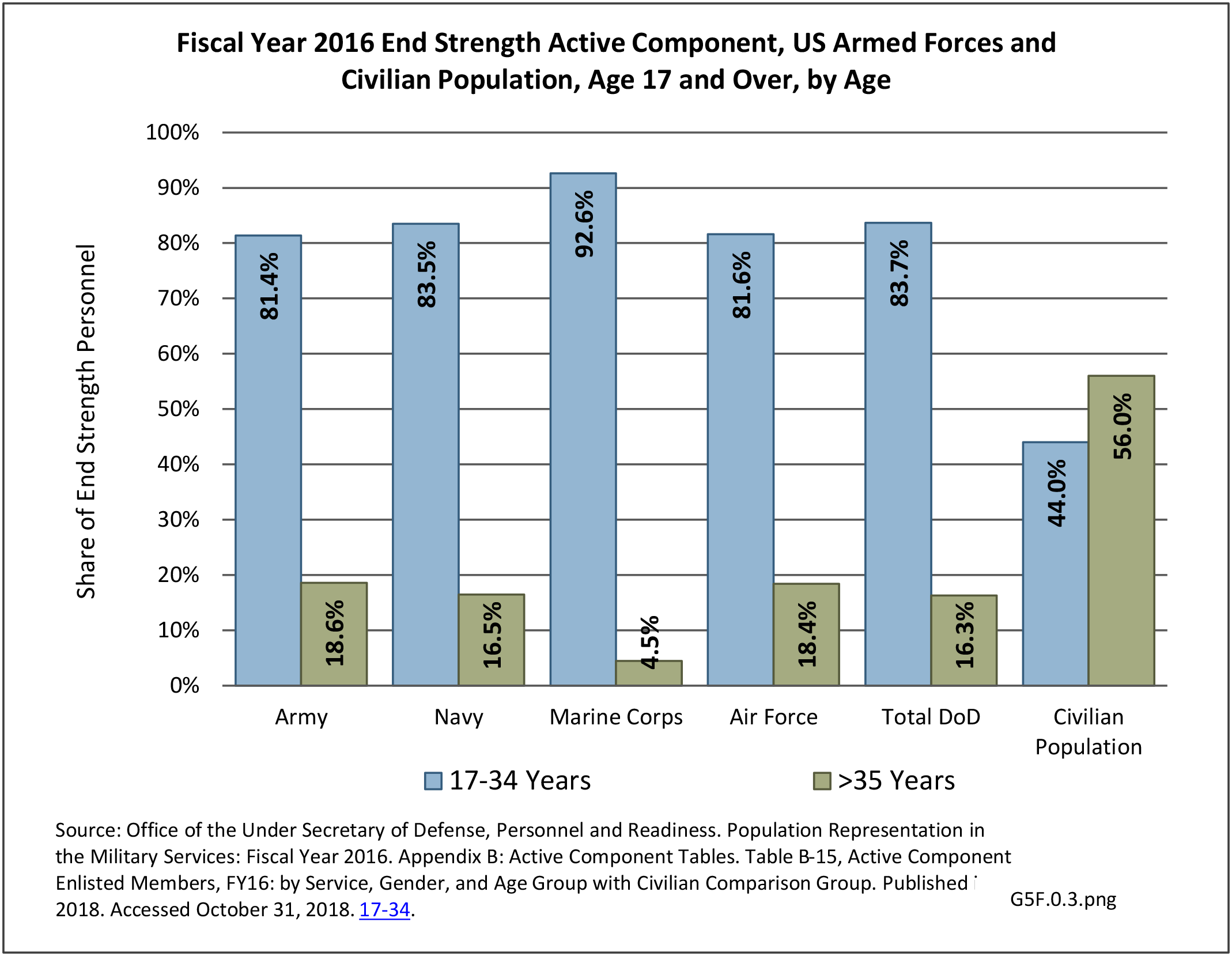
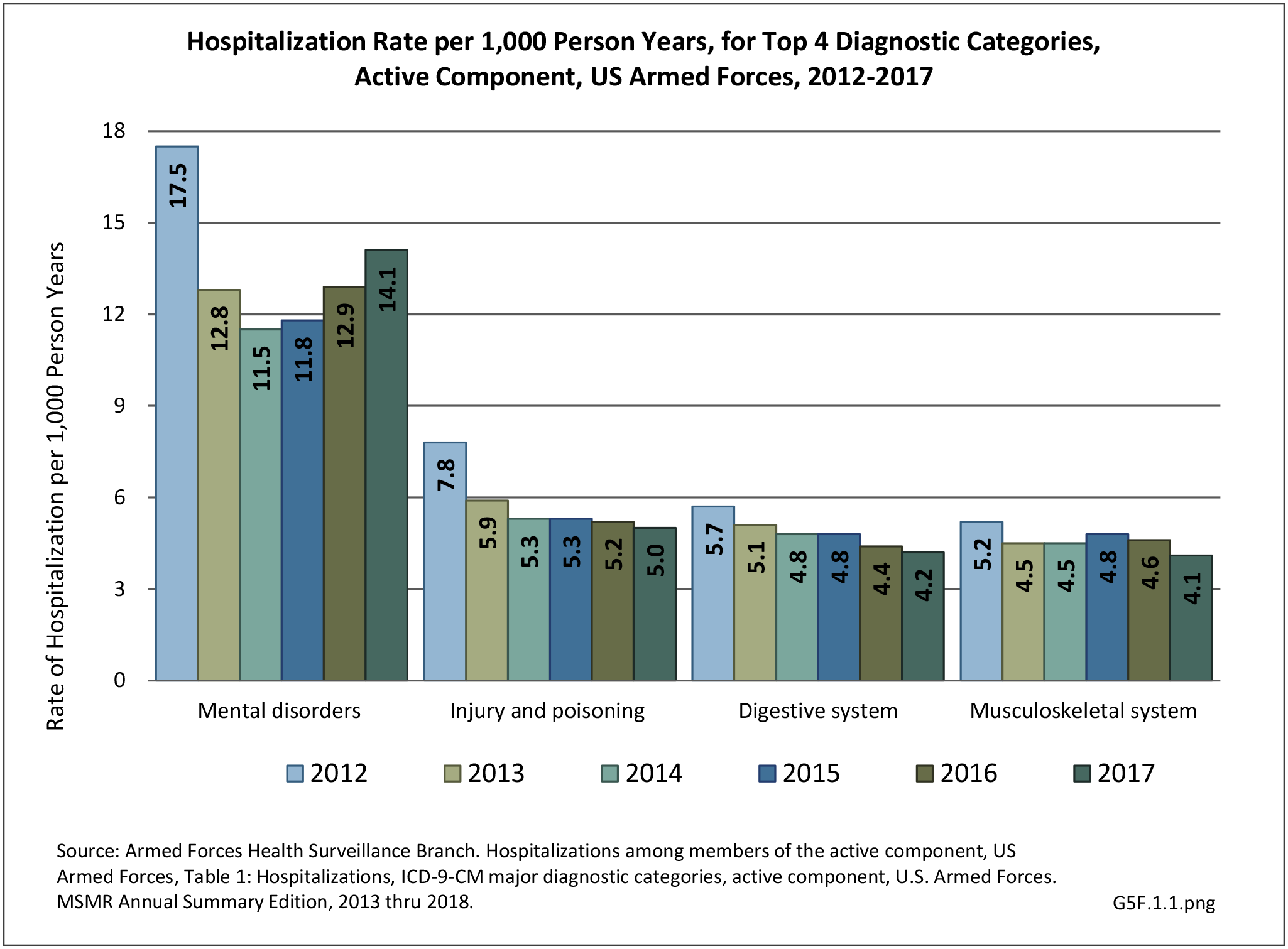
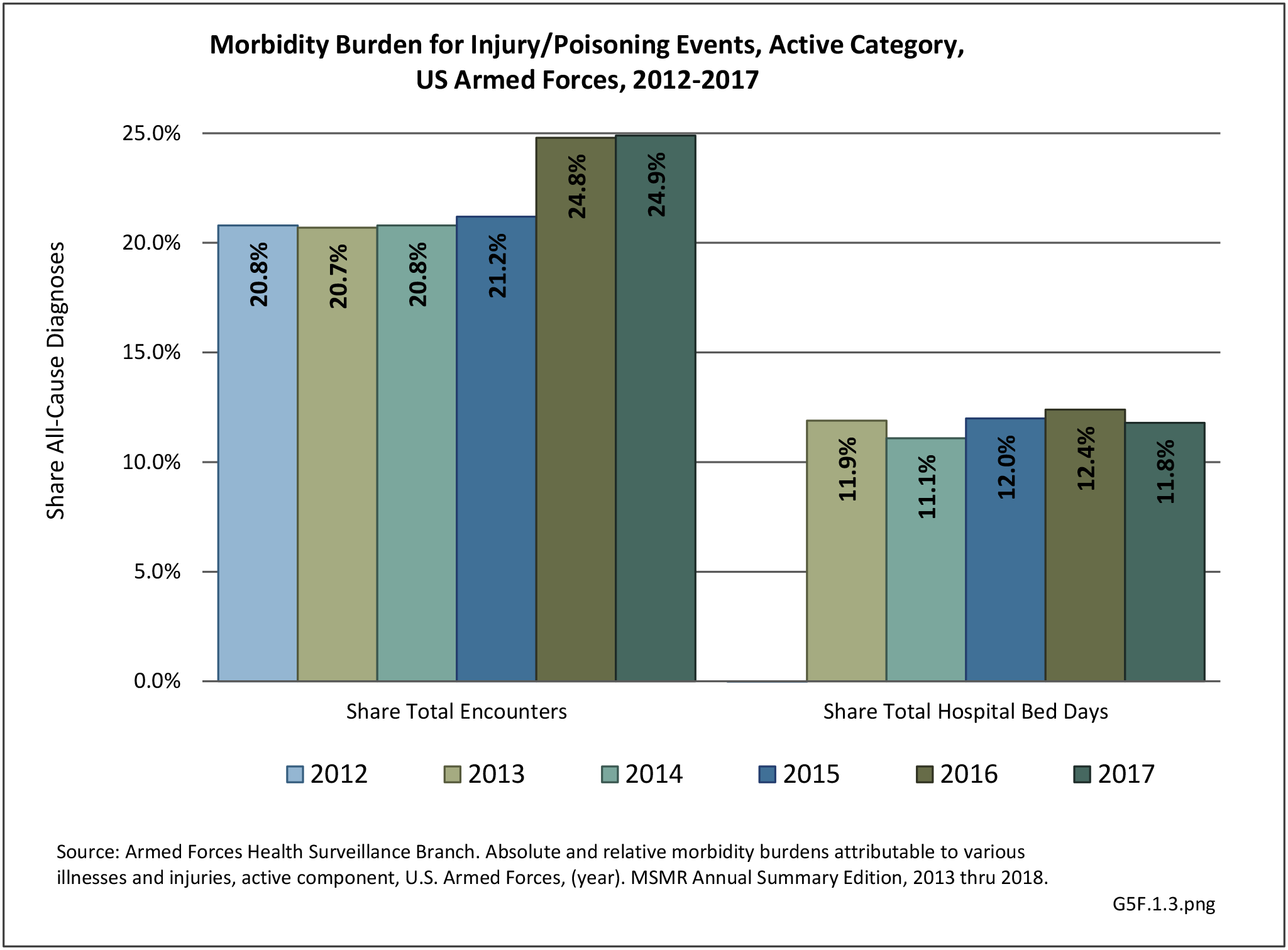
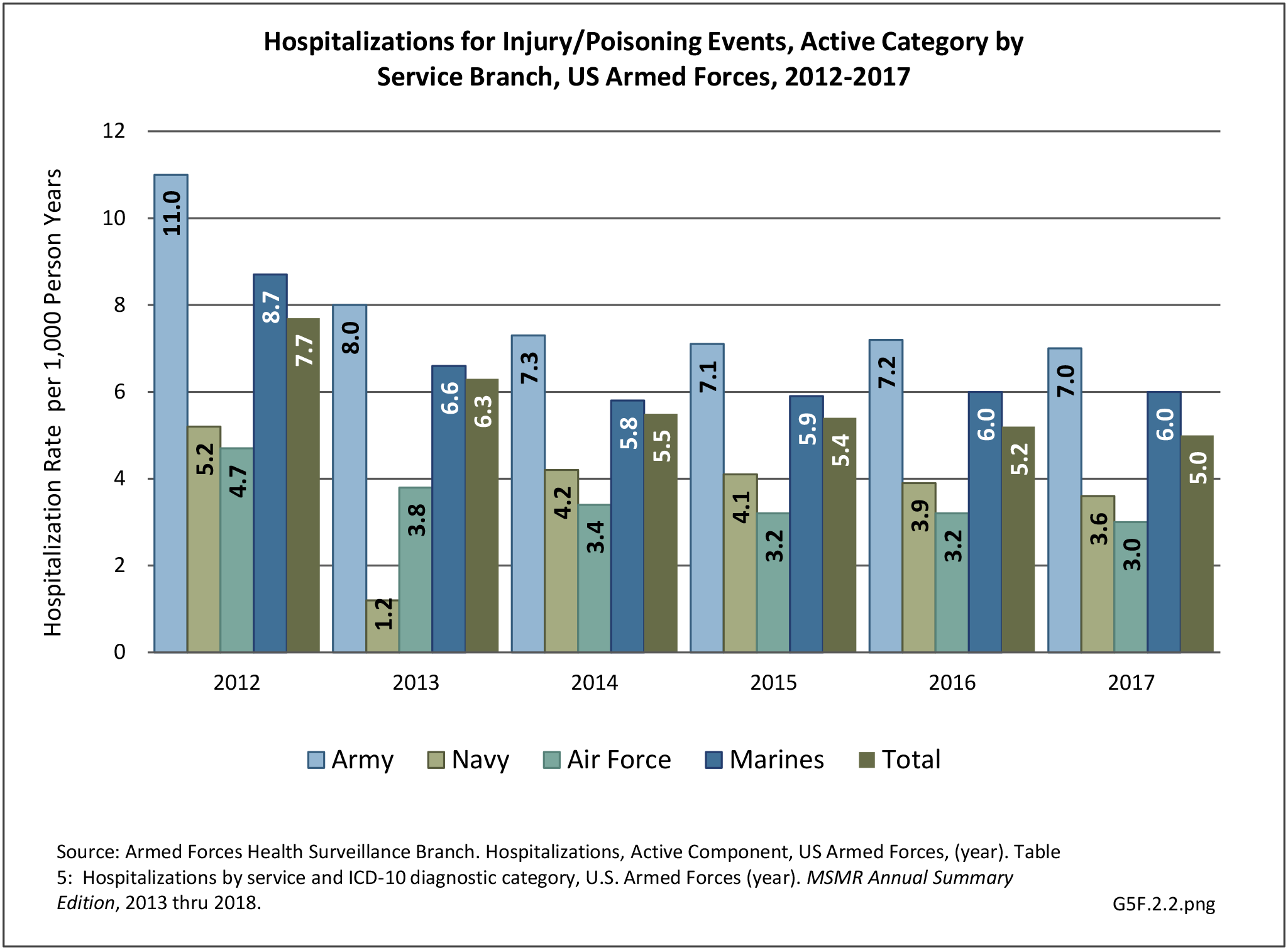
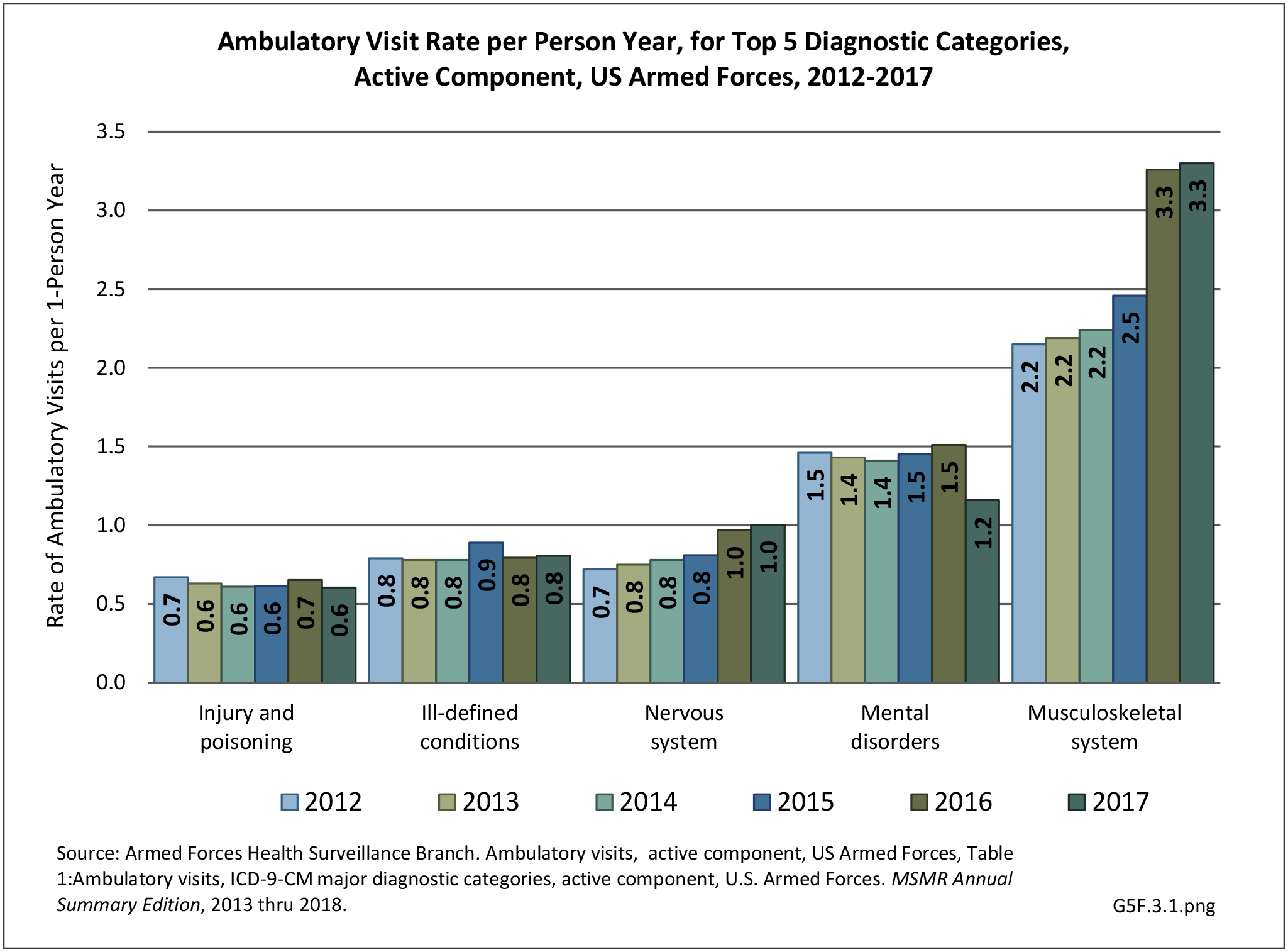
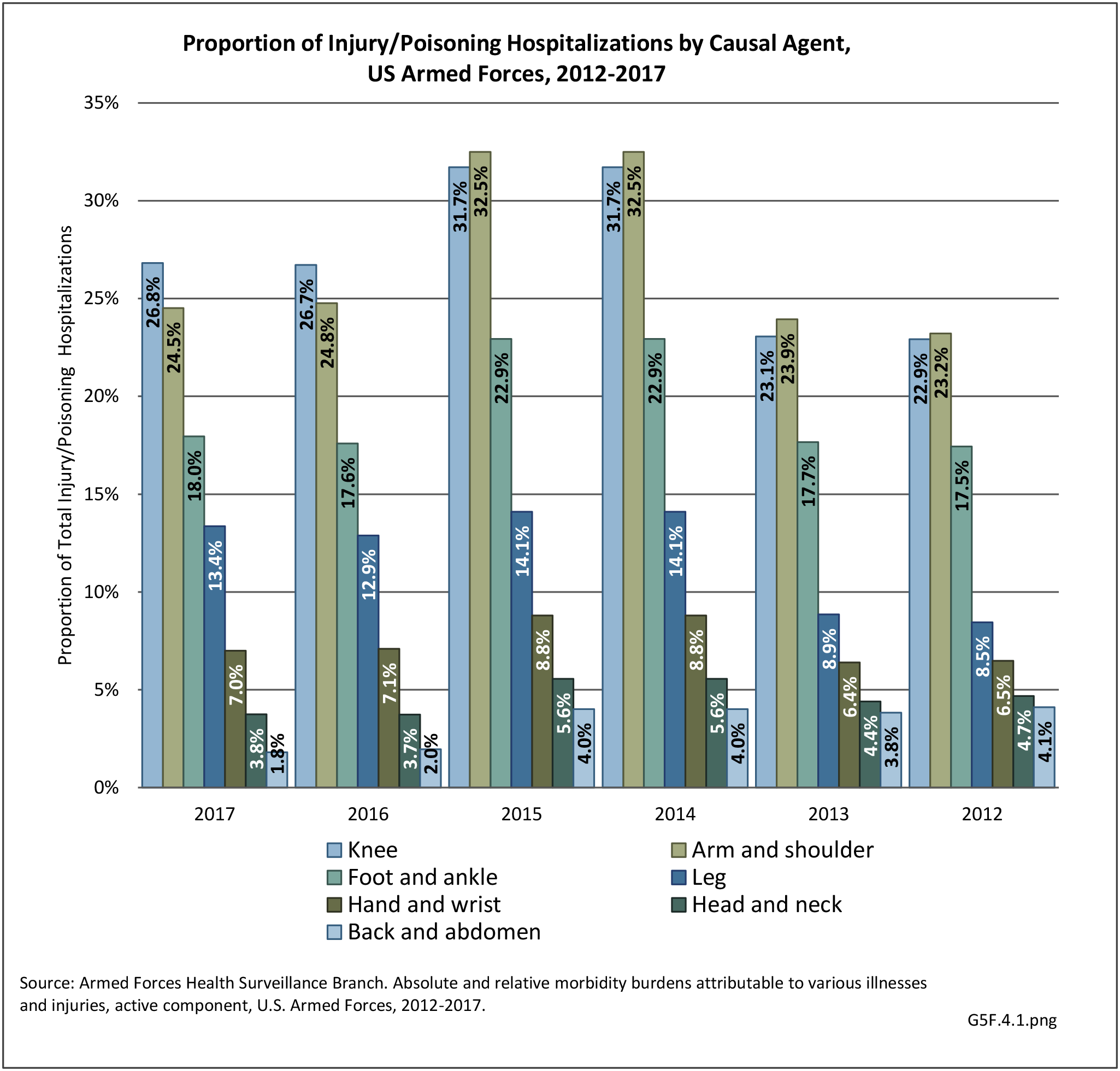
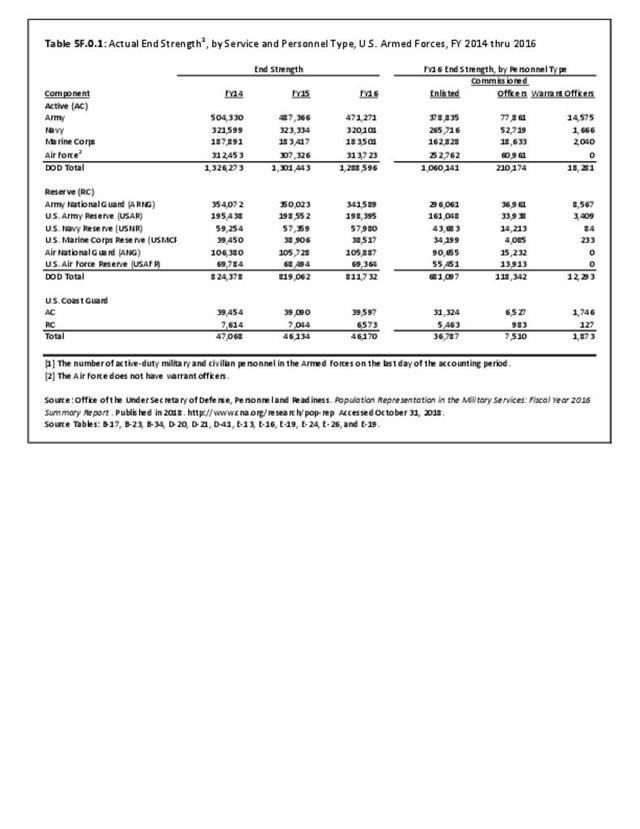
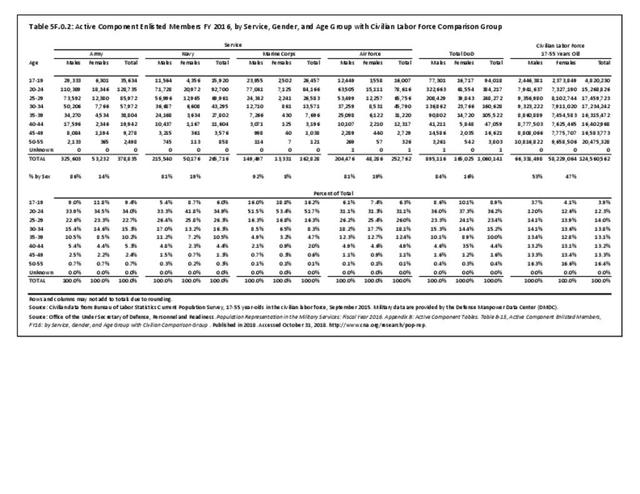
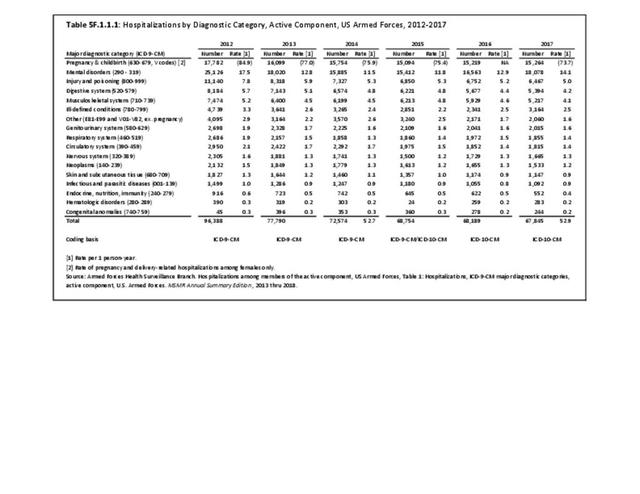
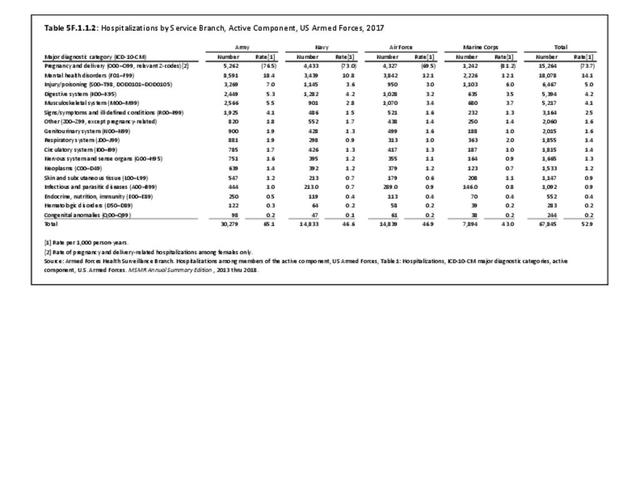
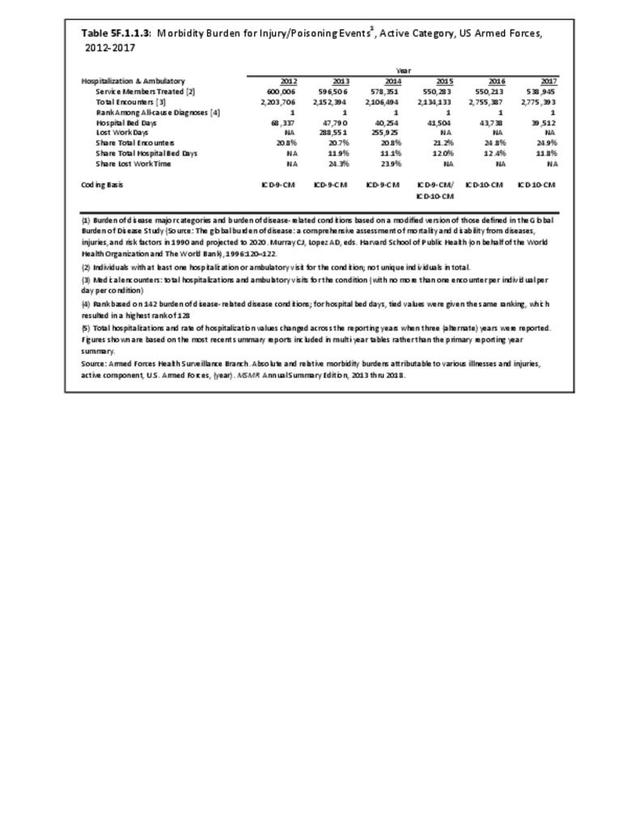
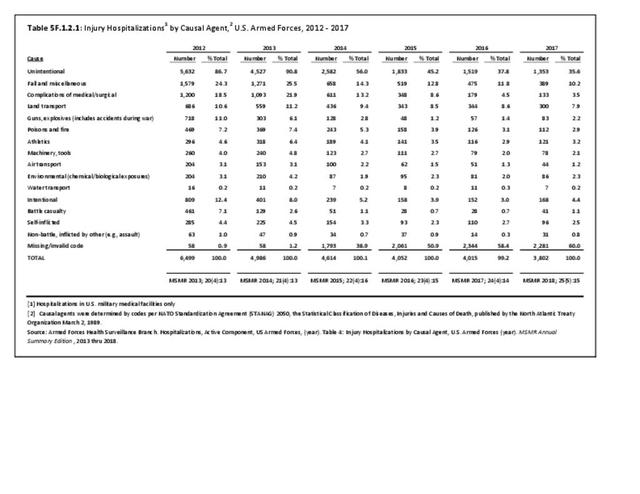
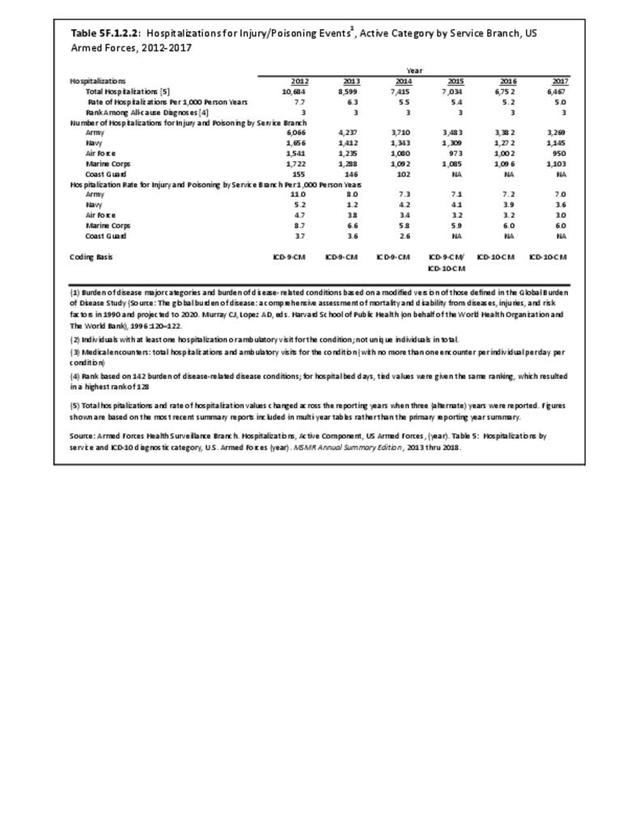
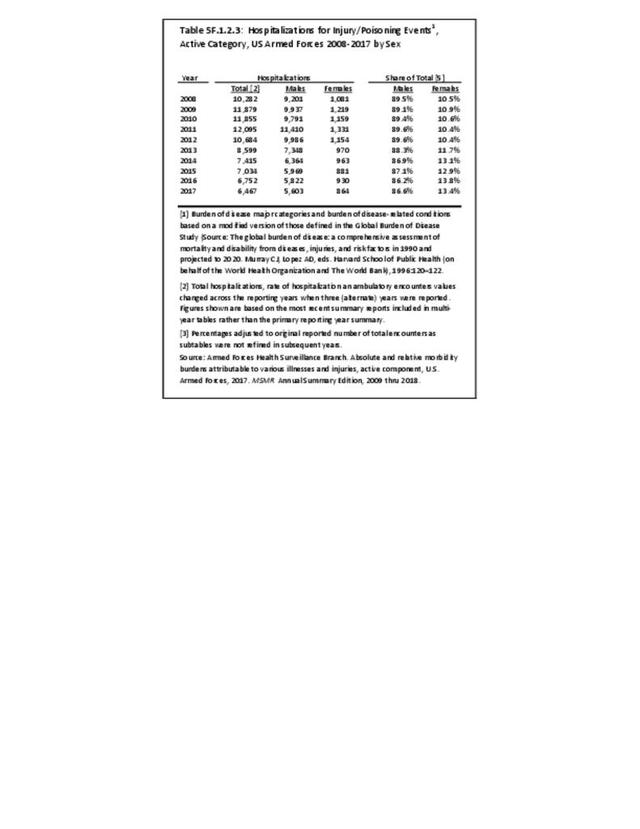
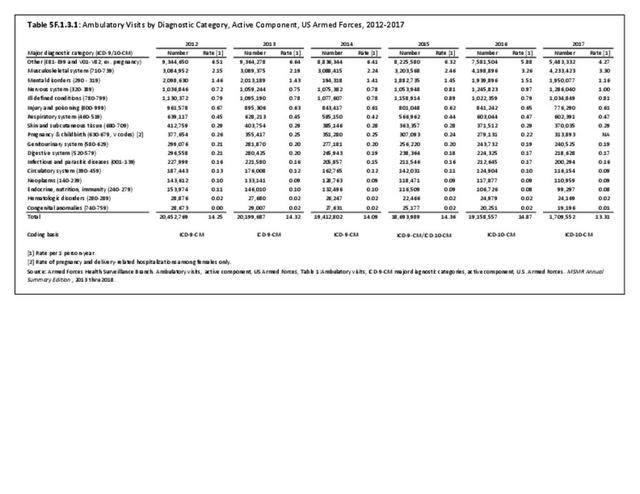
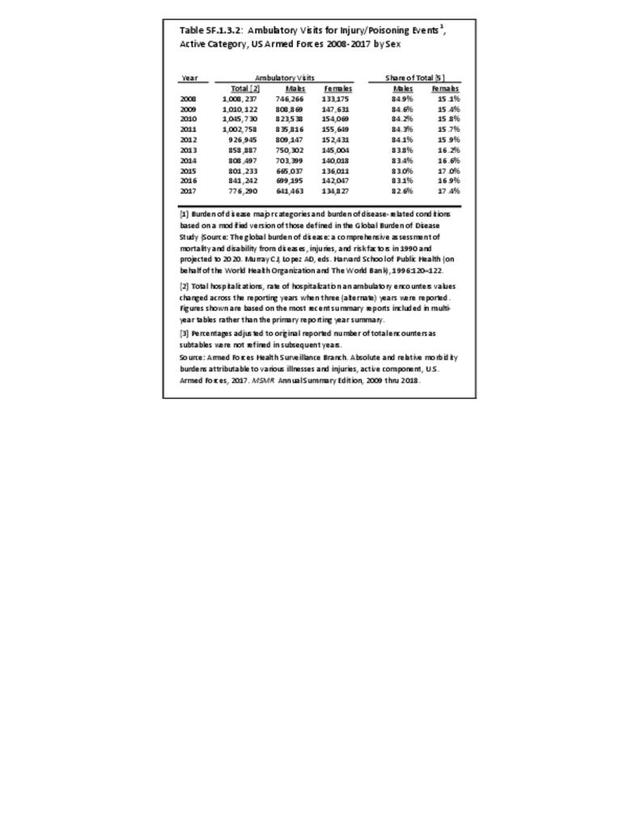
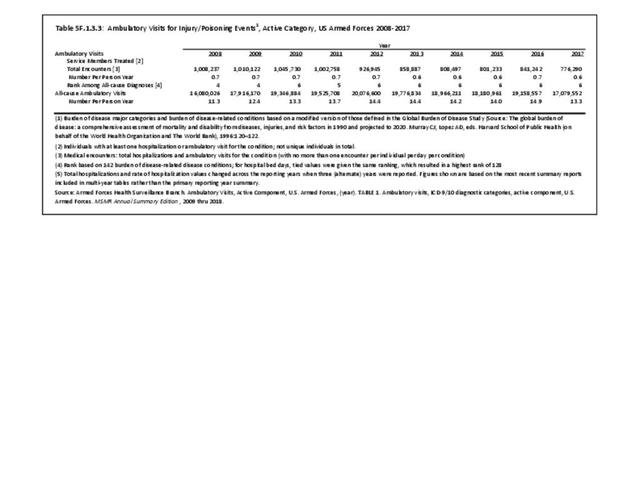
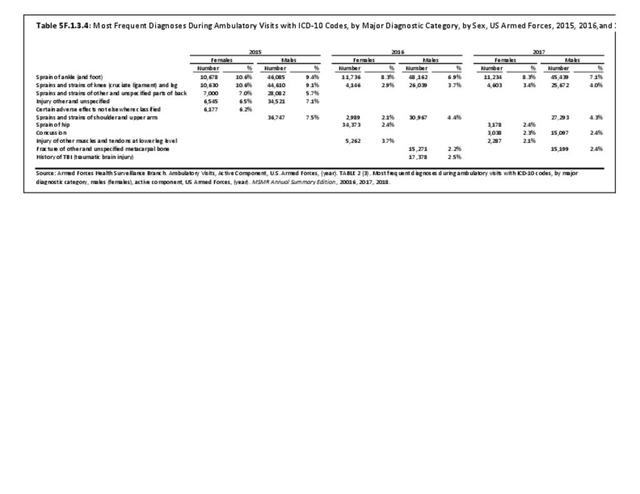
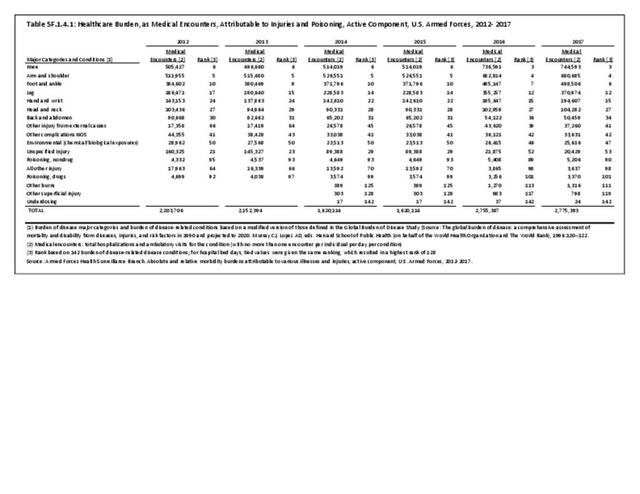
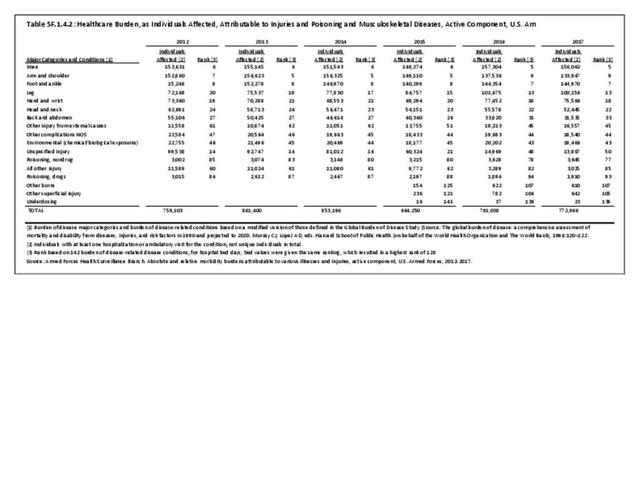
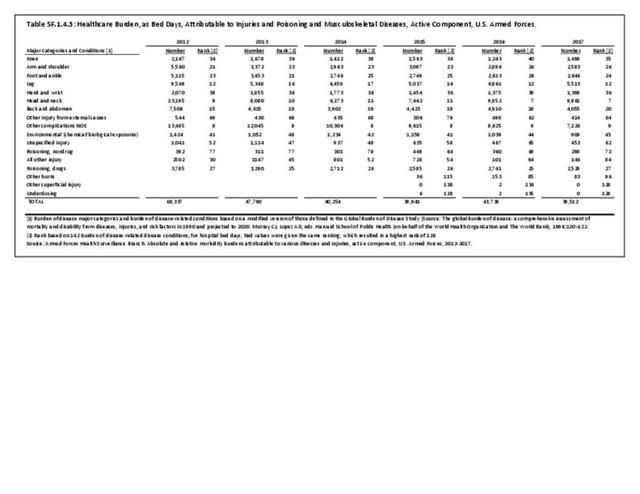
Military Injuries: Military injuries include injuries that occur in both nonactive and active duty personnel, and across the five major branches of military duty: Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard. Data is compiled from annual summaries published by the Armed Forces Health Surveillance Branch.
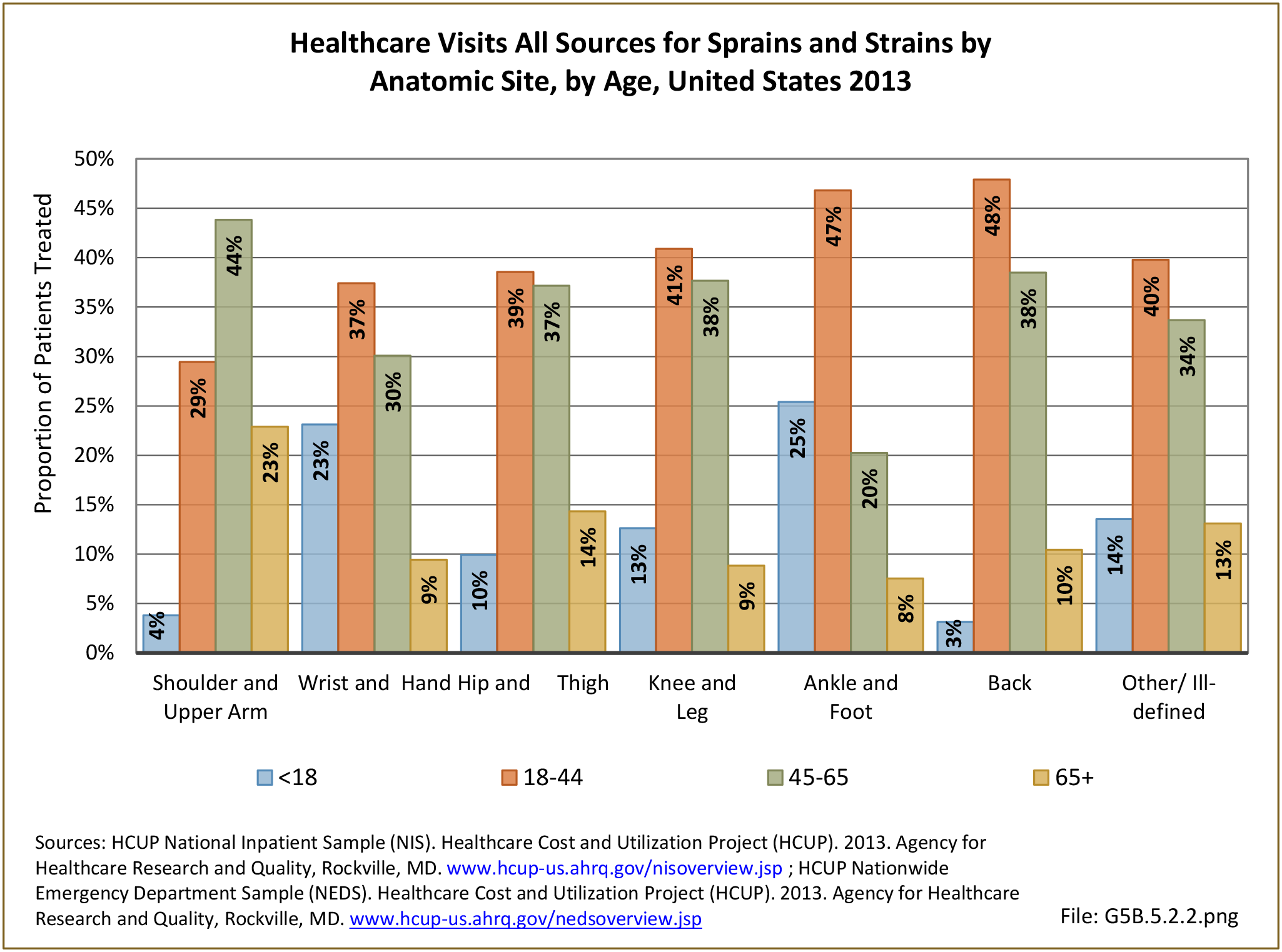
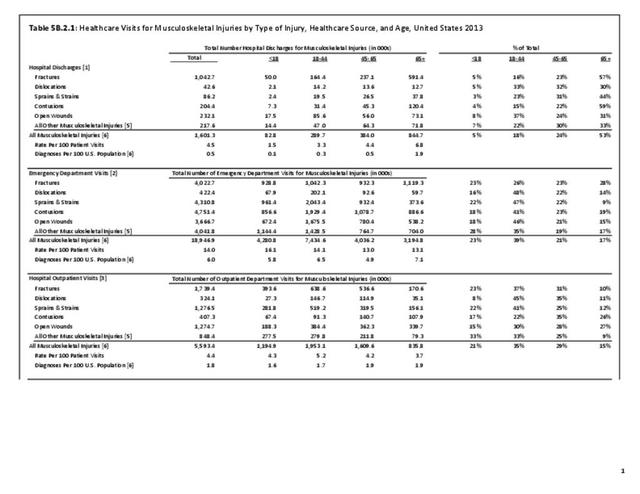
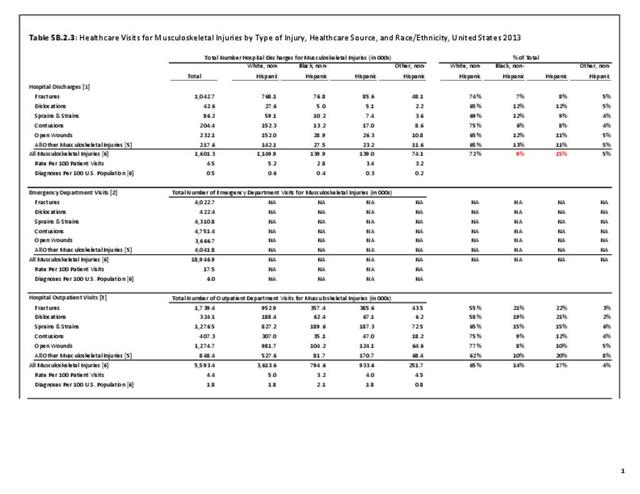
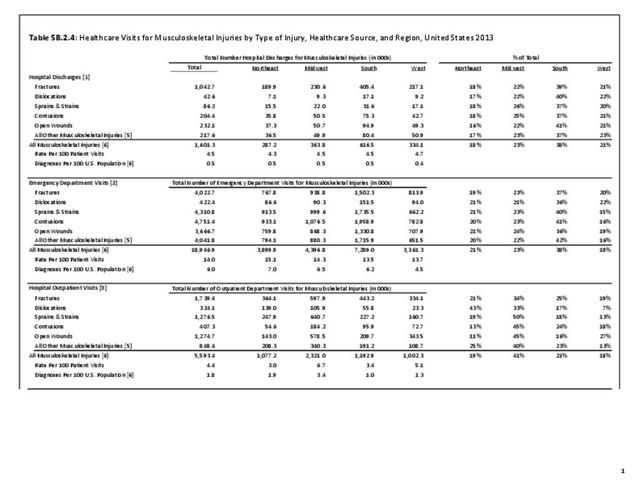
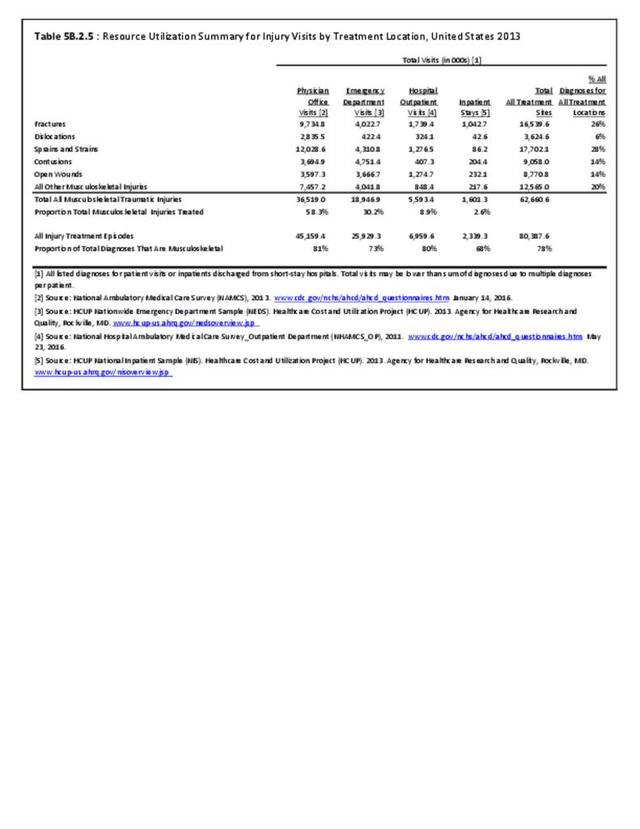
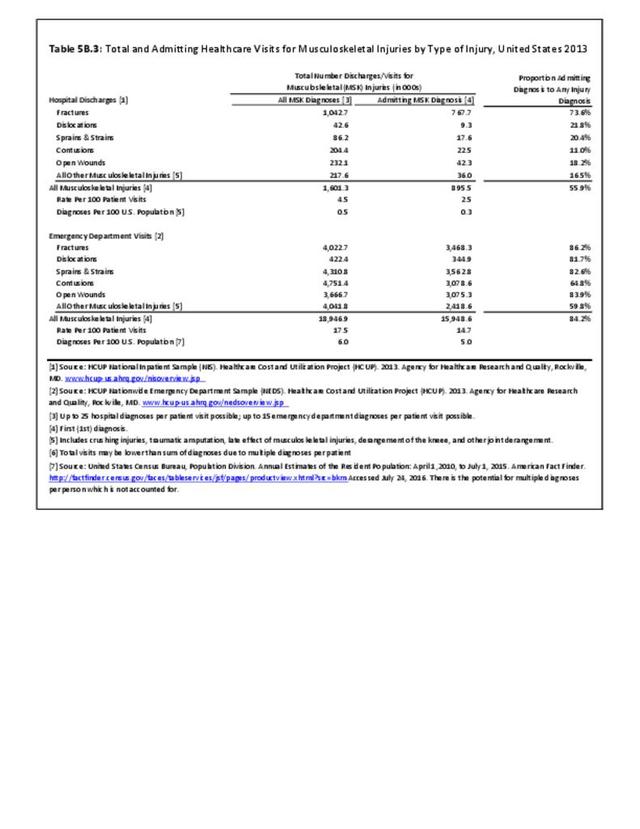
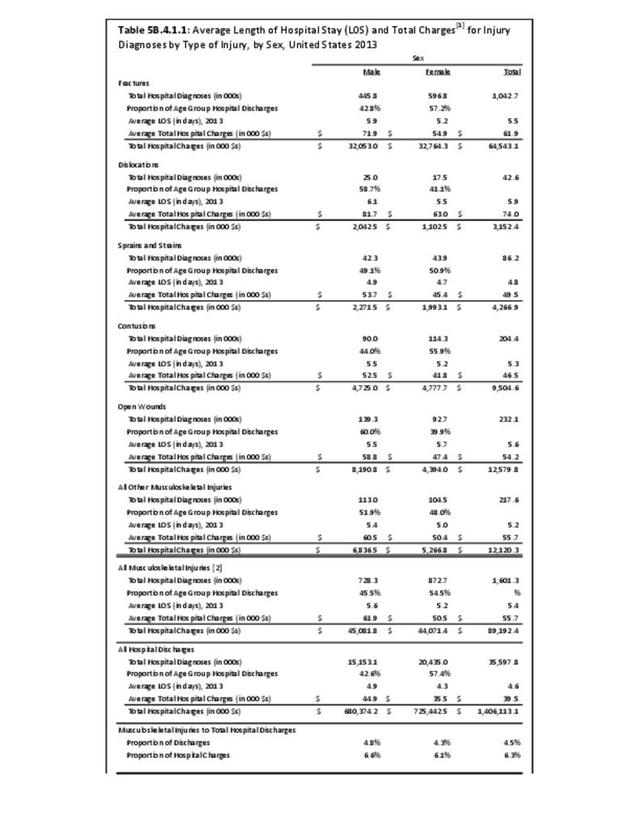
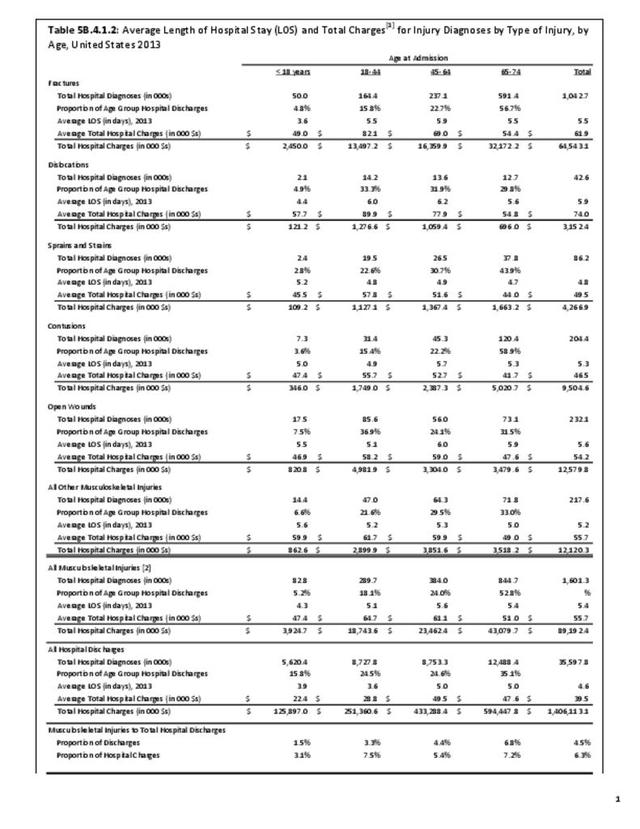
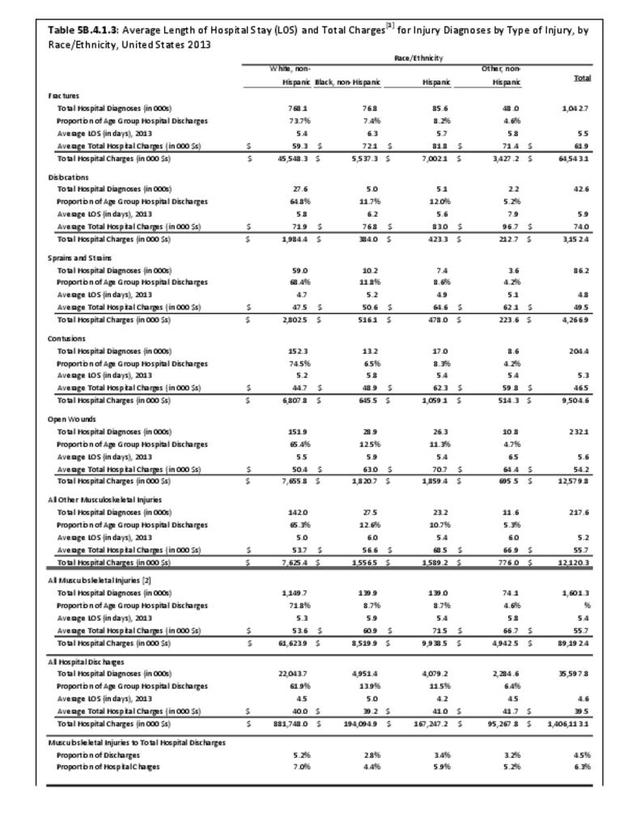
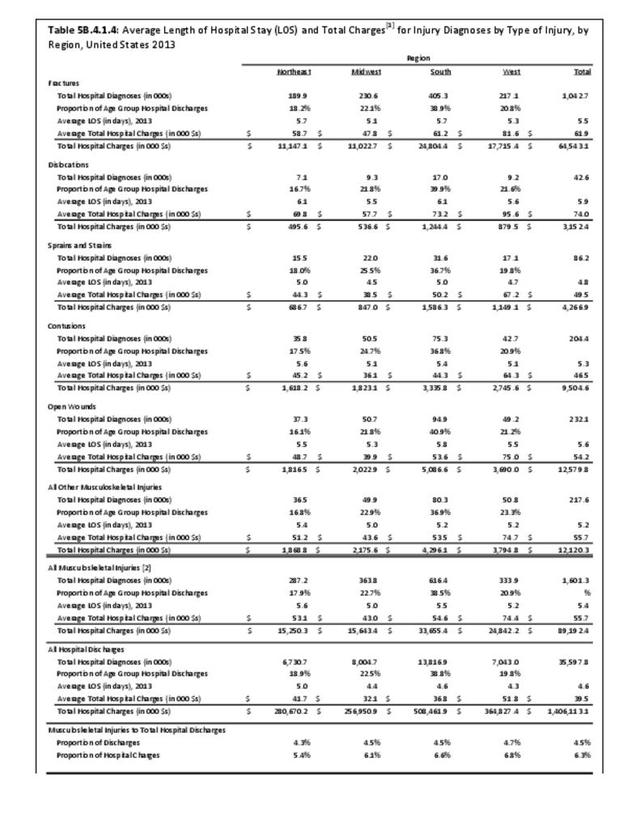
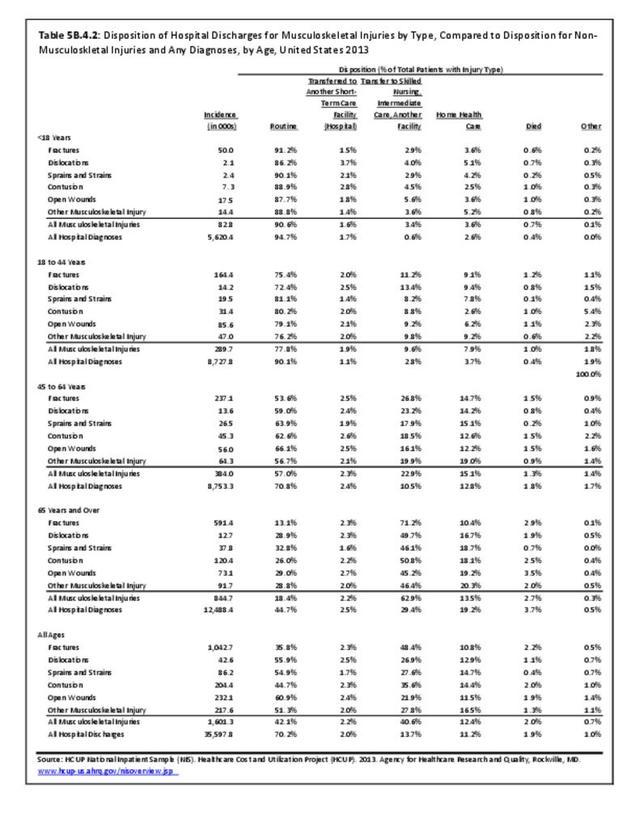
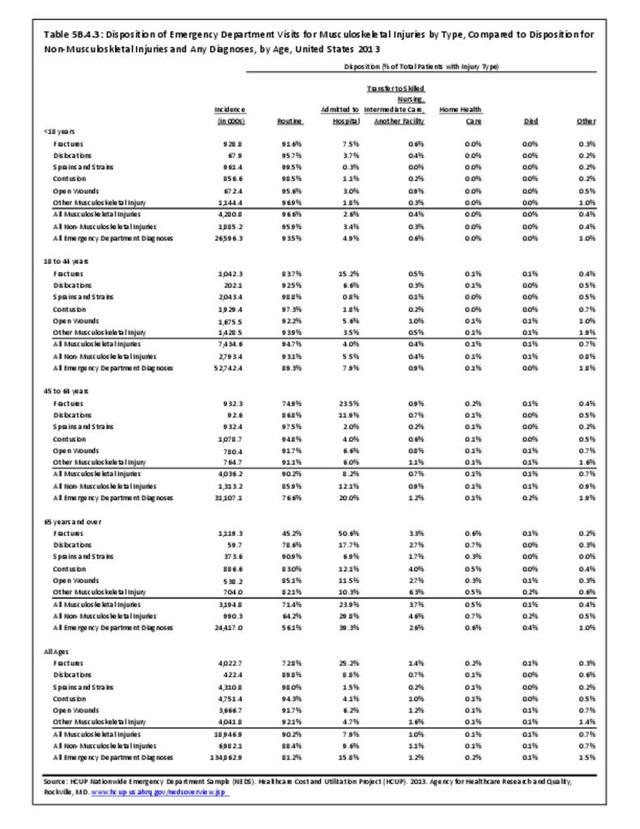
Musculoskeletal injuries represent the majority of injuries treated. Using the national healthcare databases and ICD-9-CM codes for comparison basis, the share of injuries treated classified as musculoskeletal rose from 61% to 89% of all injuries between 2006/2007 and 2013.
Edition:
- Fourth Edition