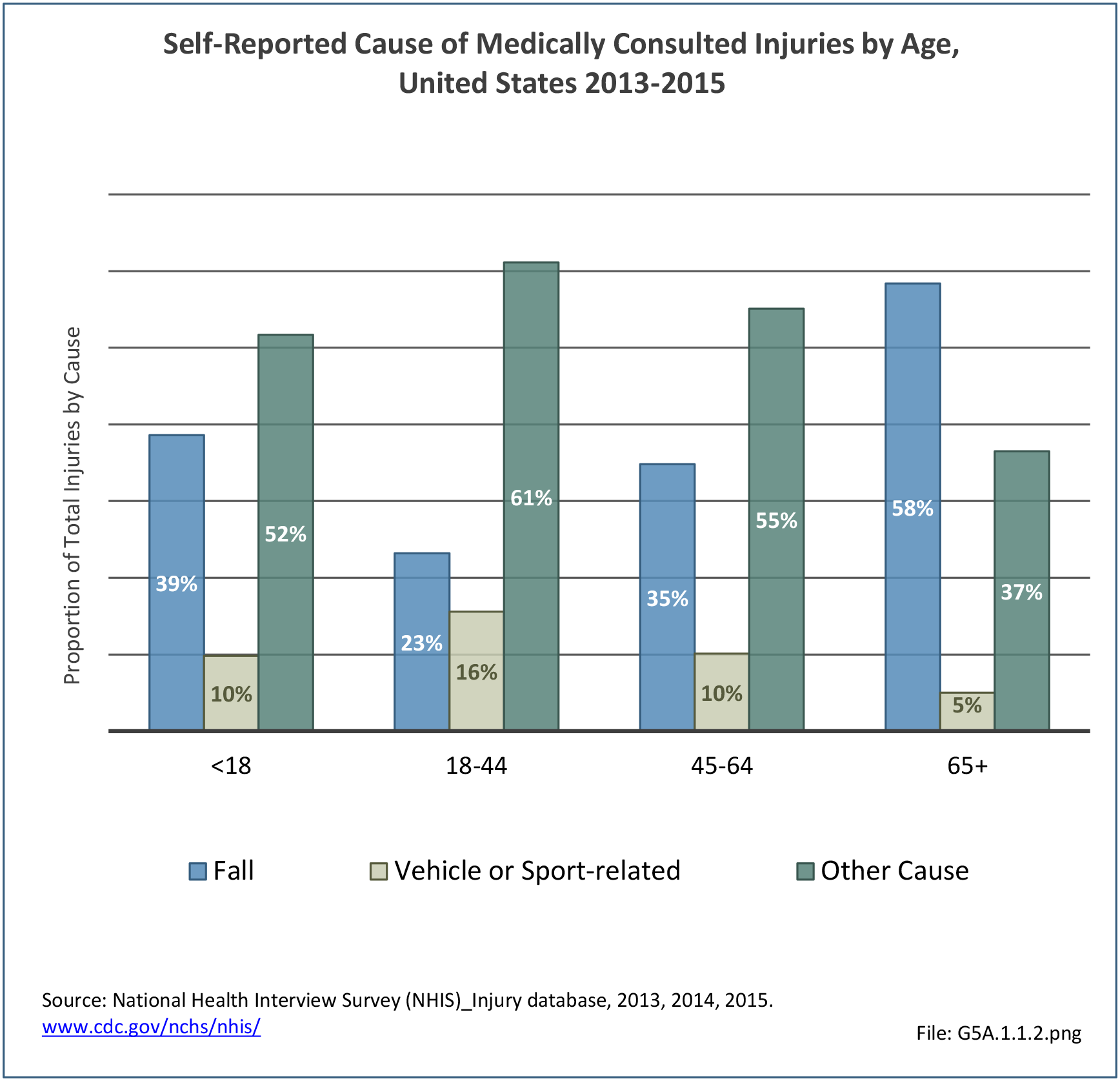
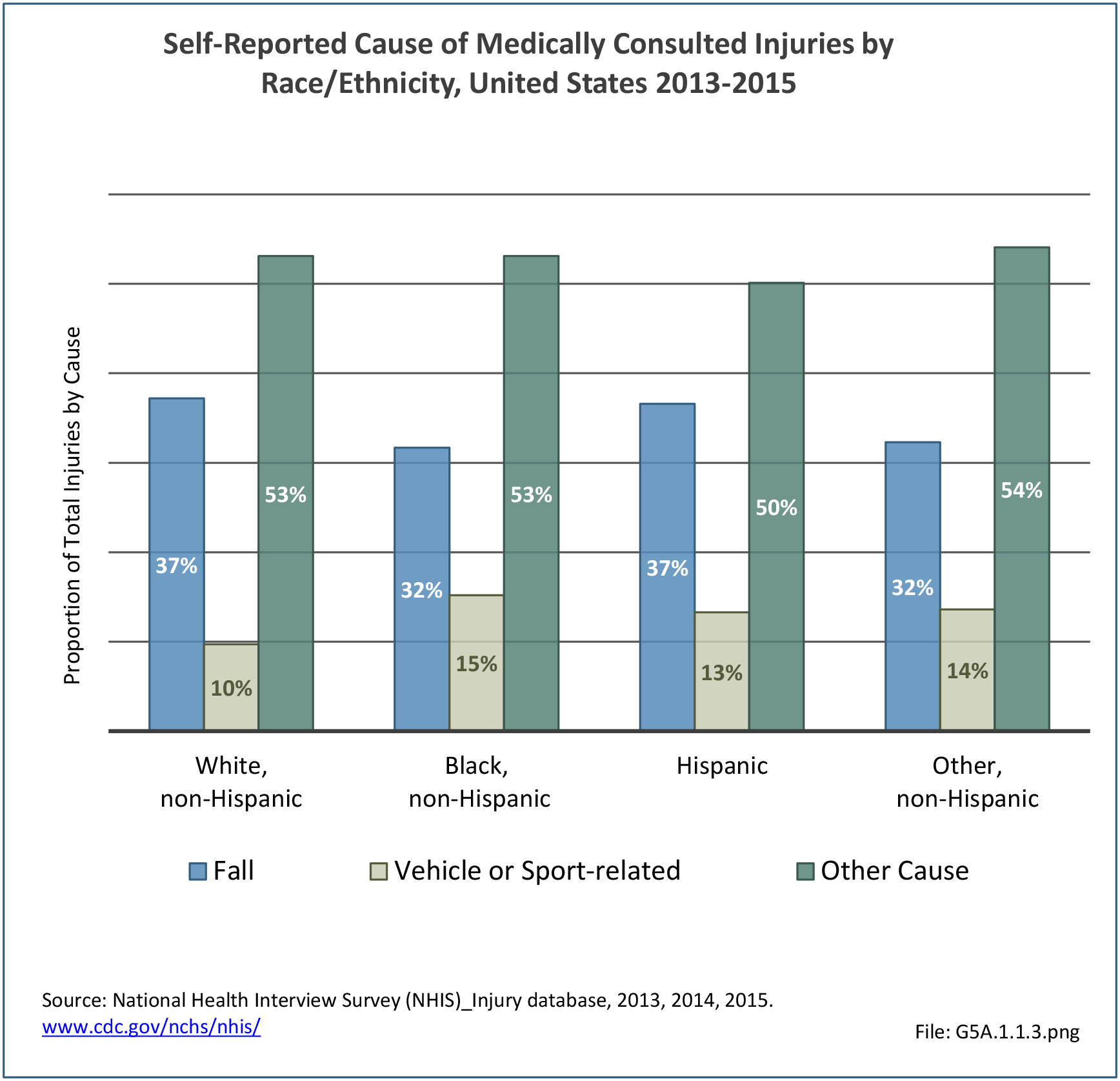
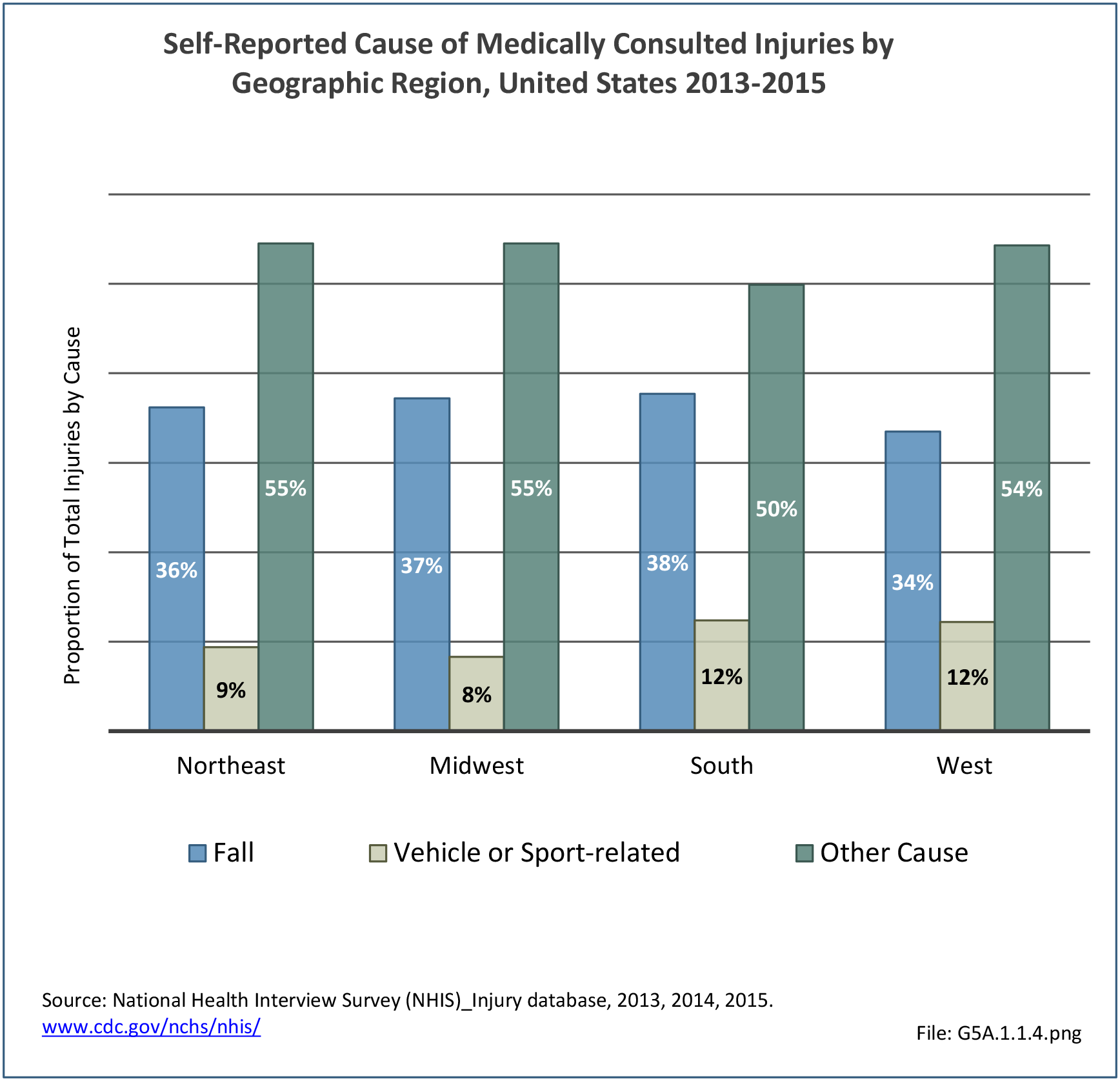
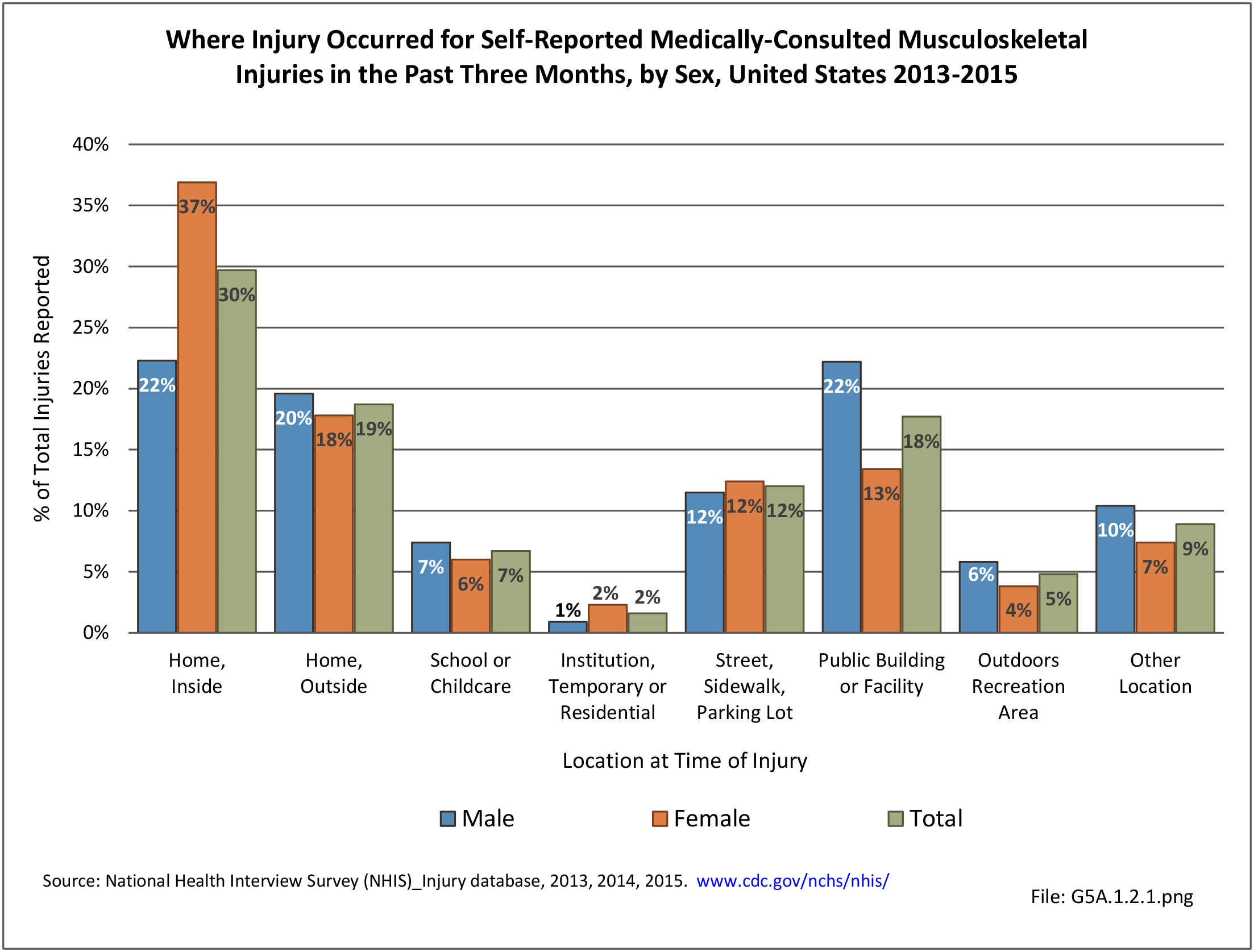
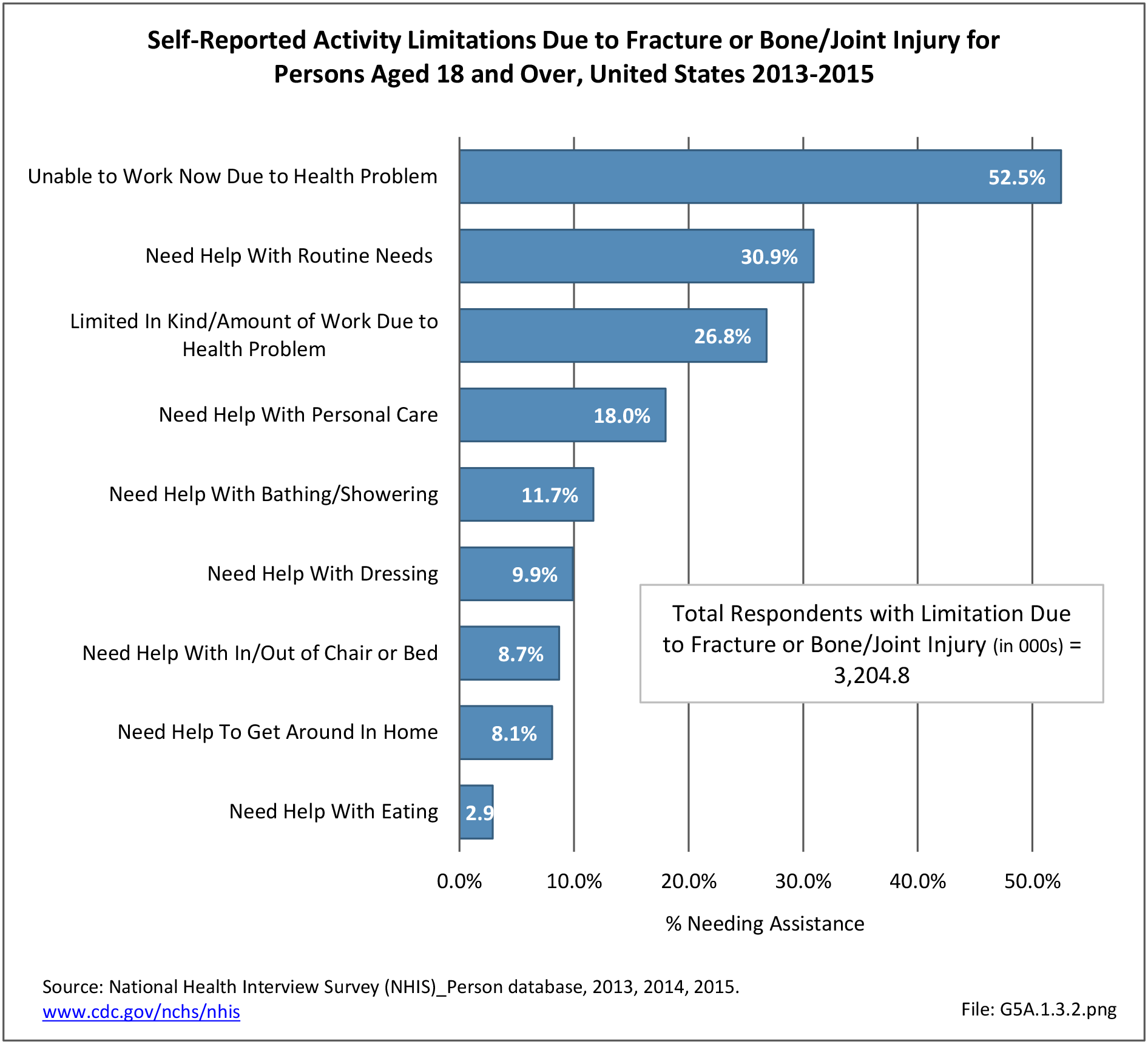
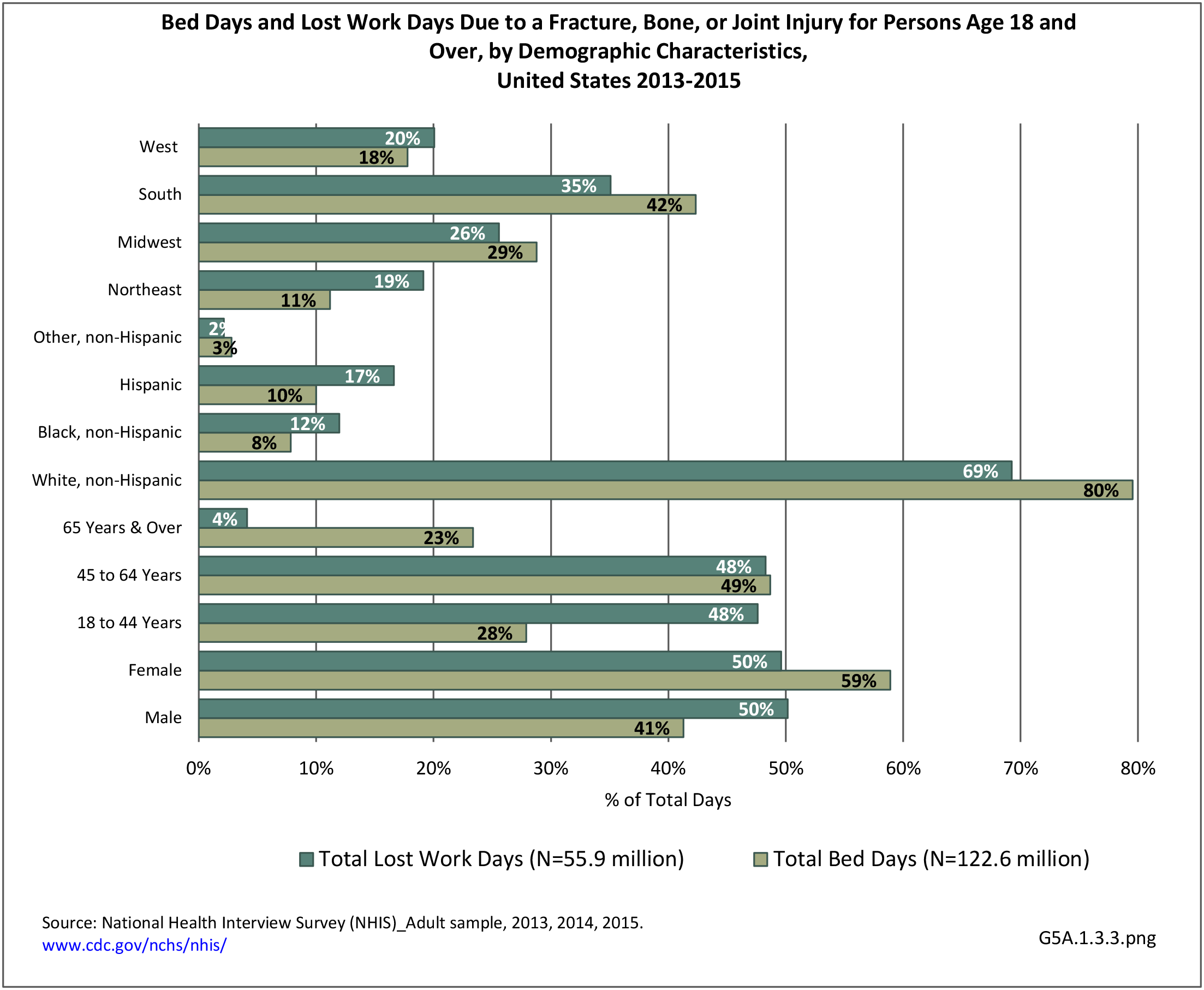
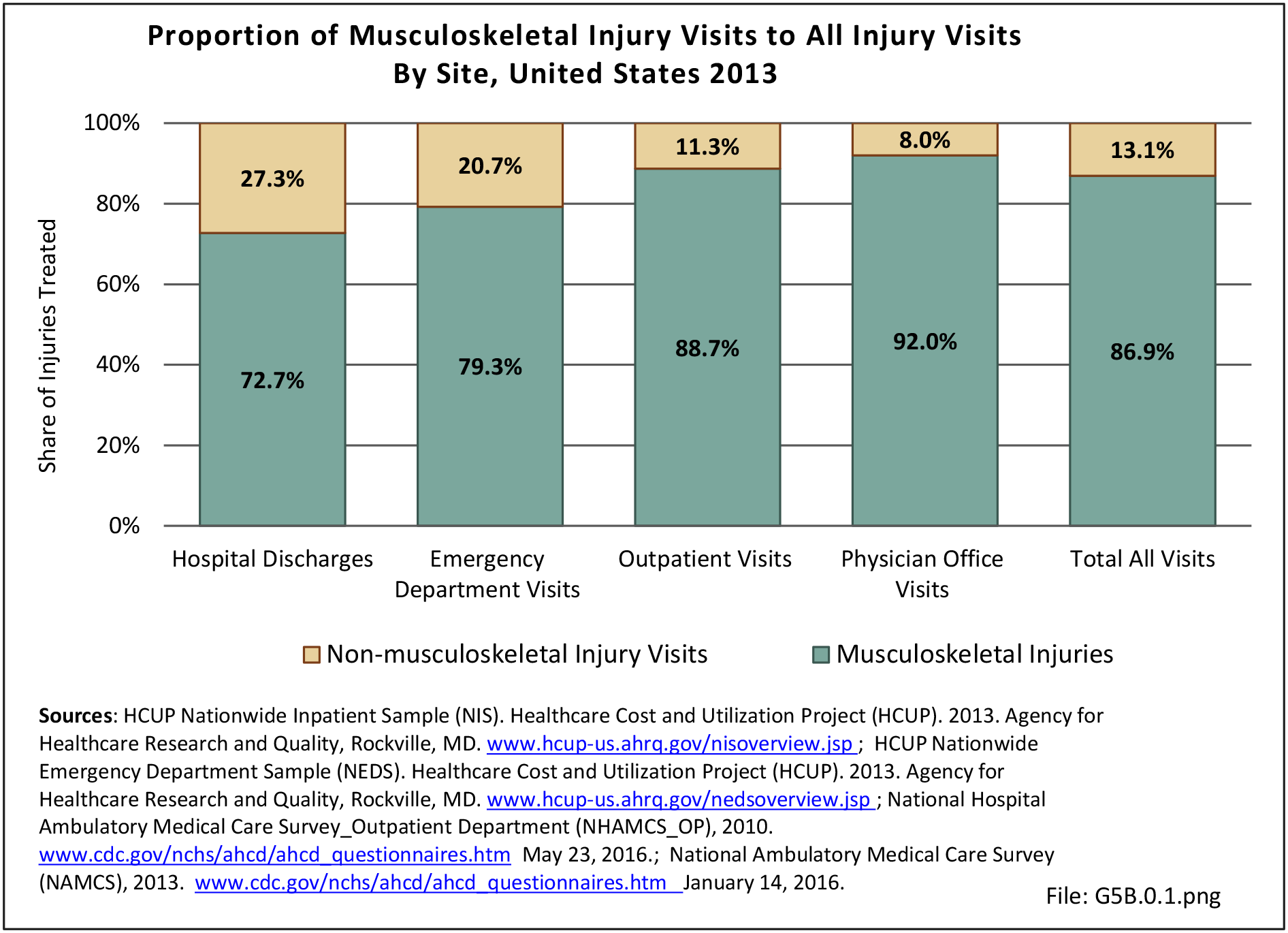
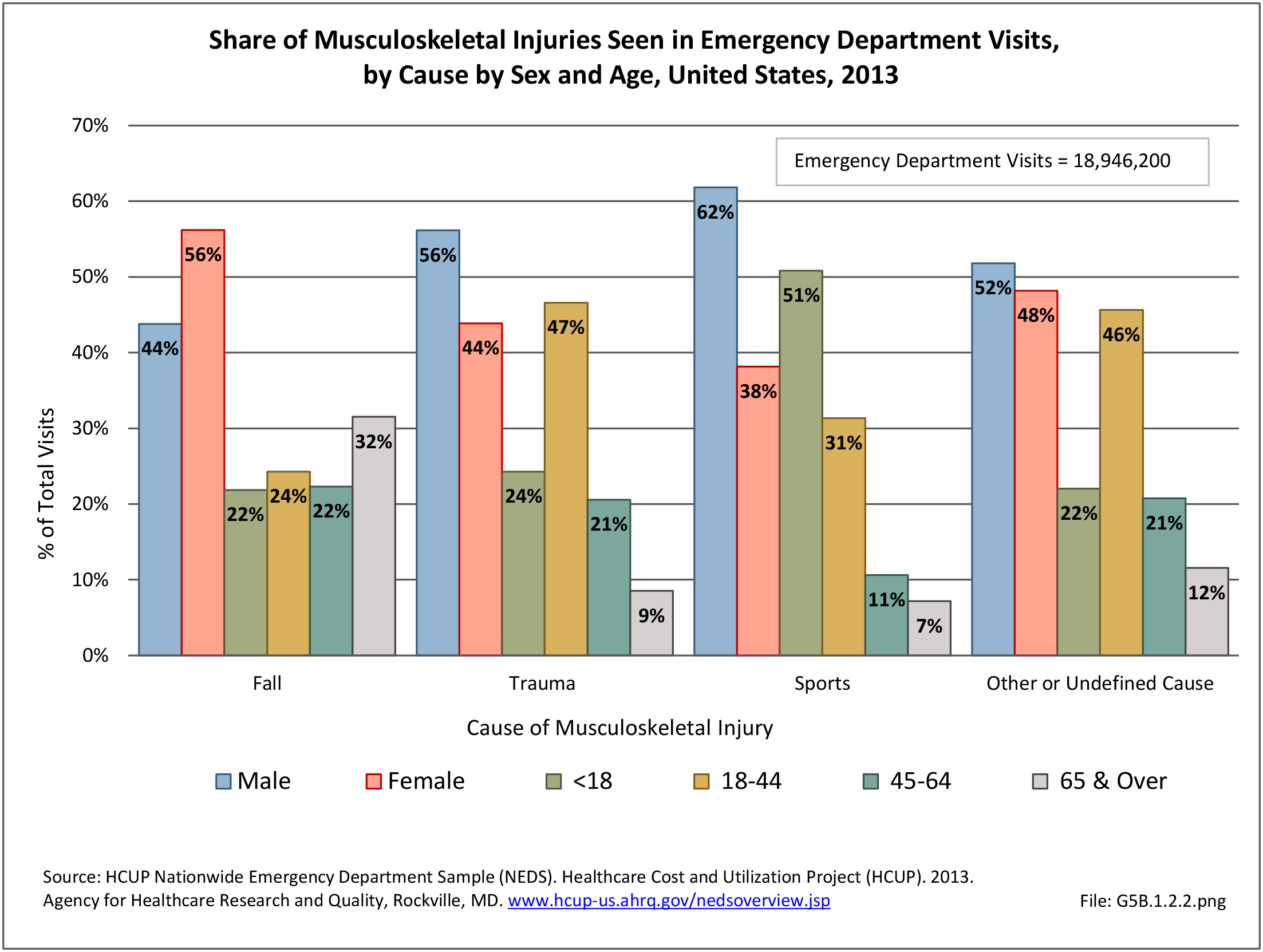
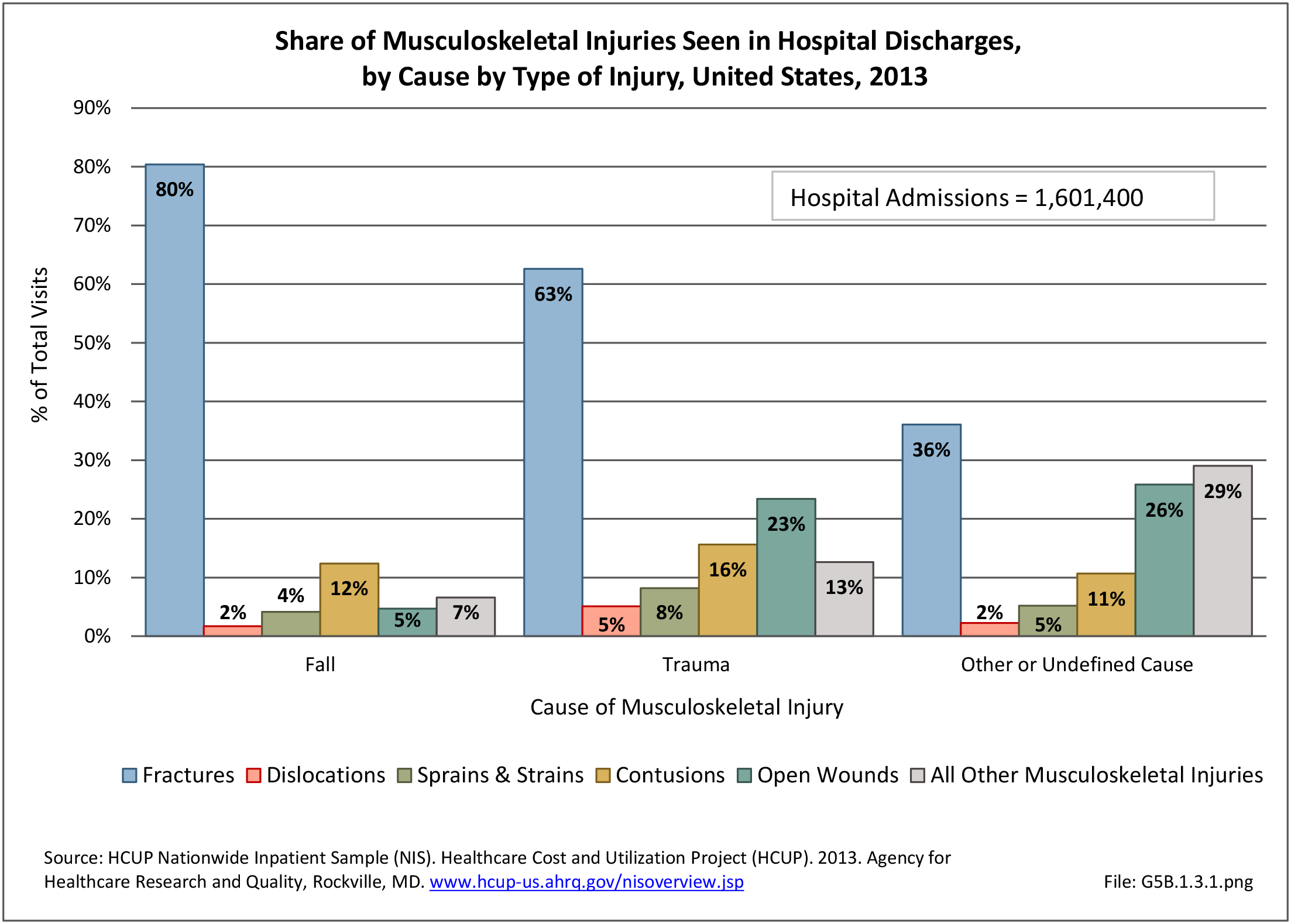
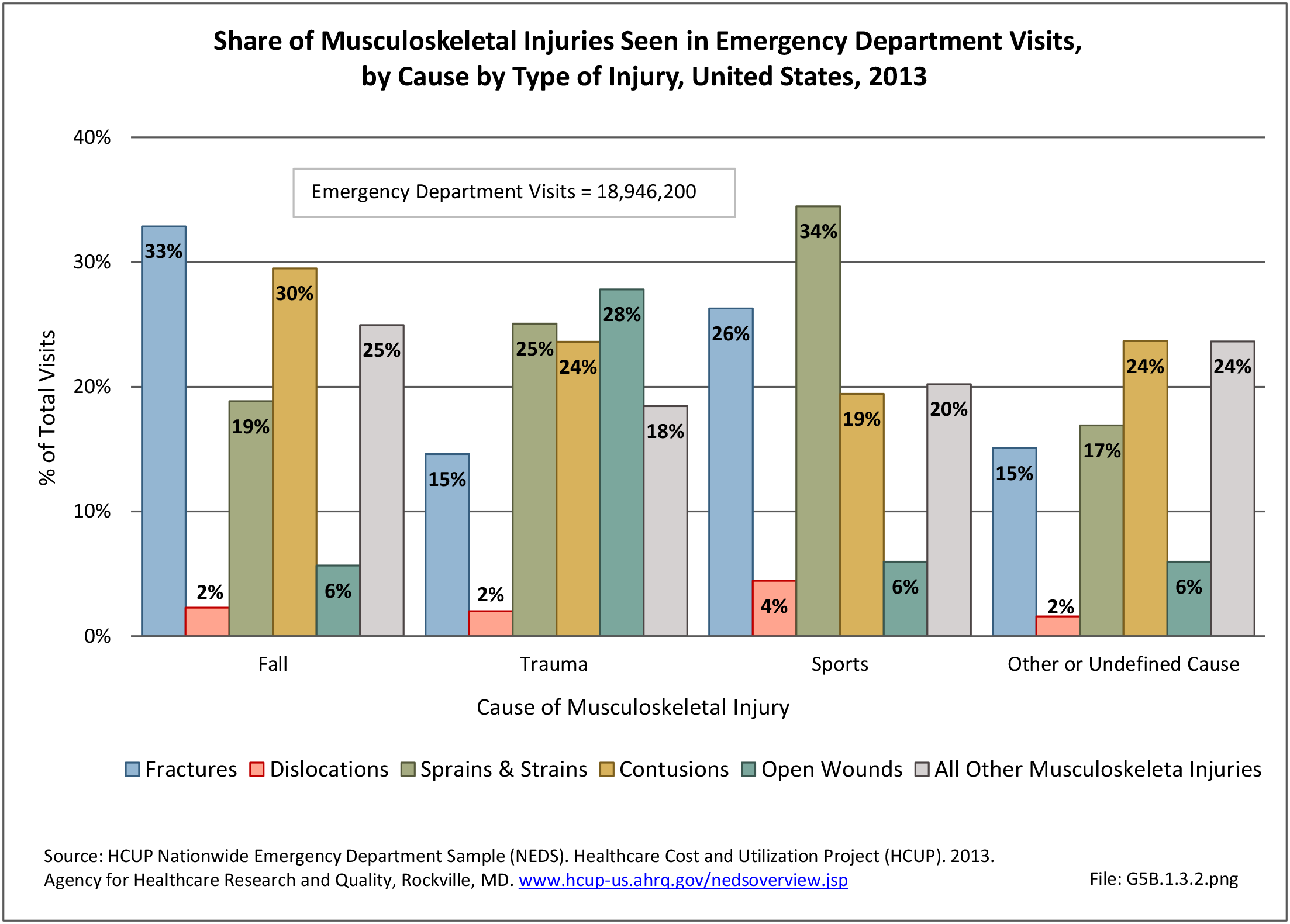
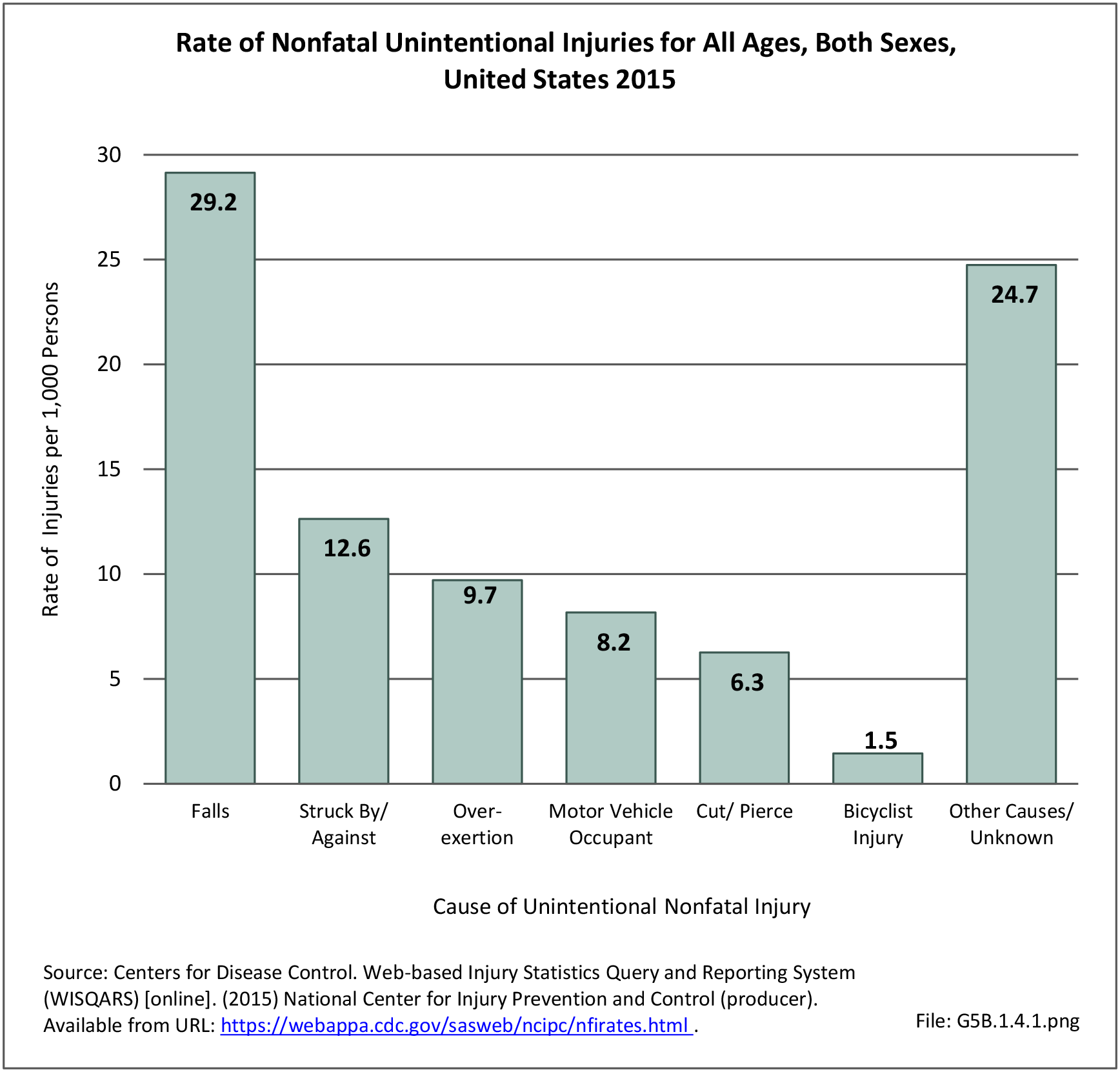
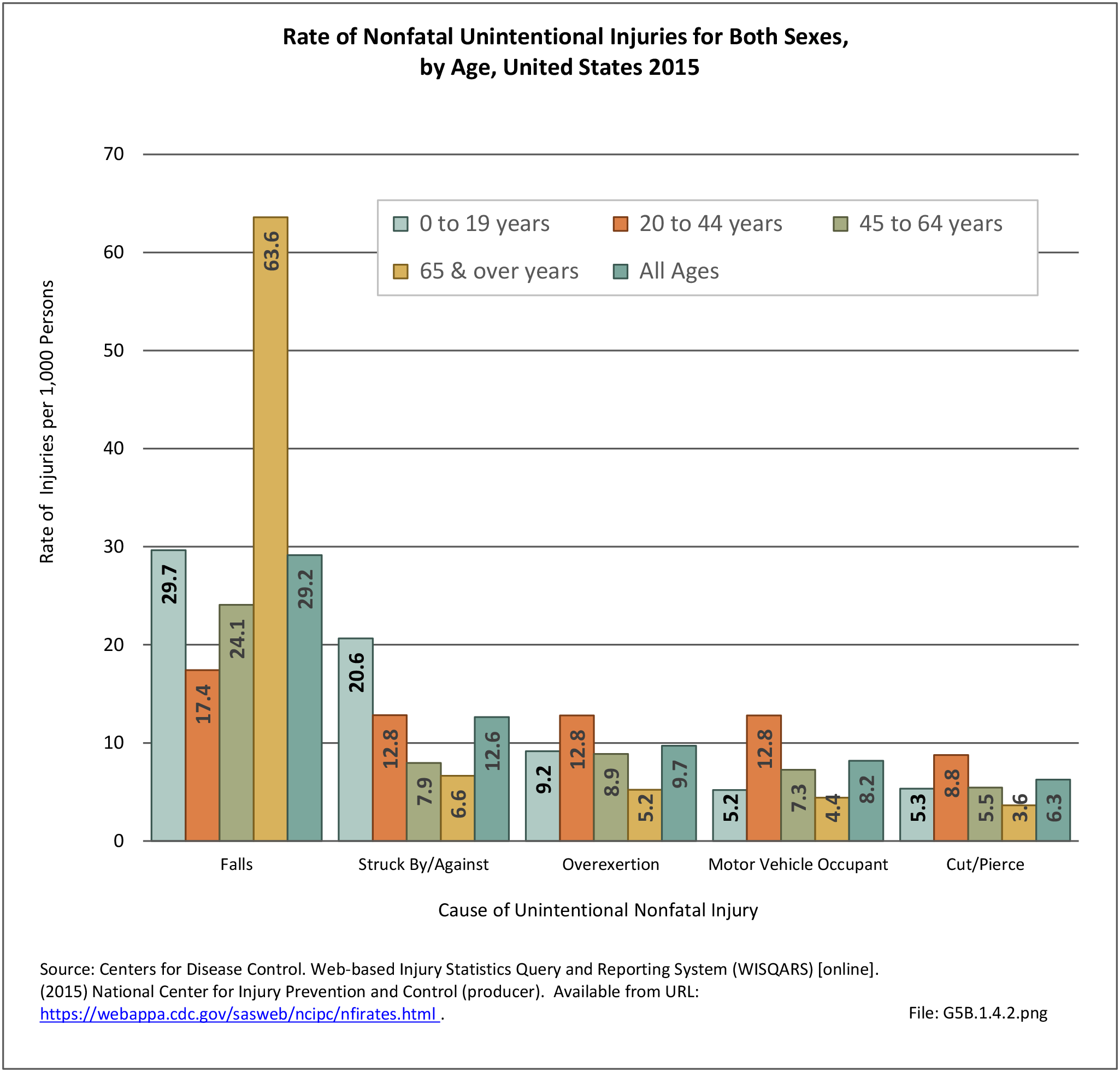
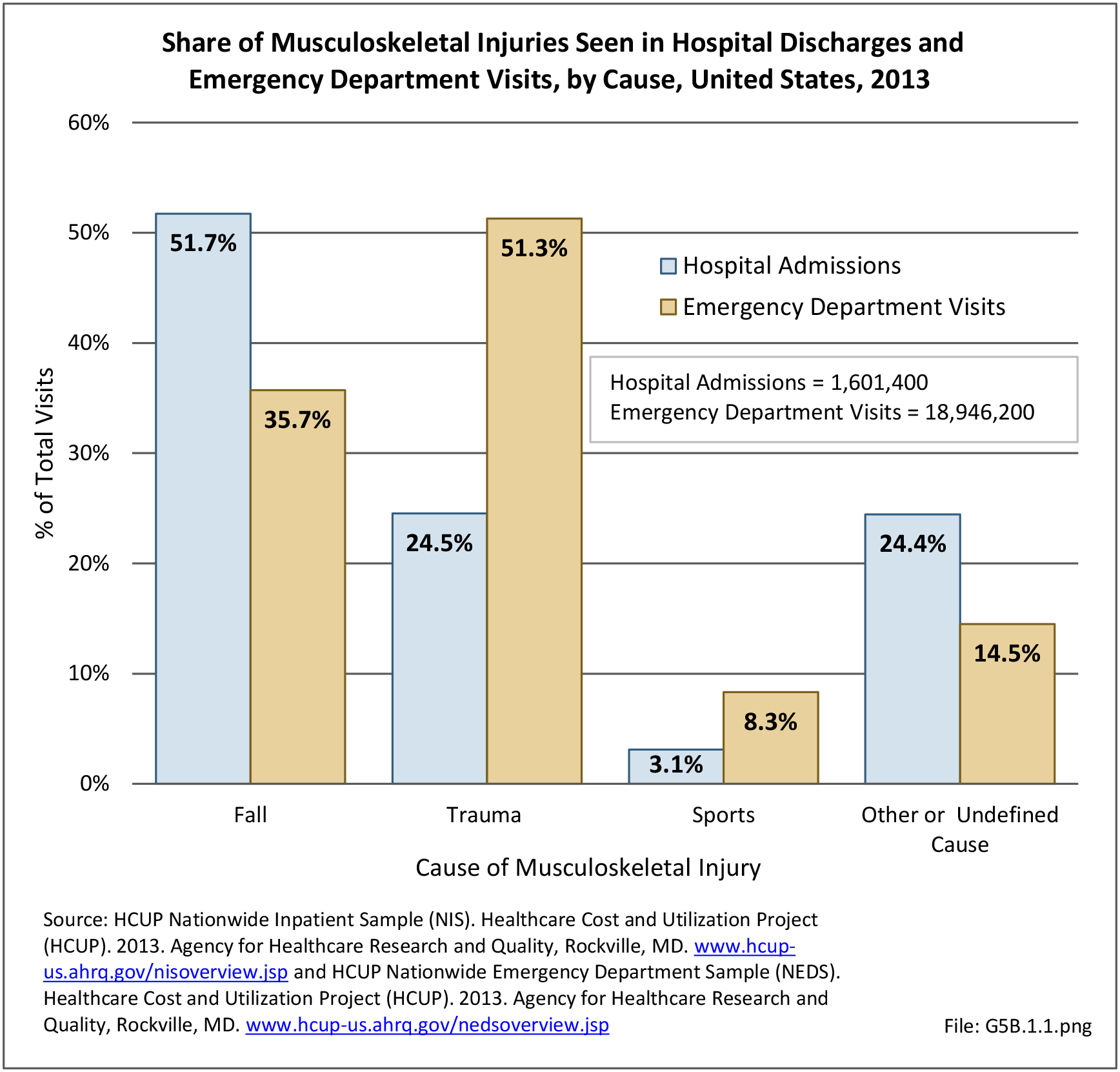
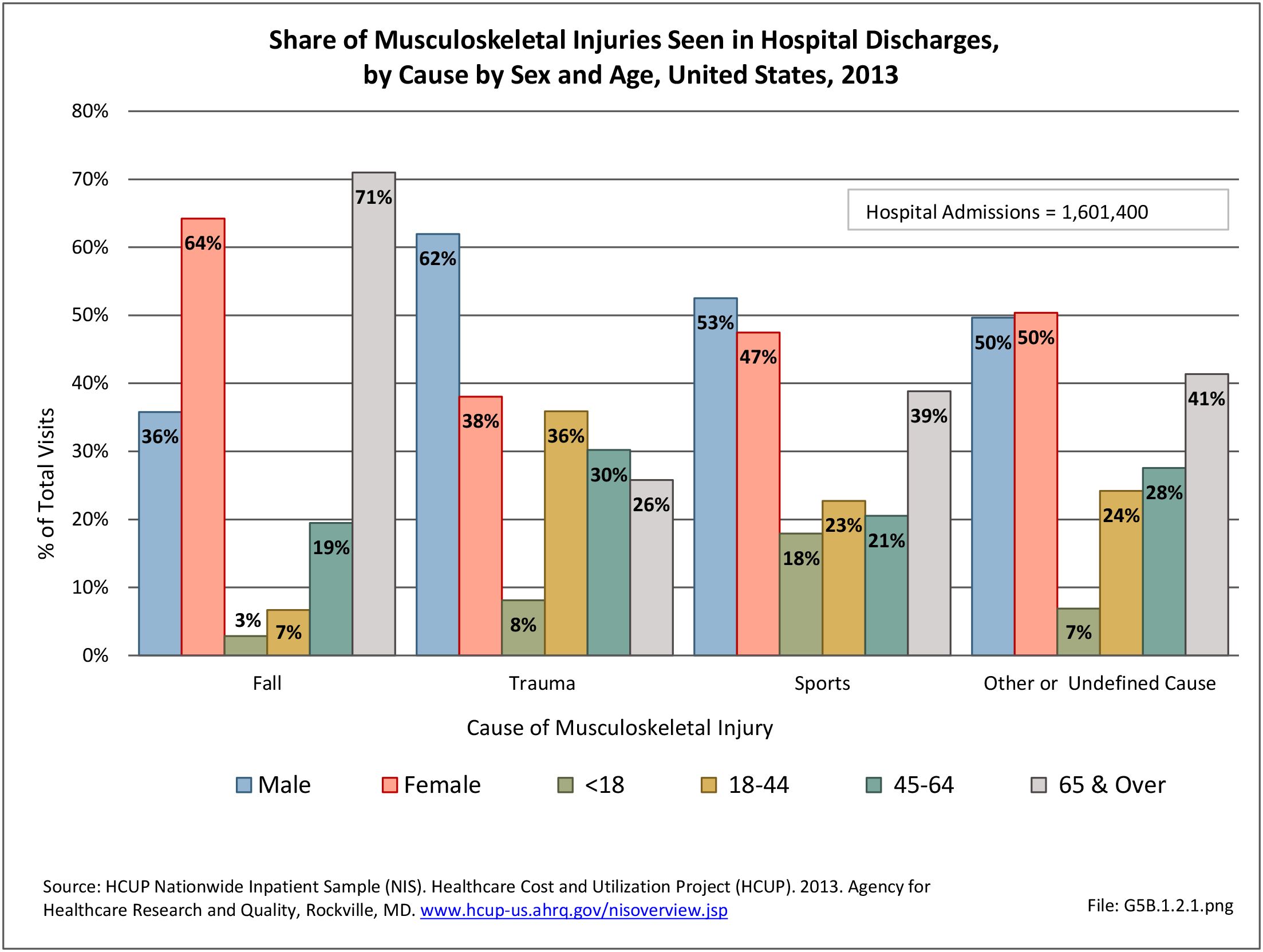
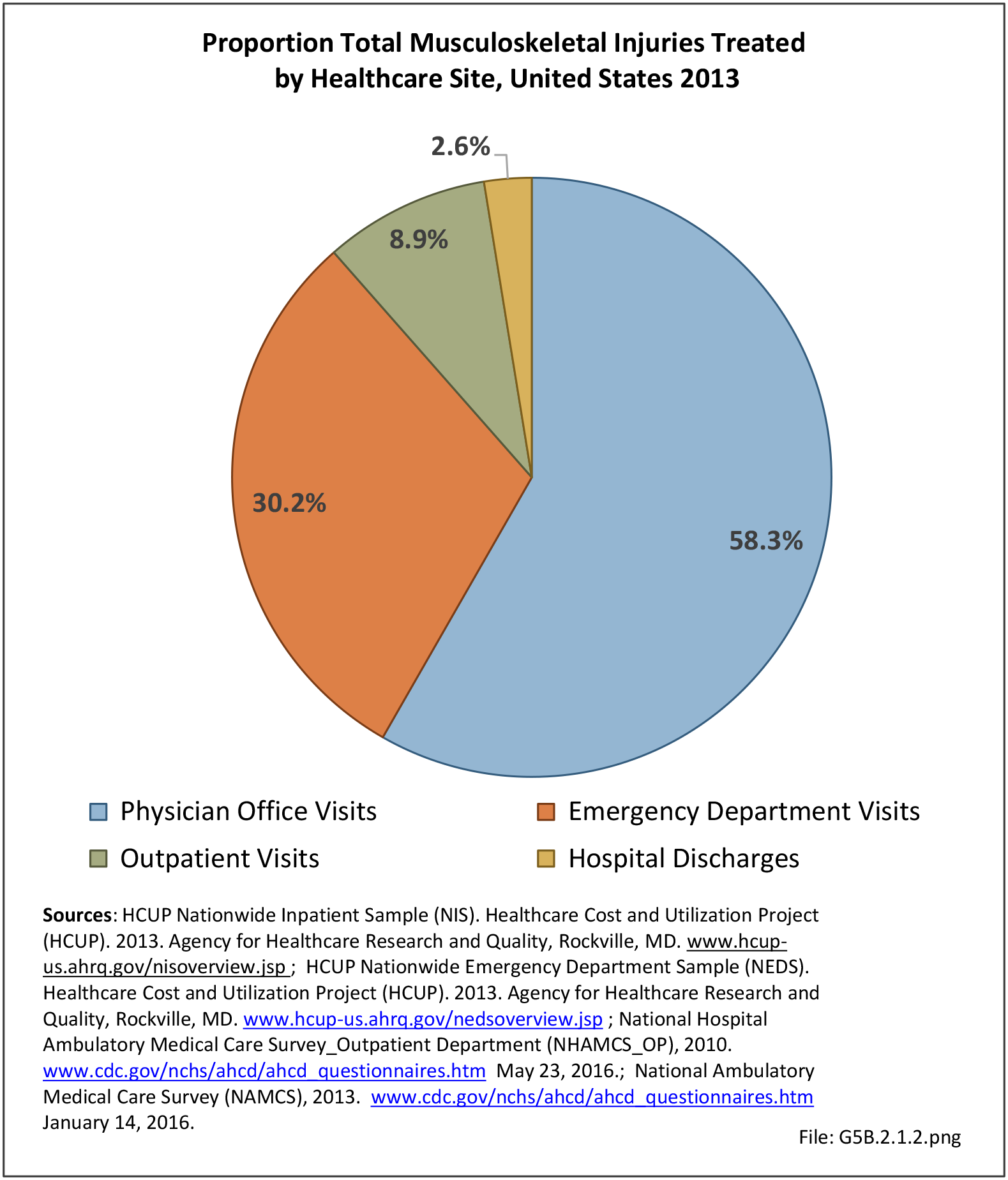
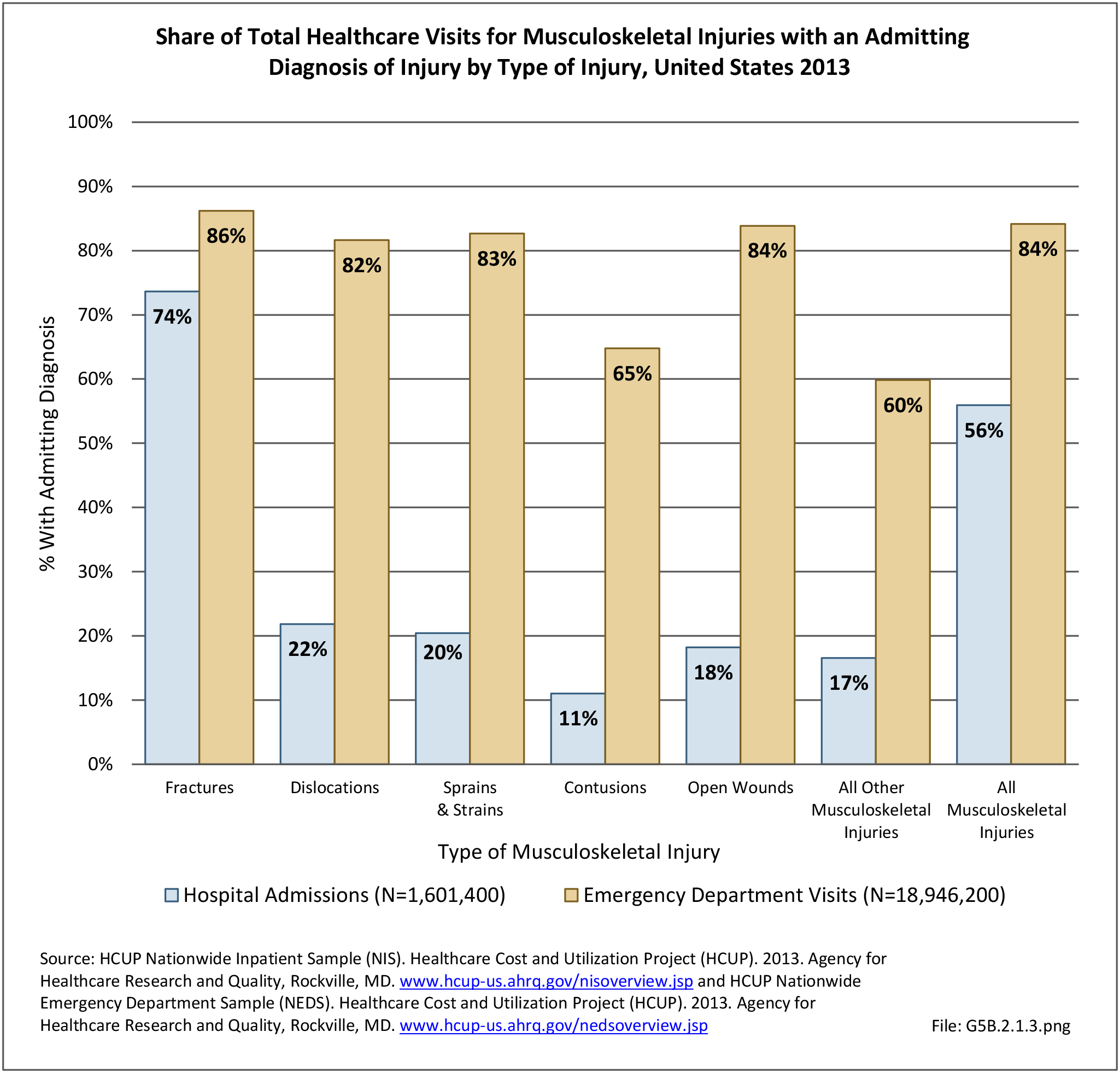
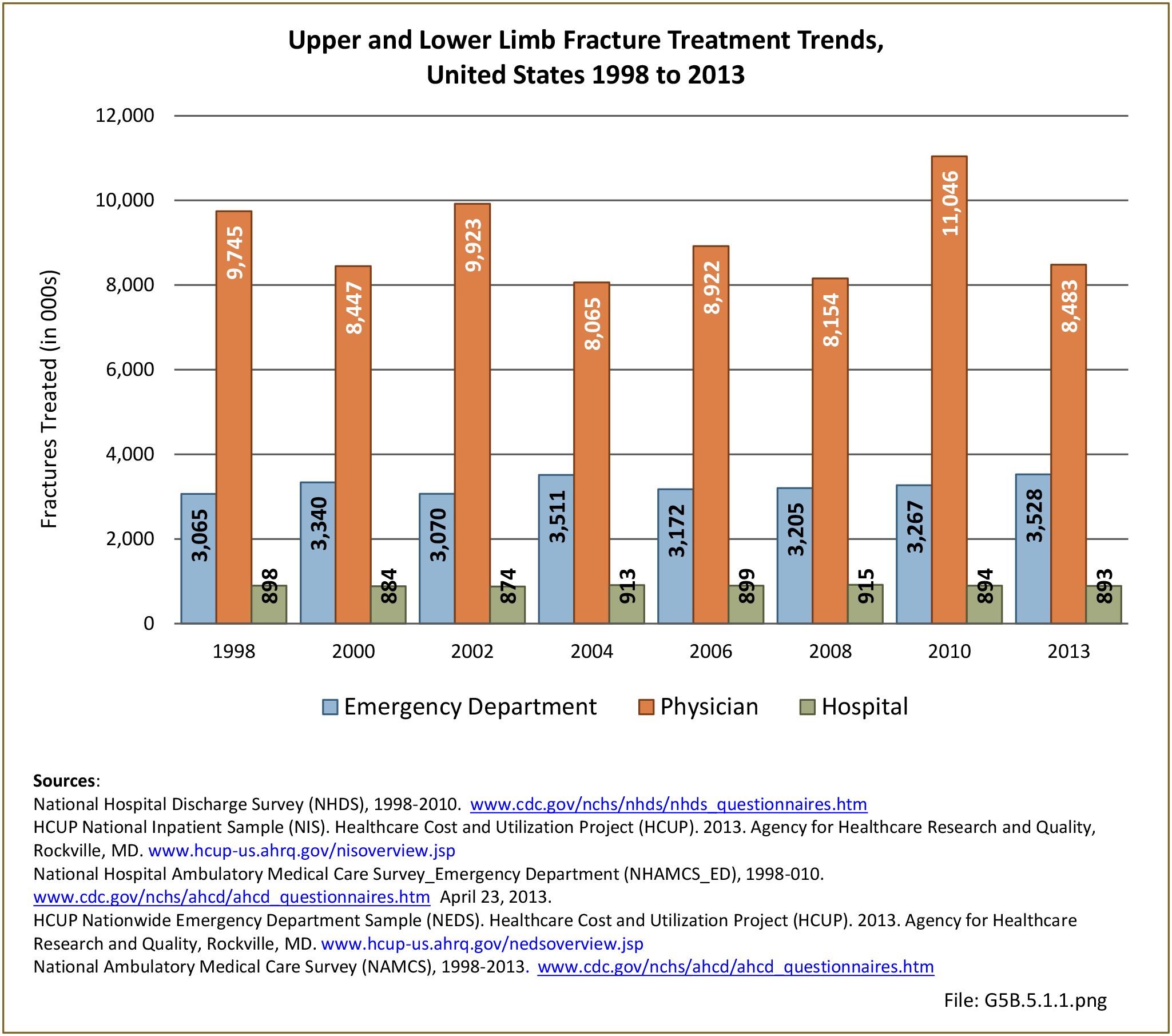
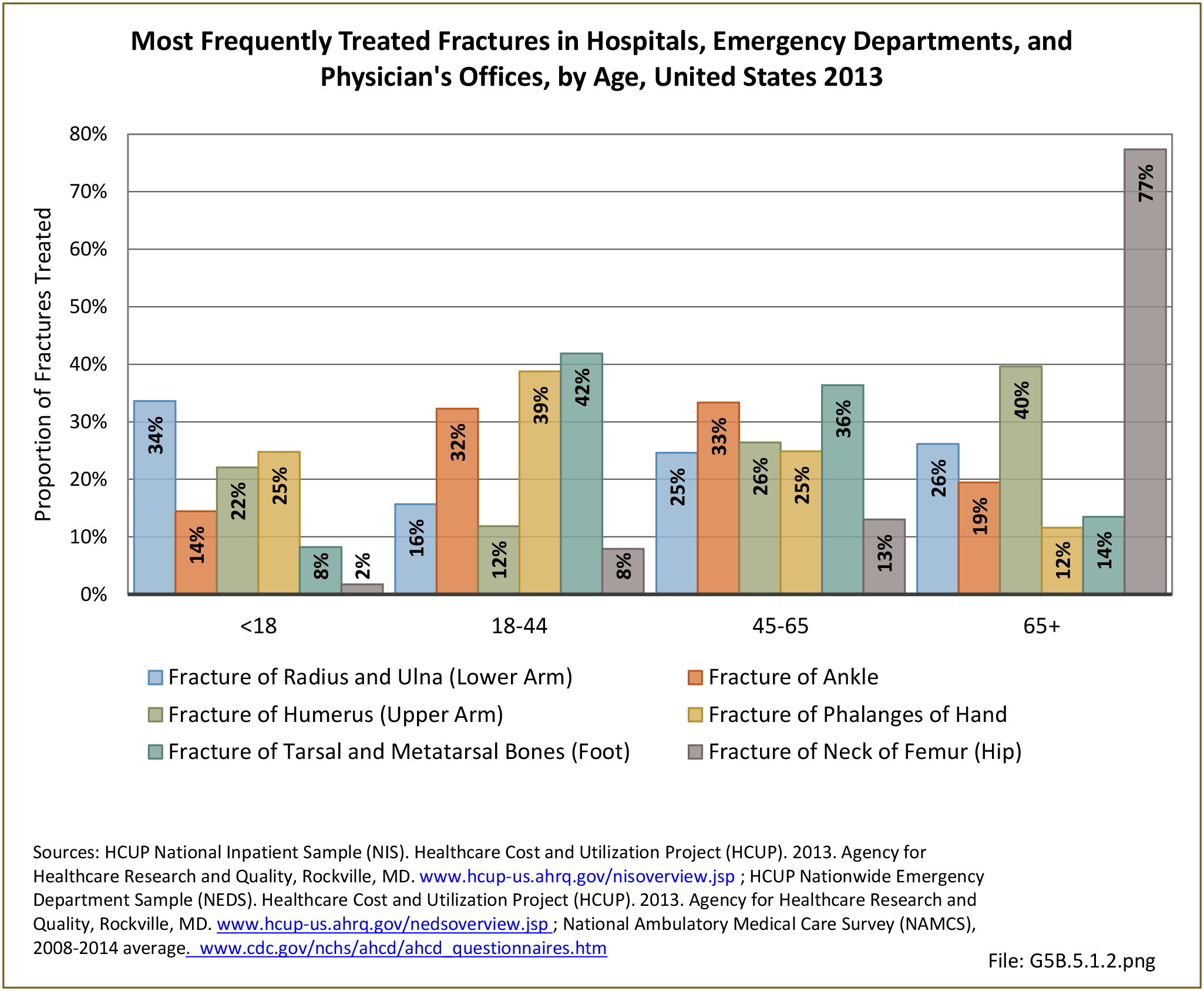
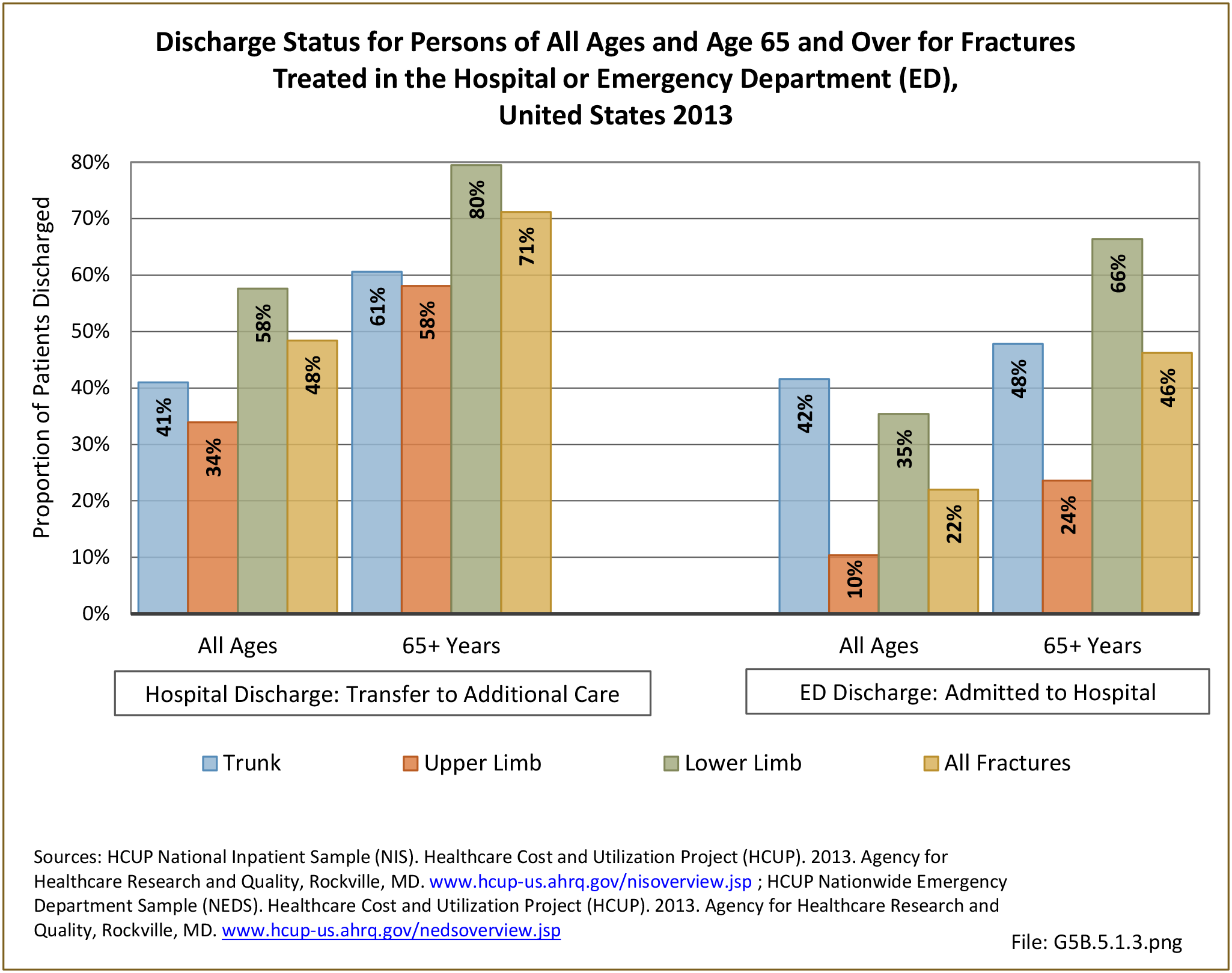
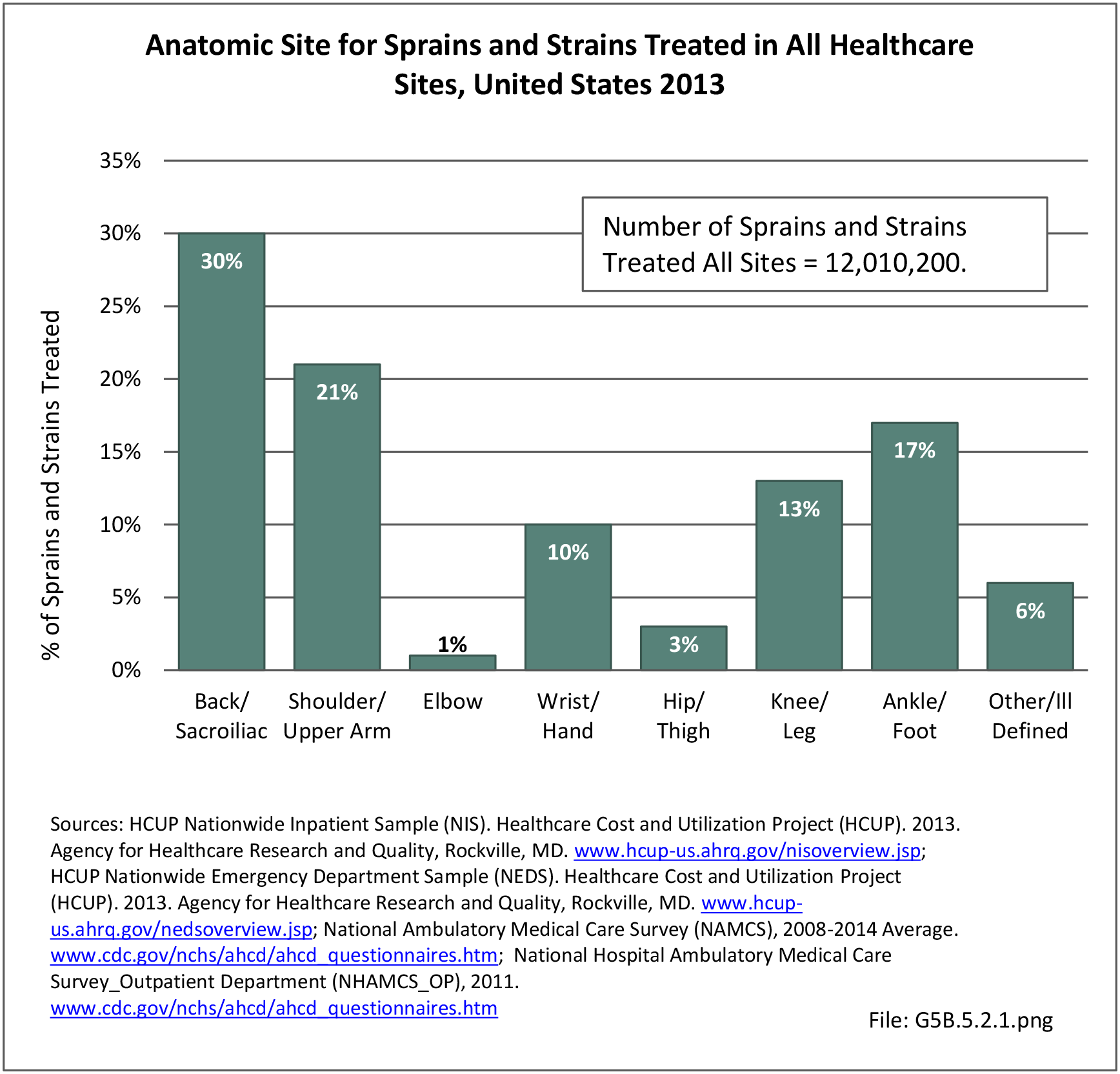
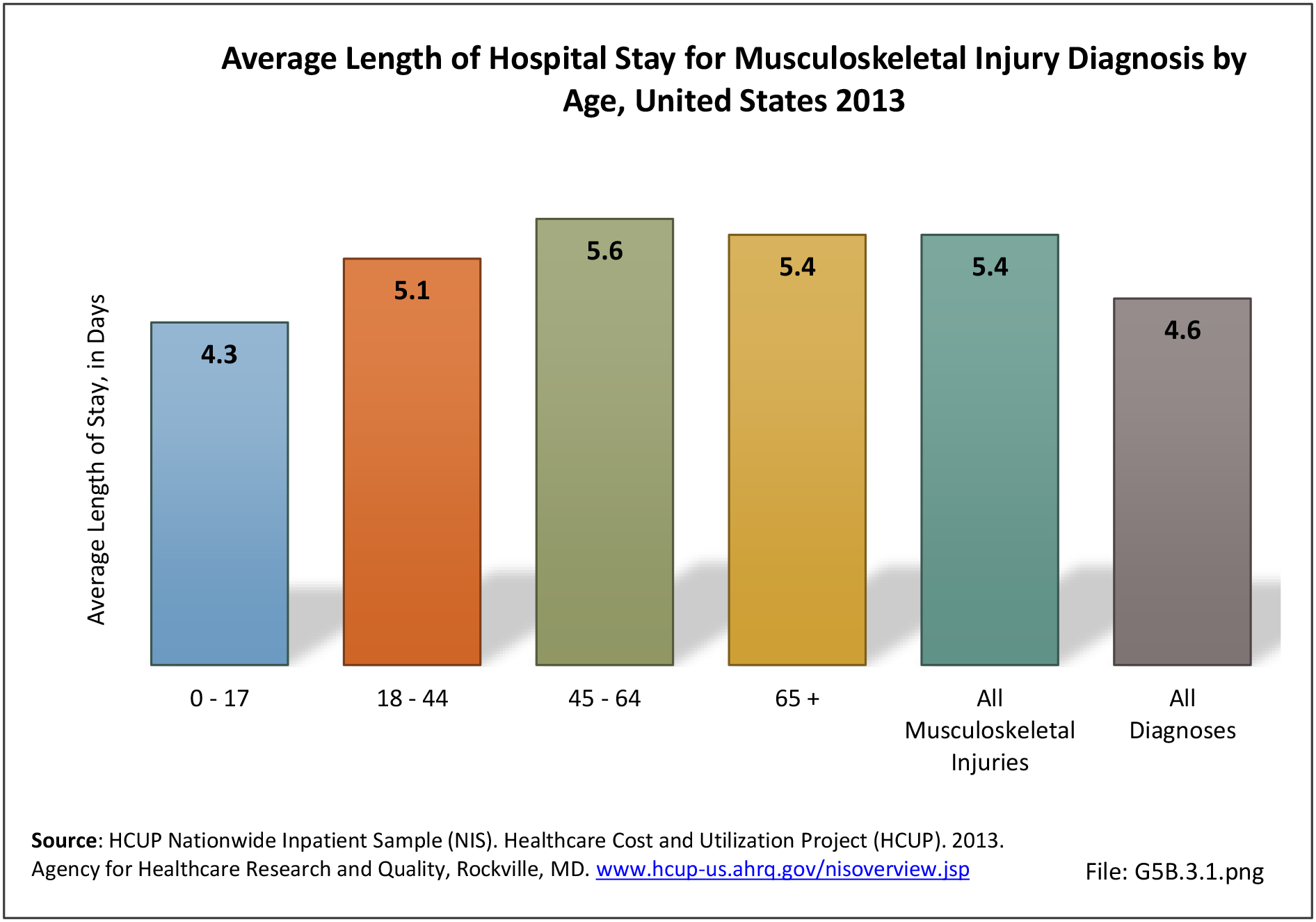
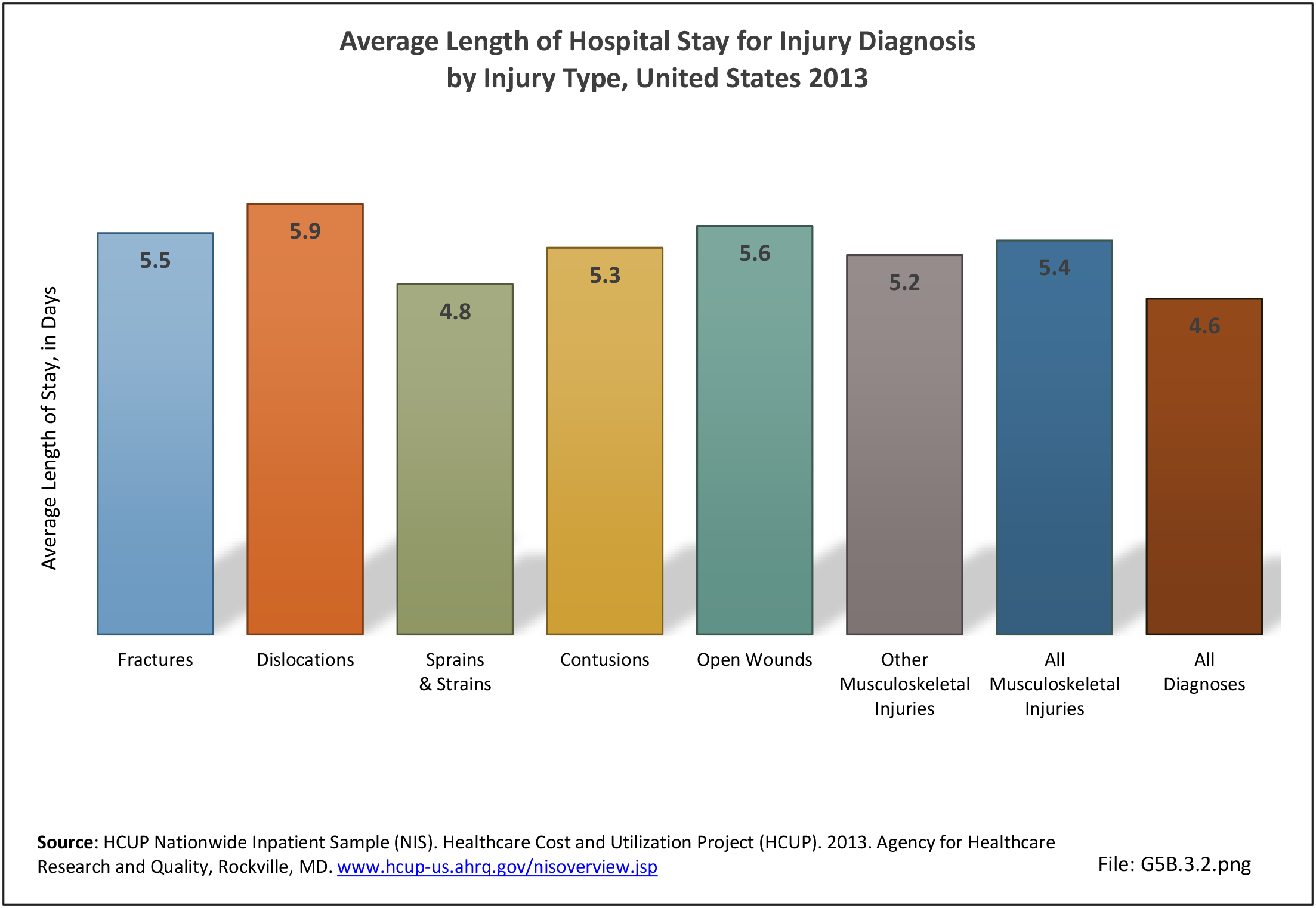
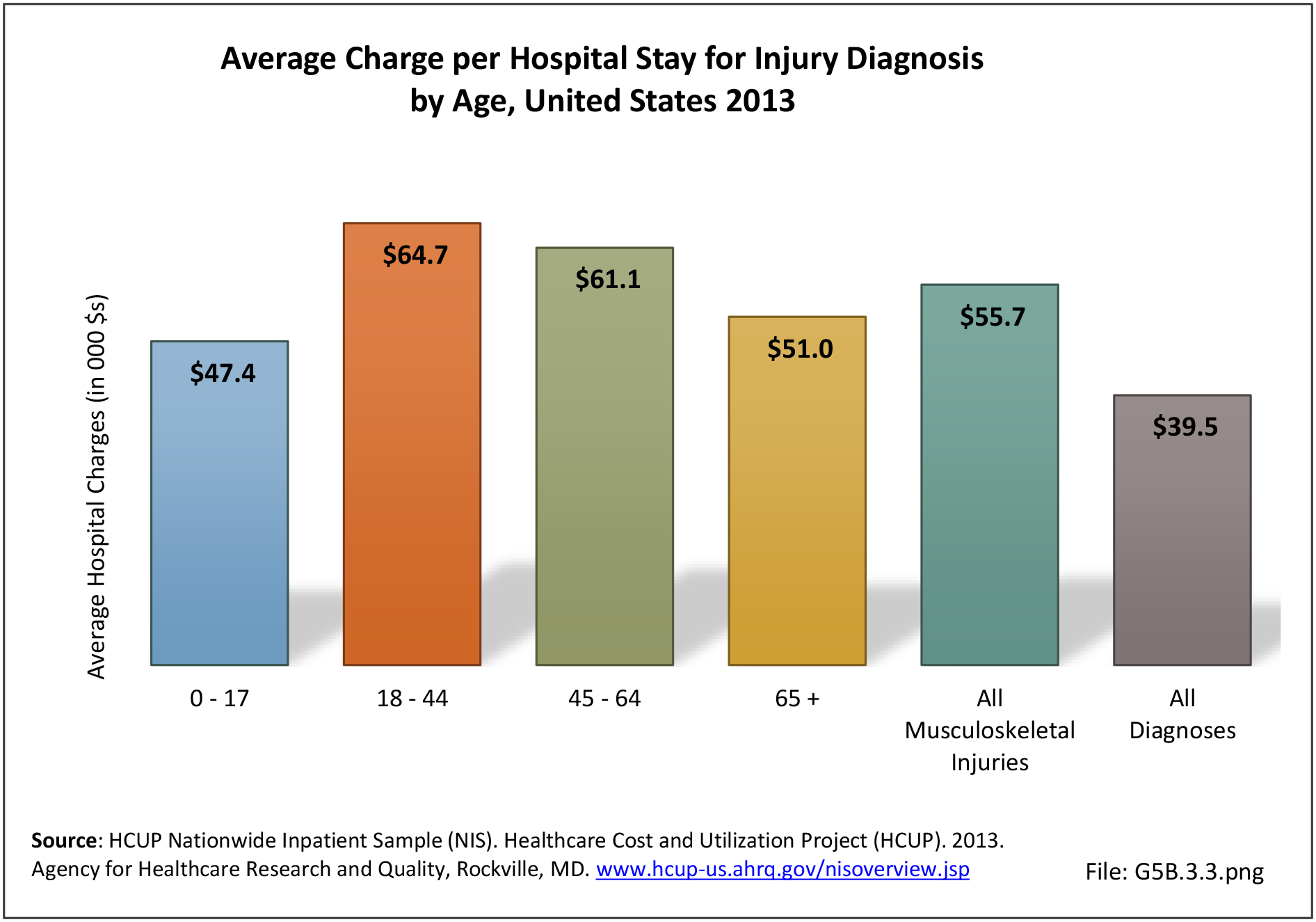
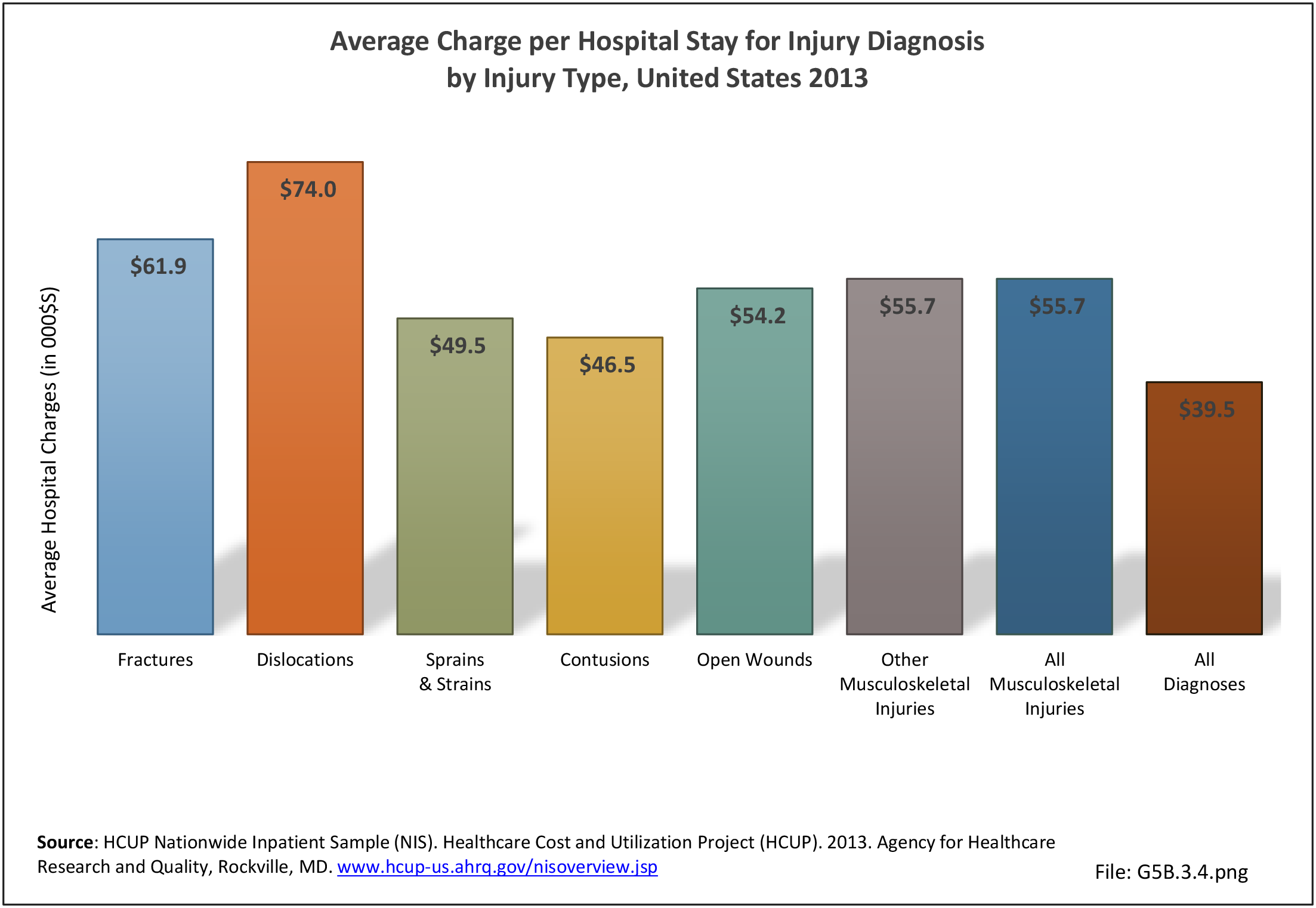
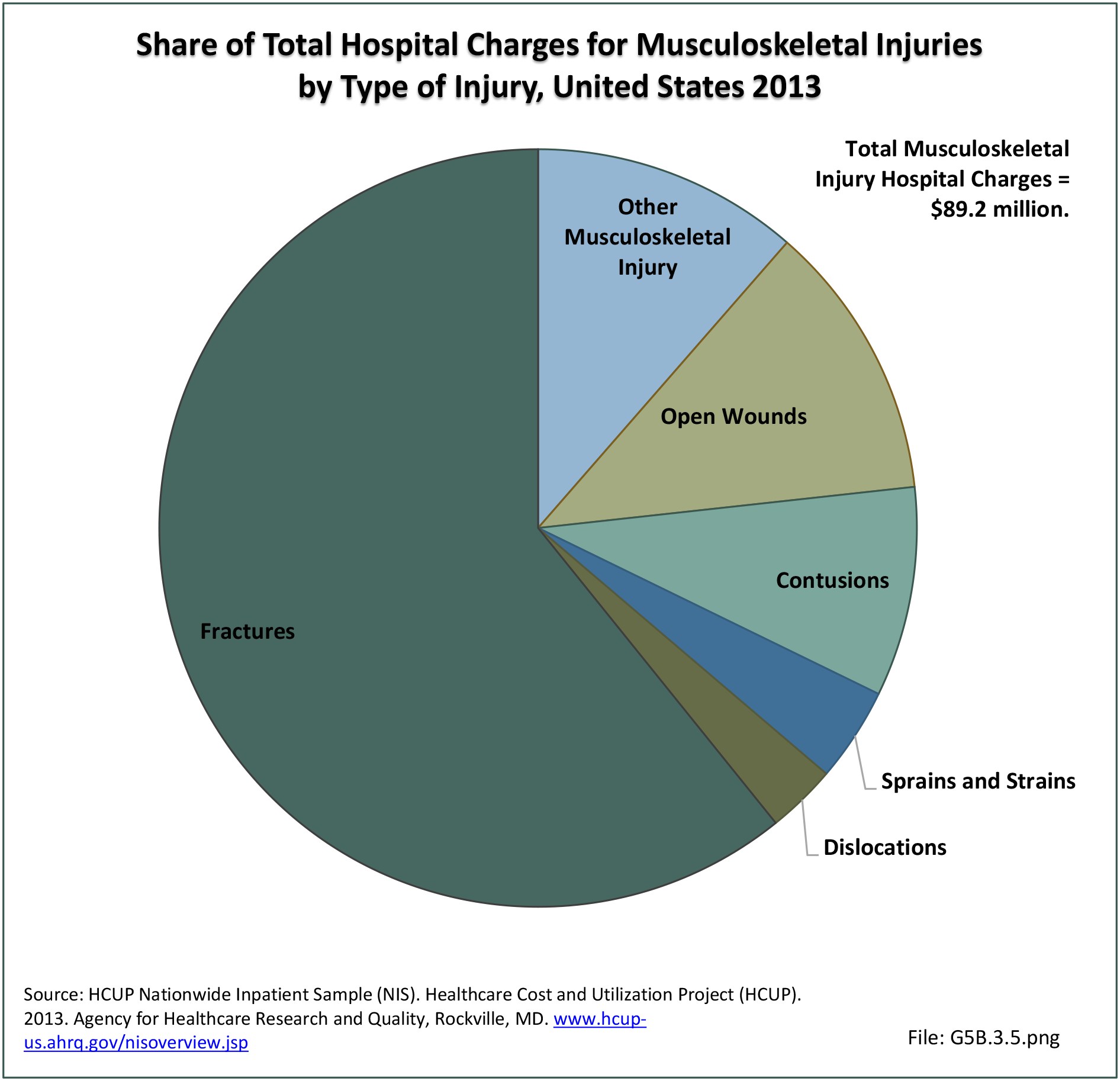
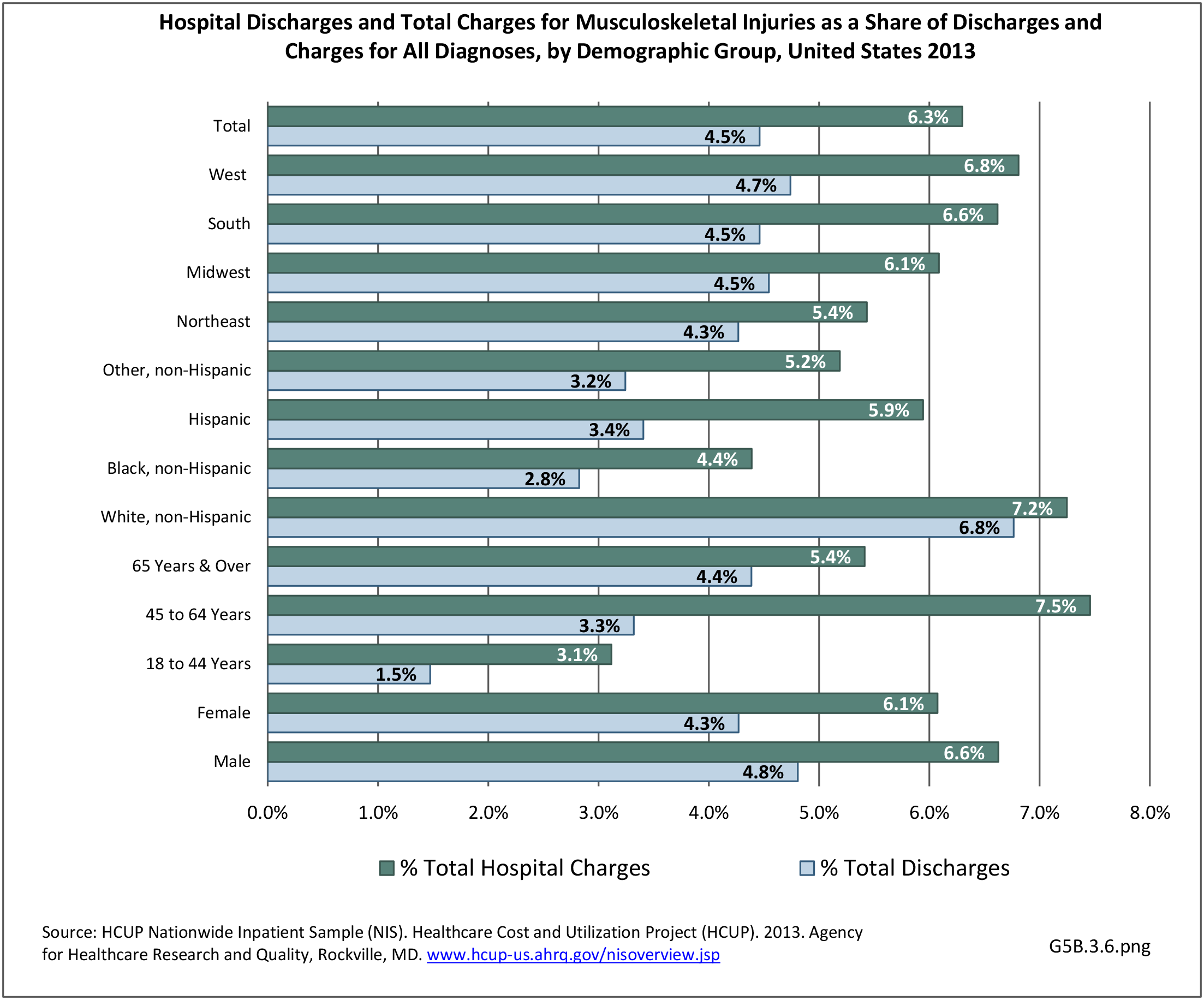
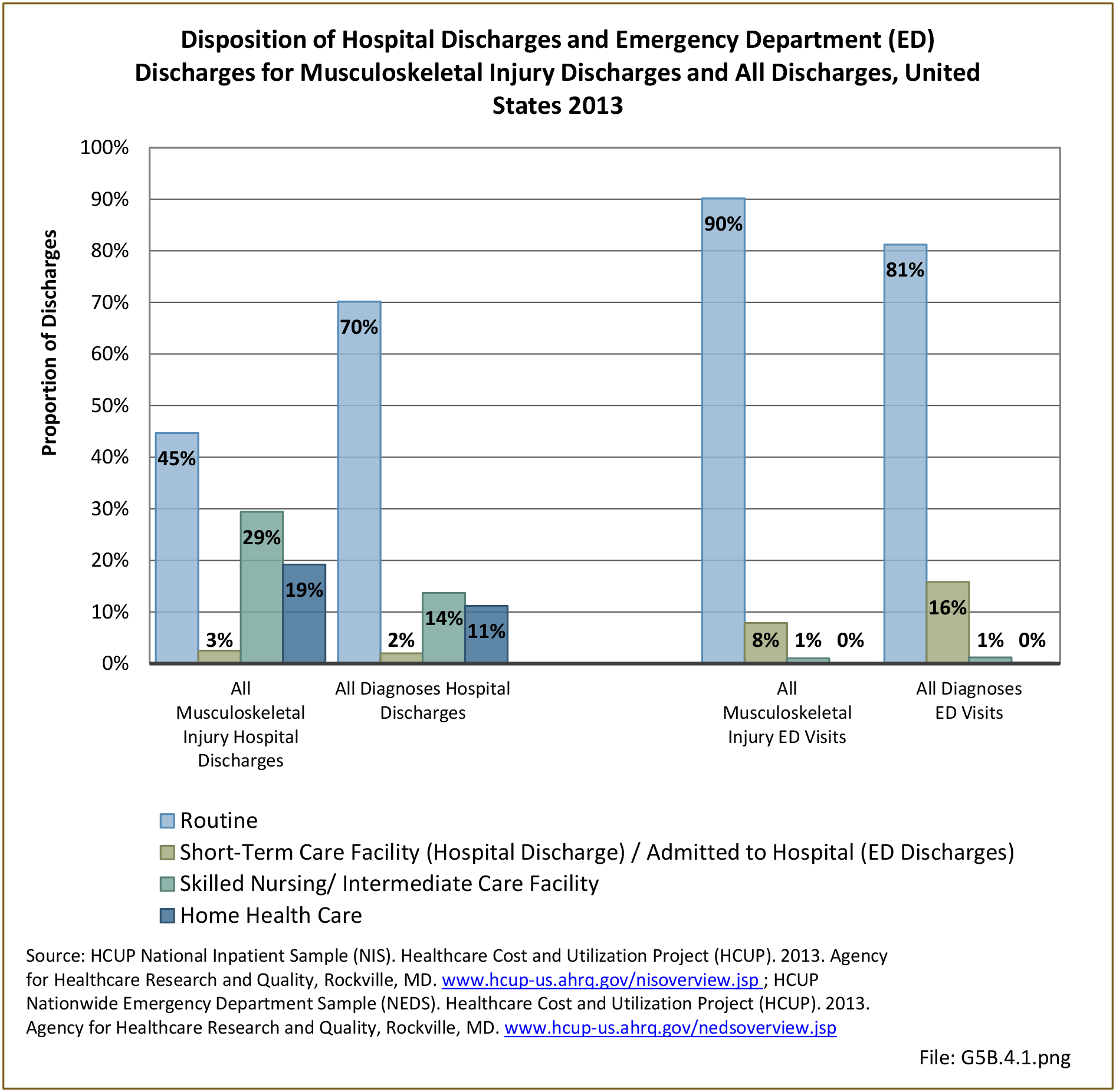
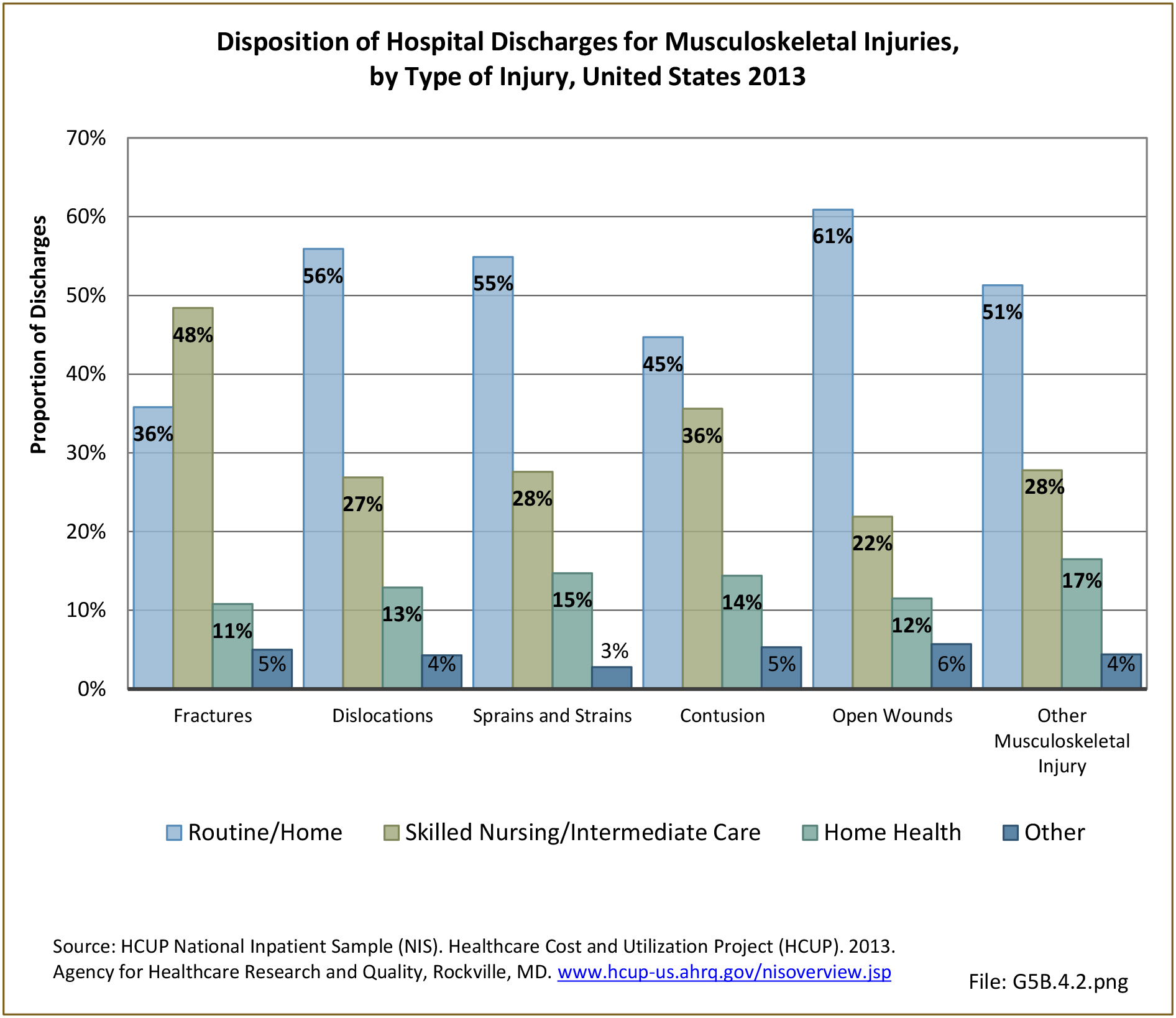
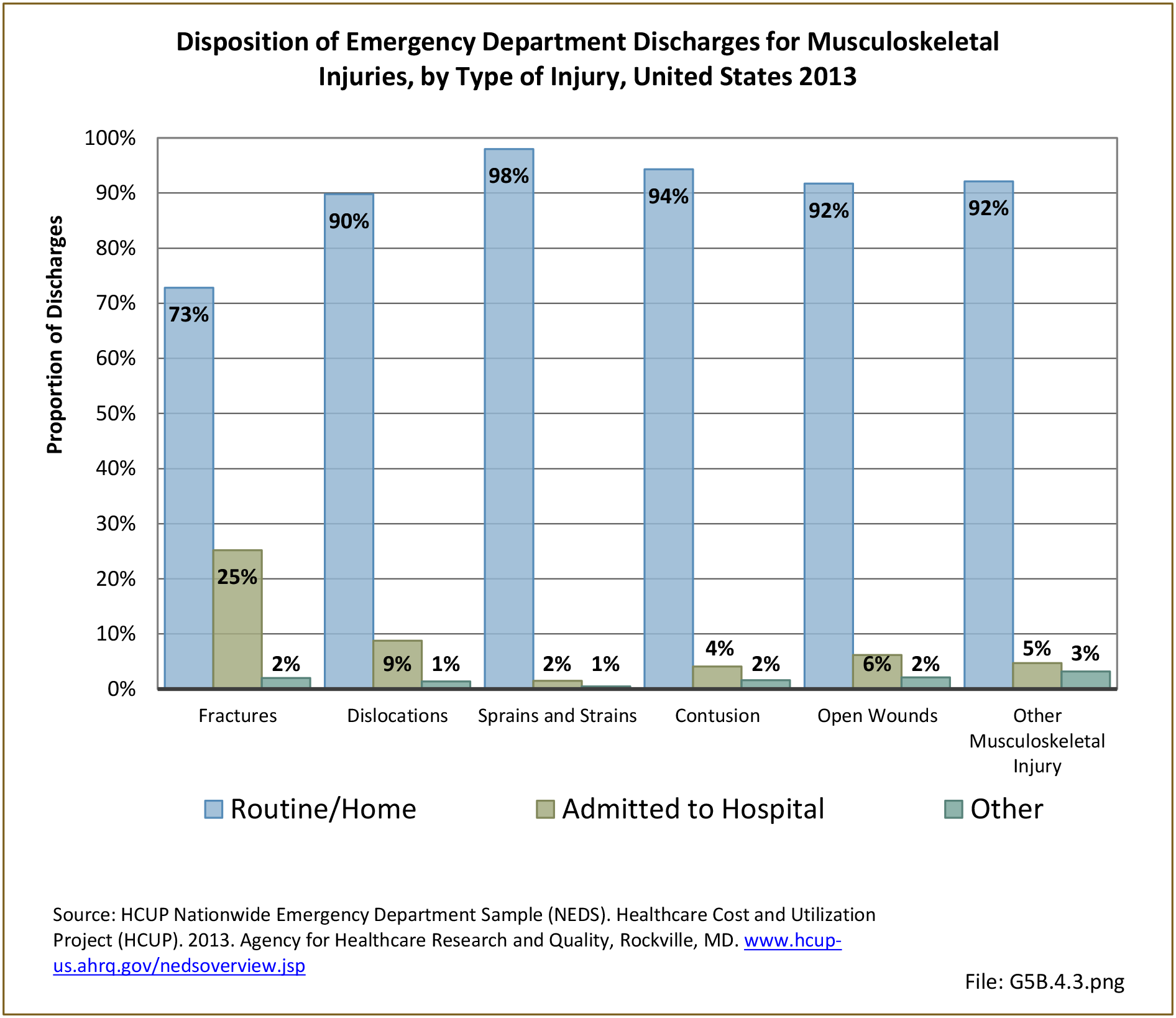
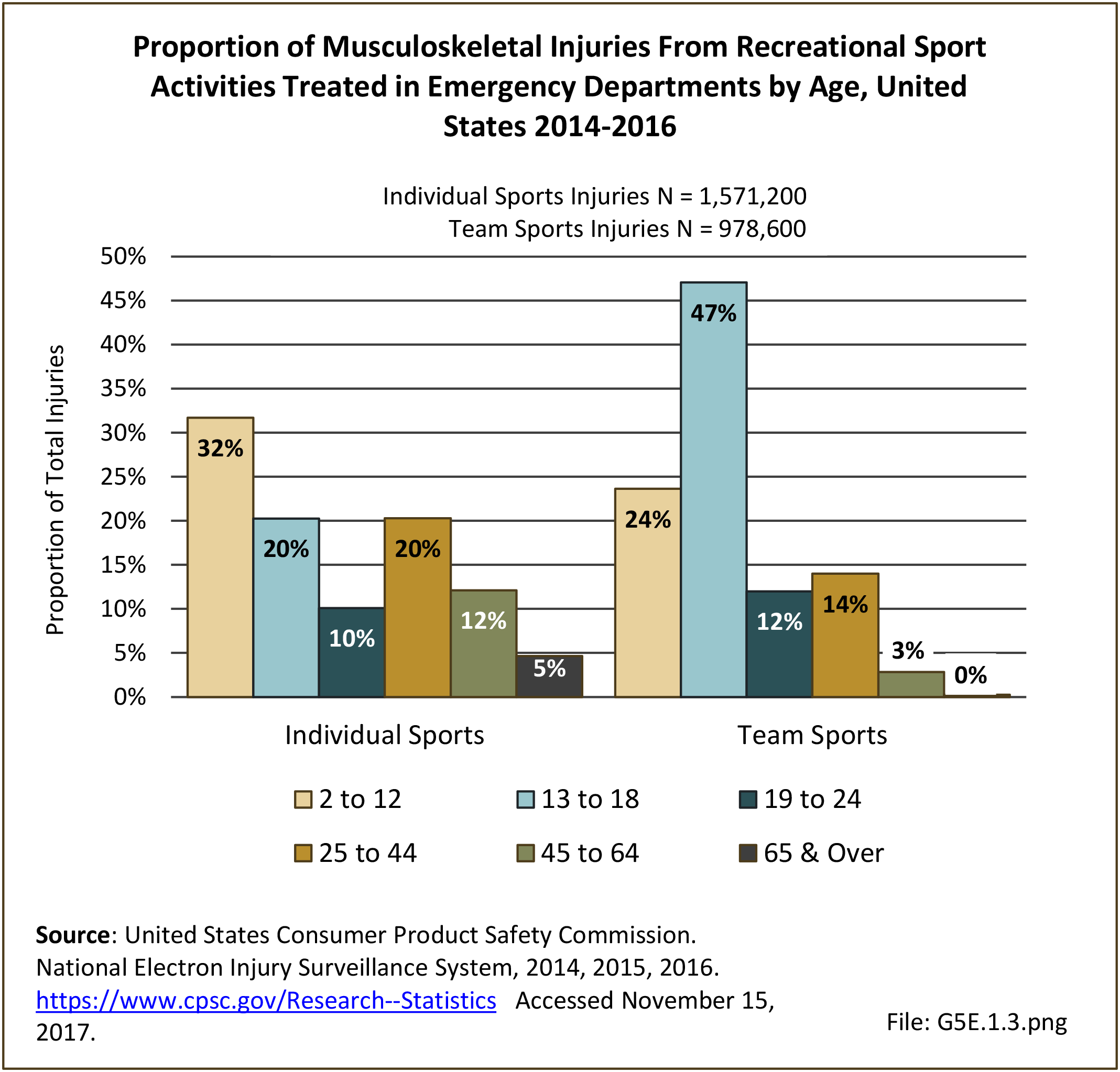
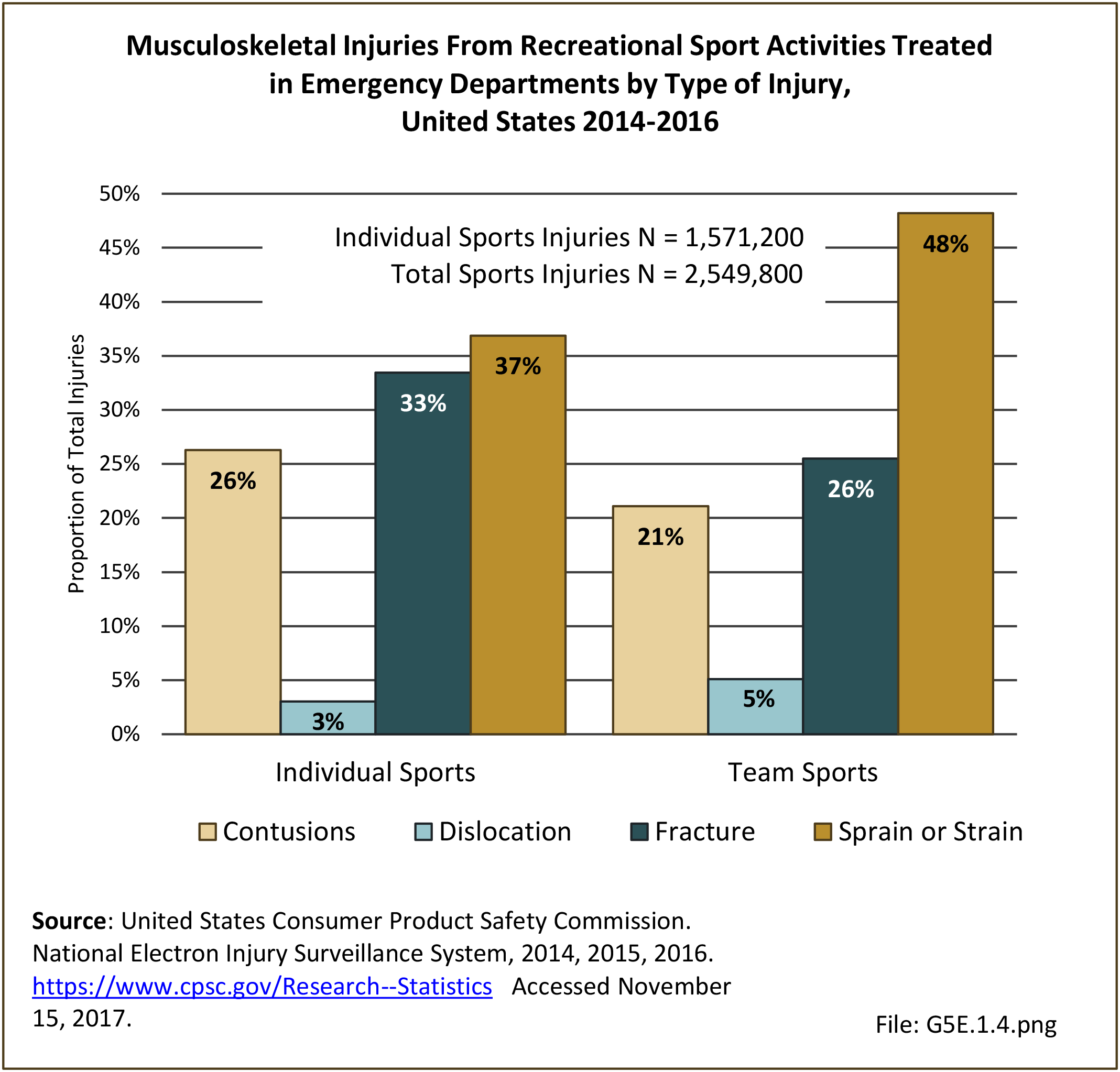
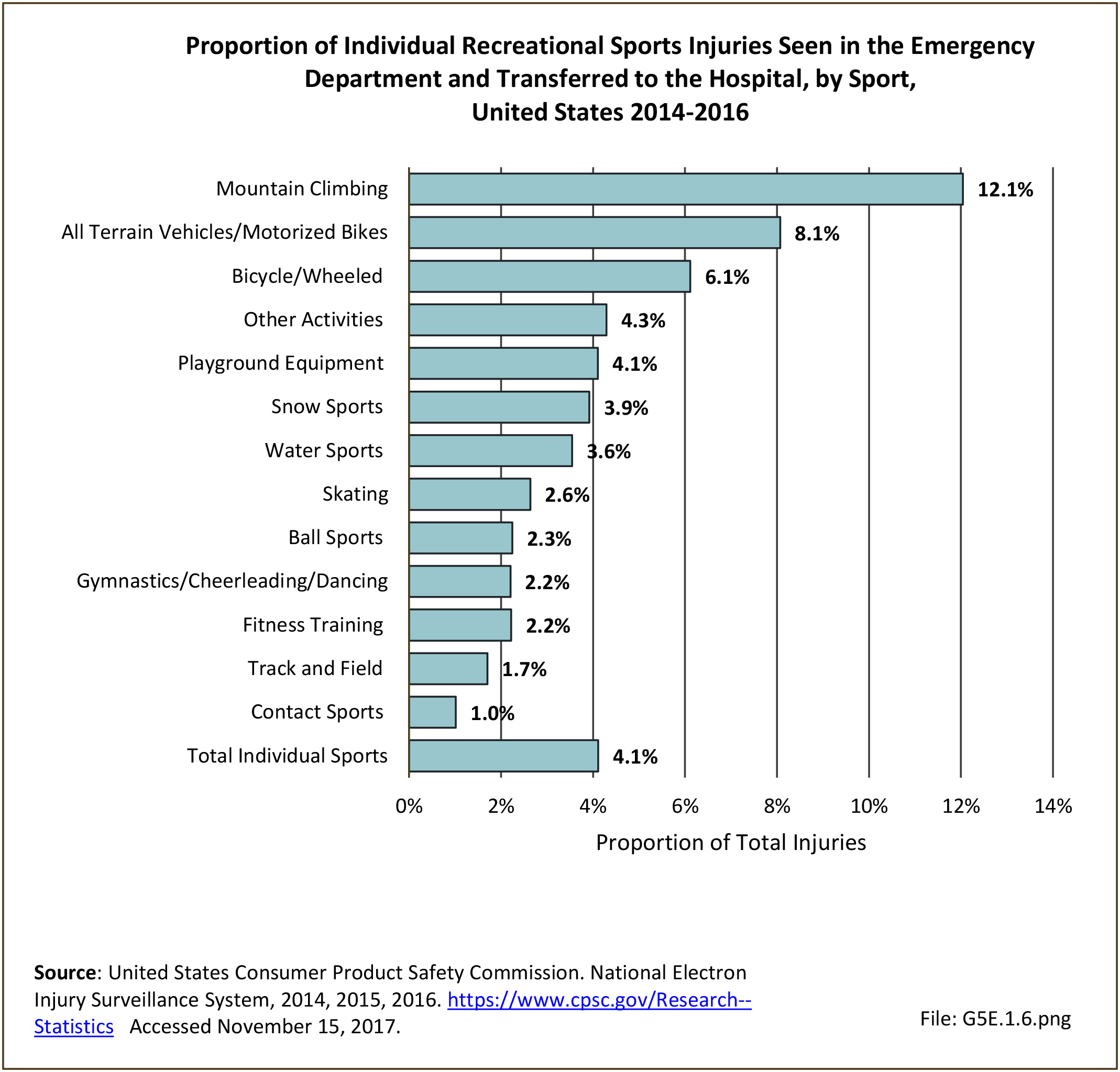
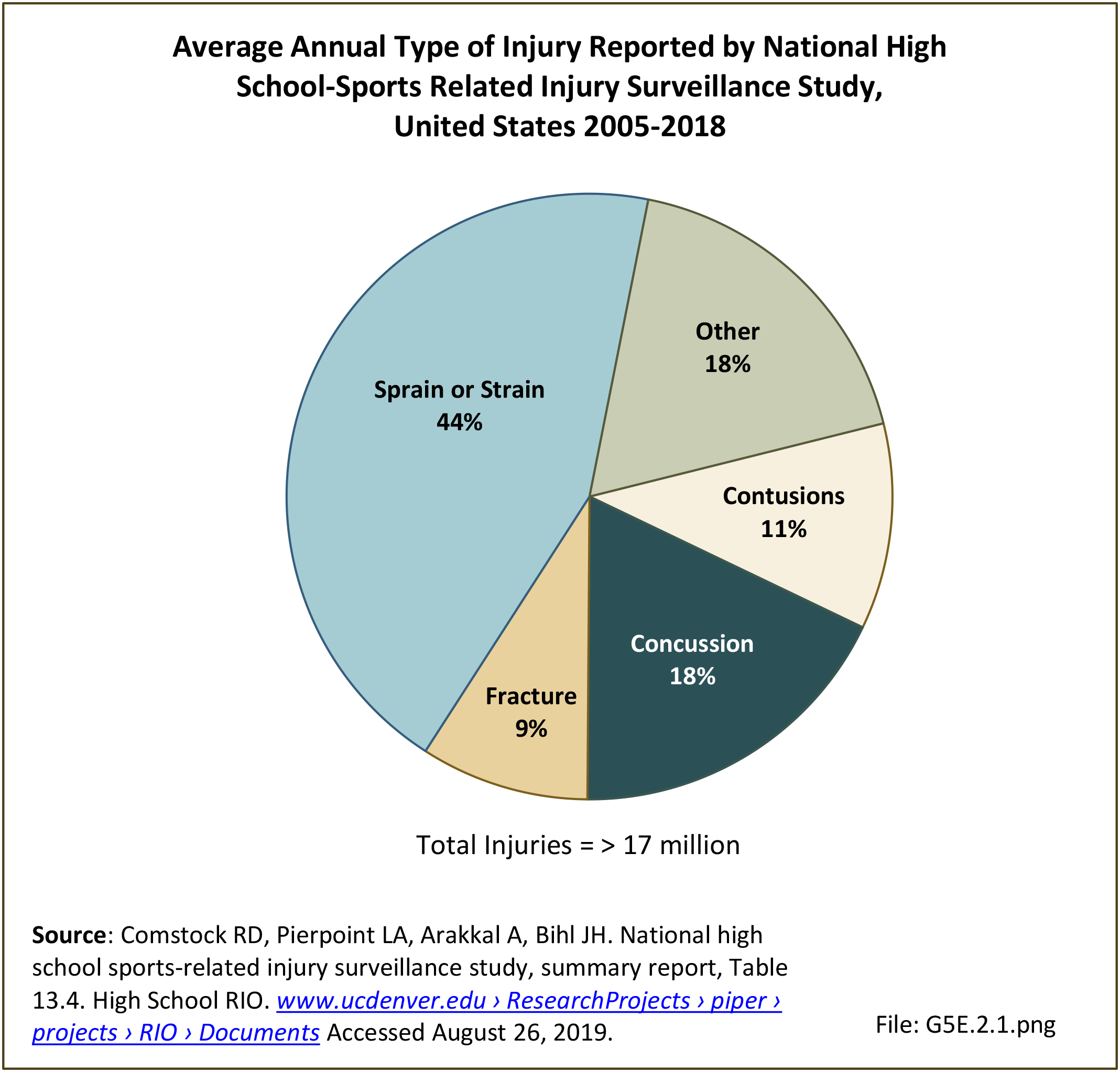
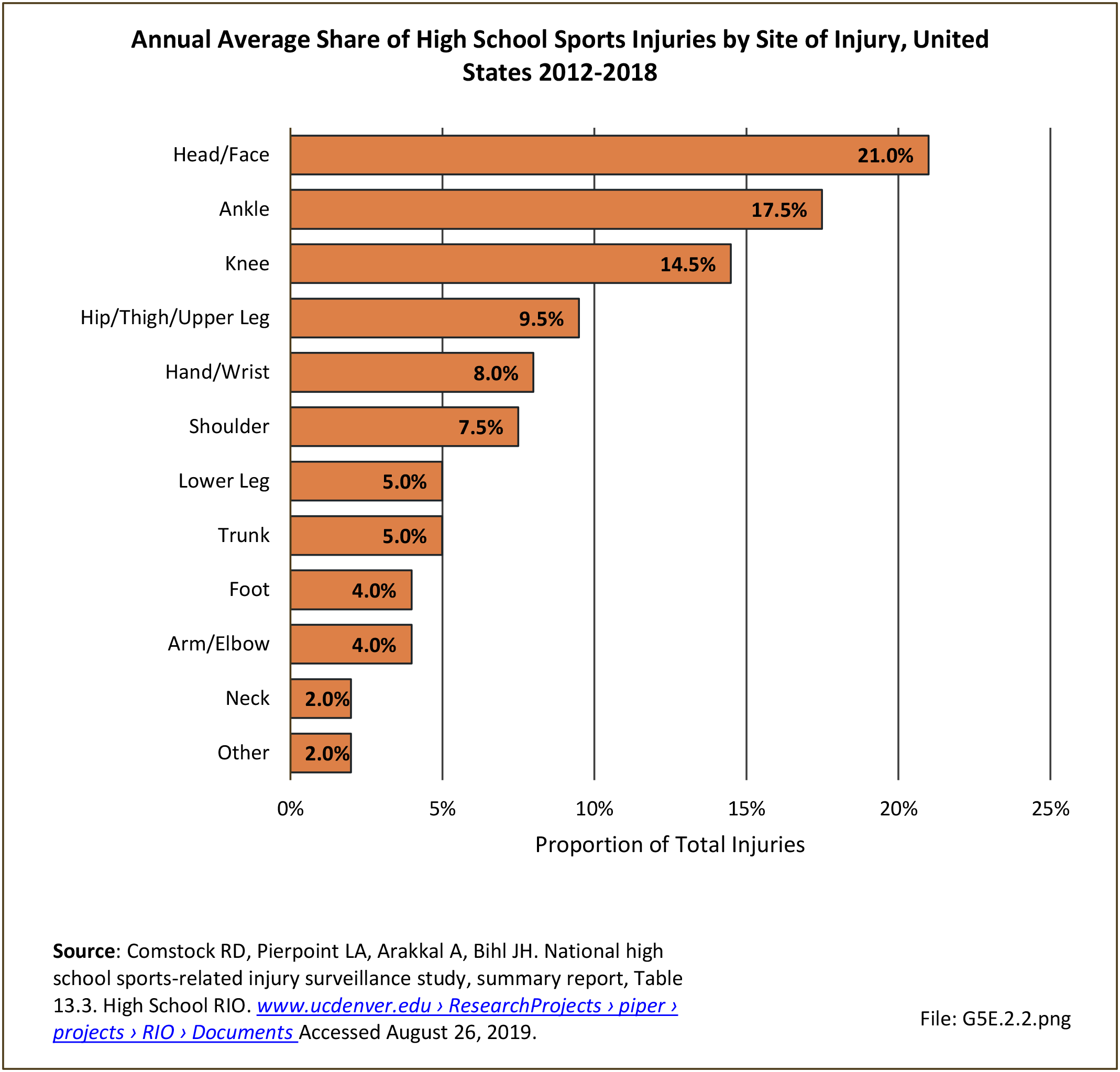
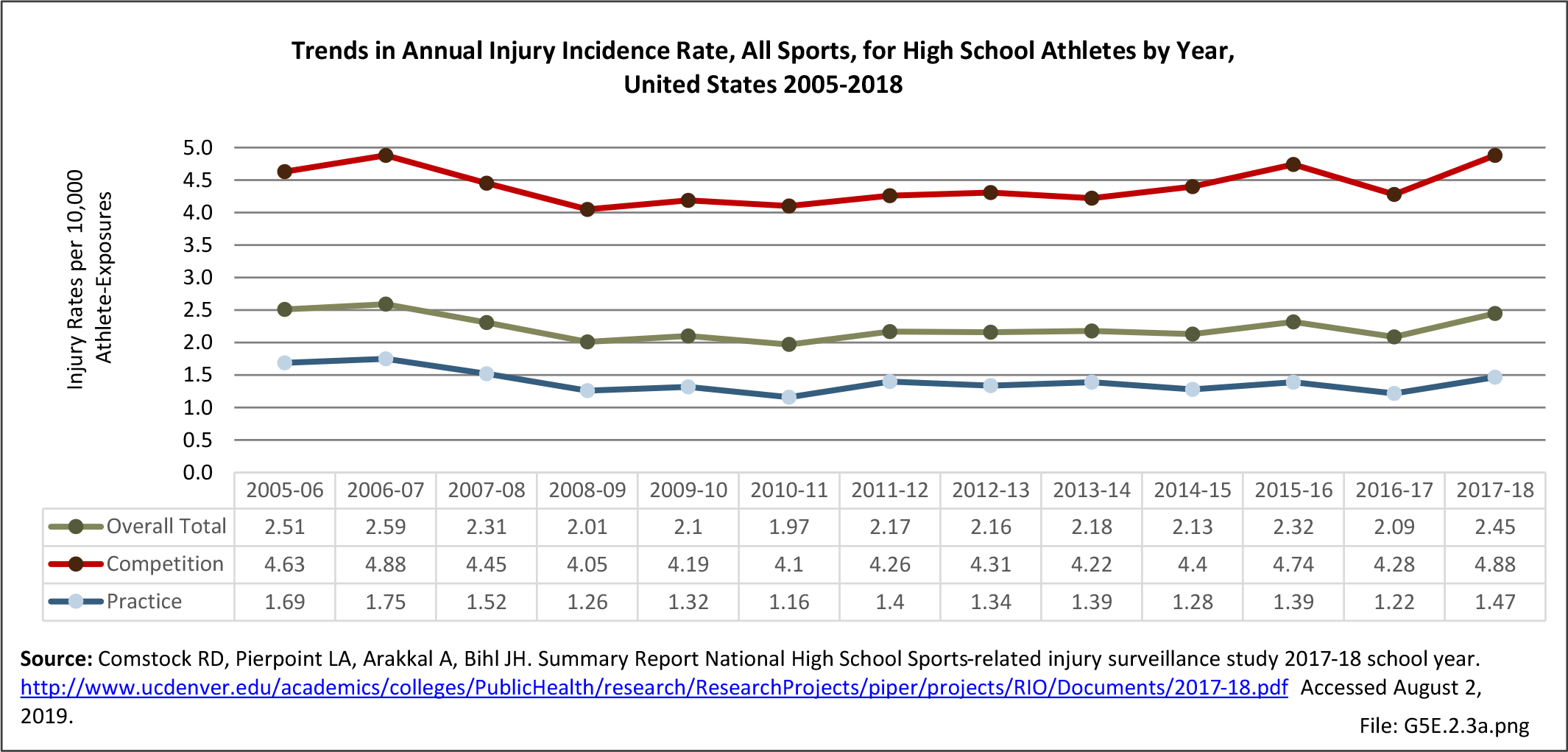
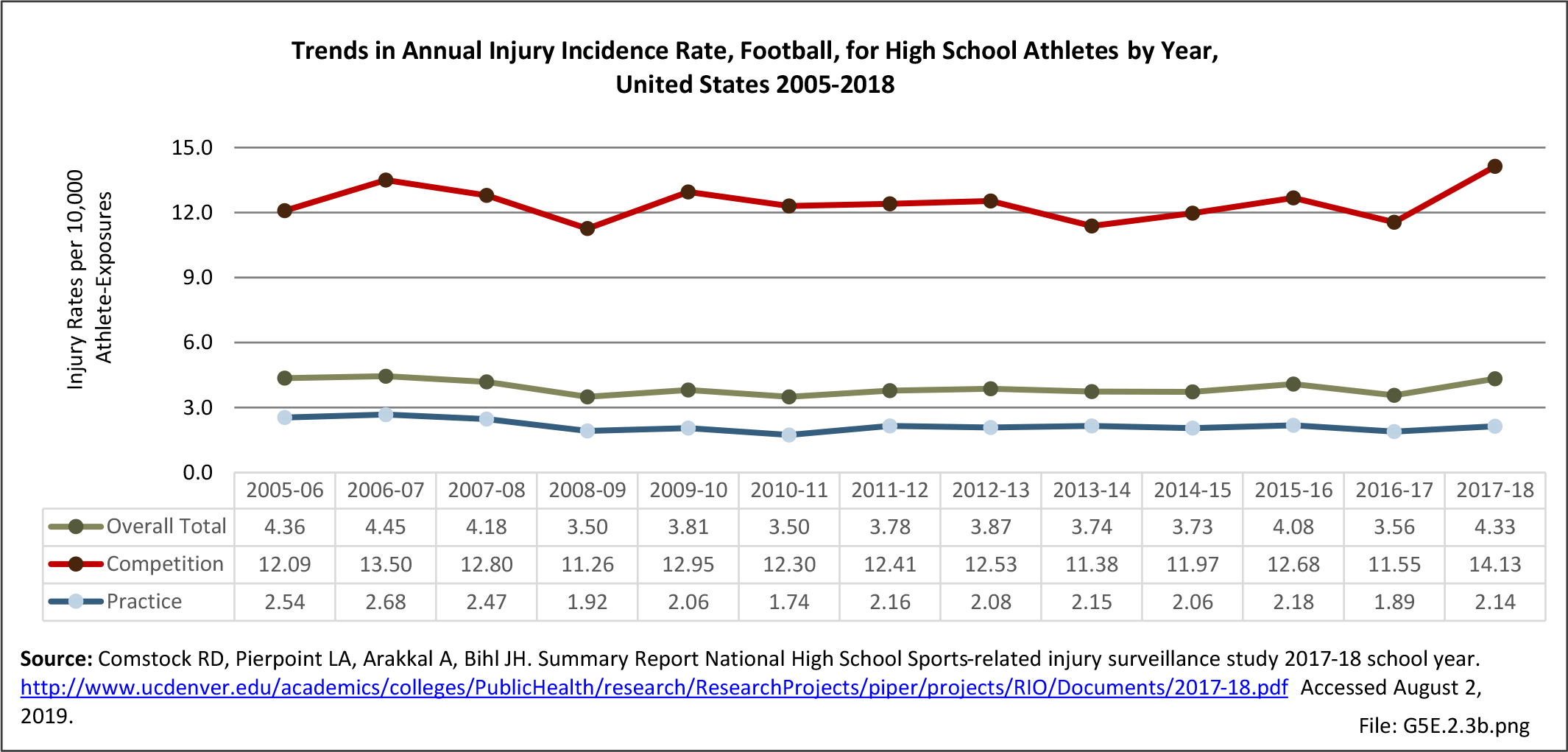
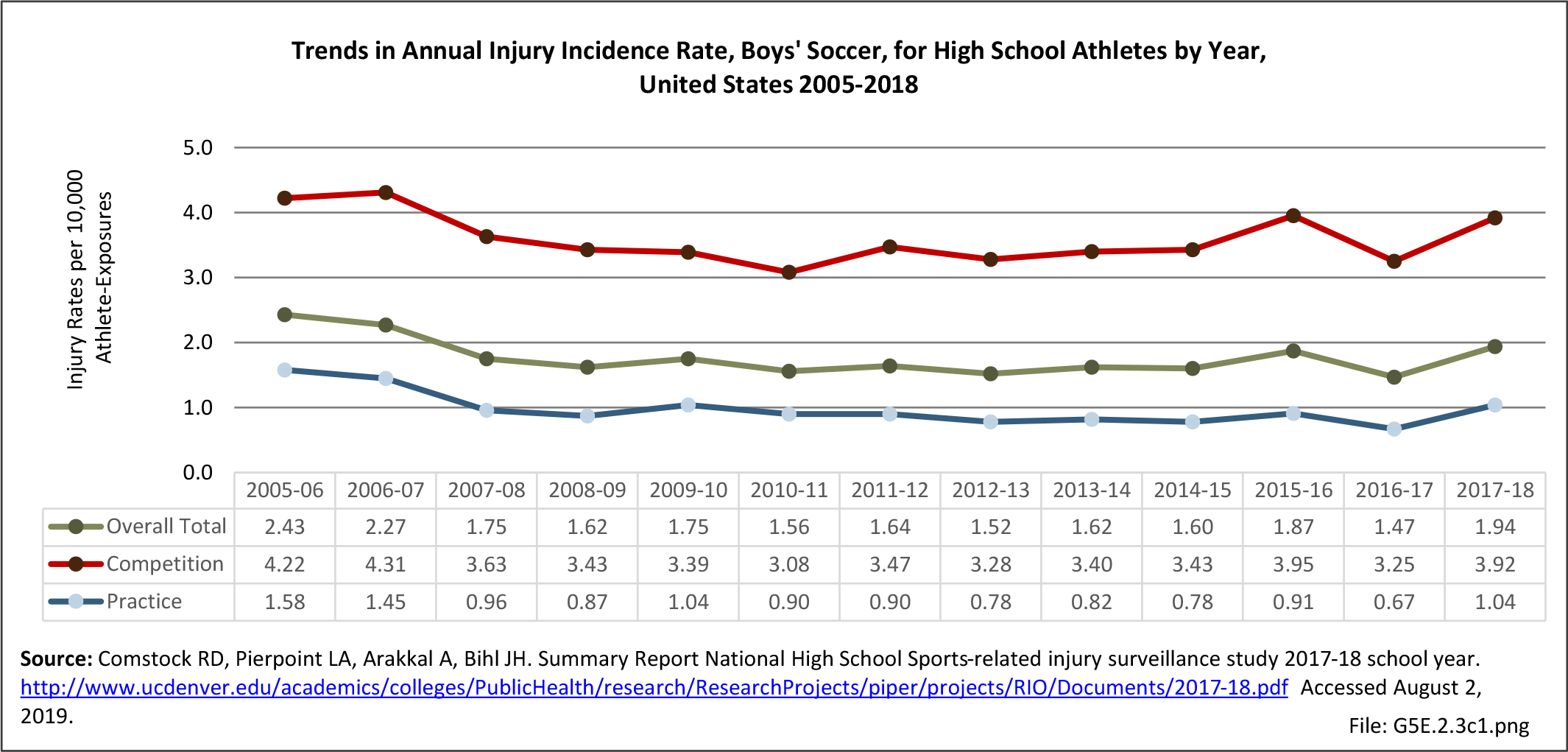
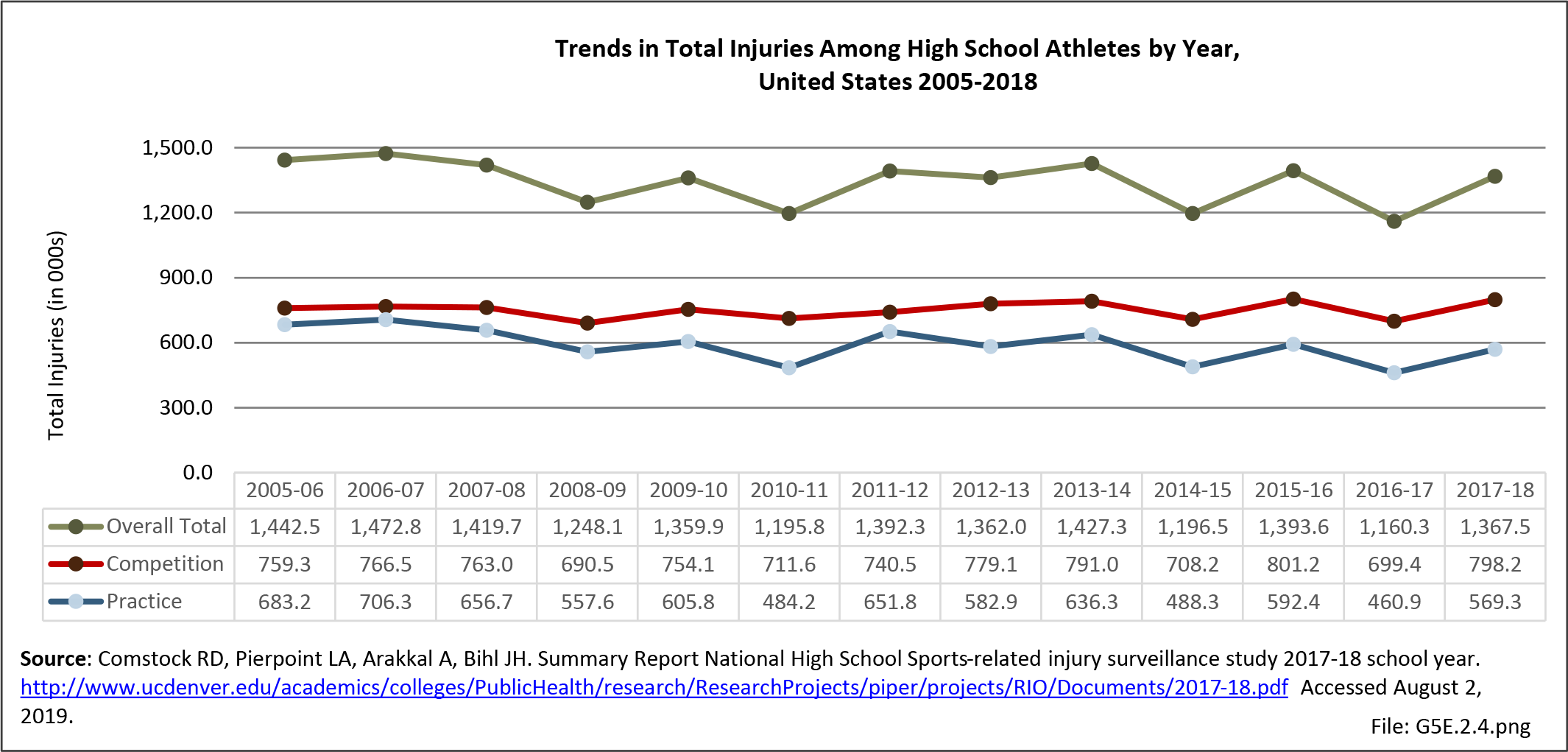
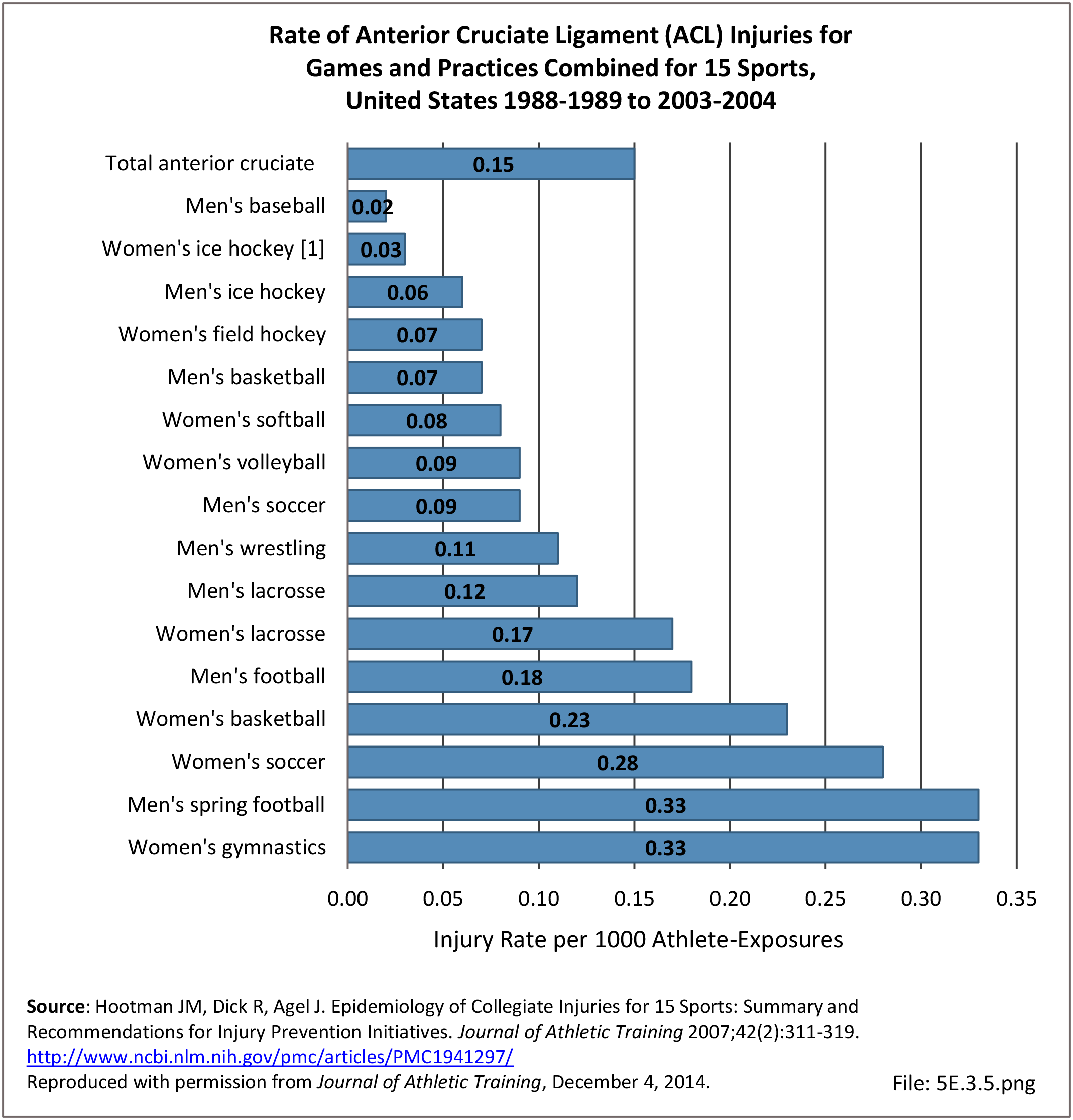
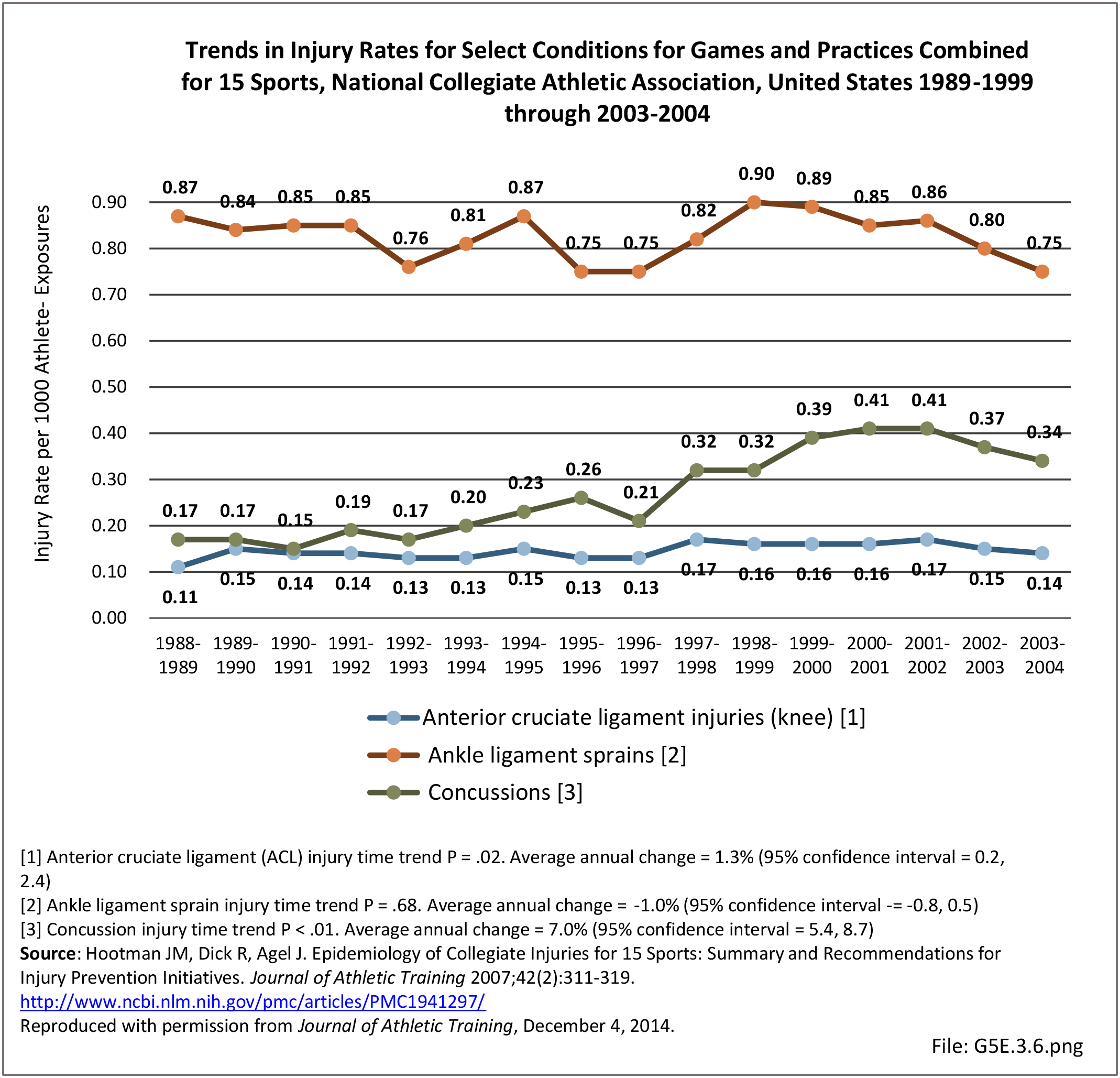
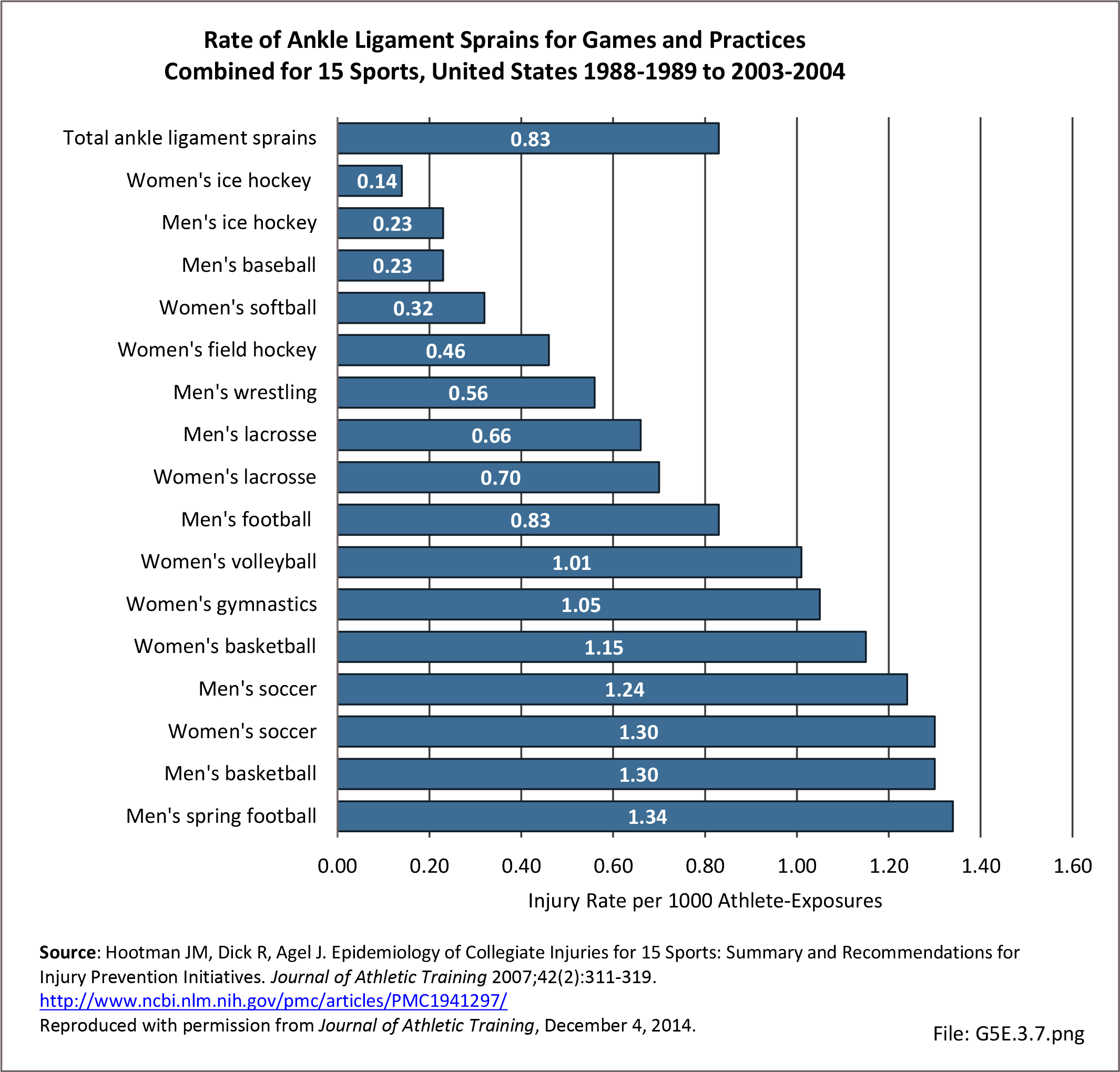
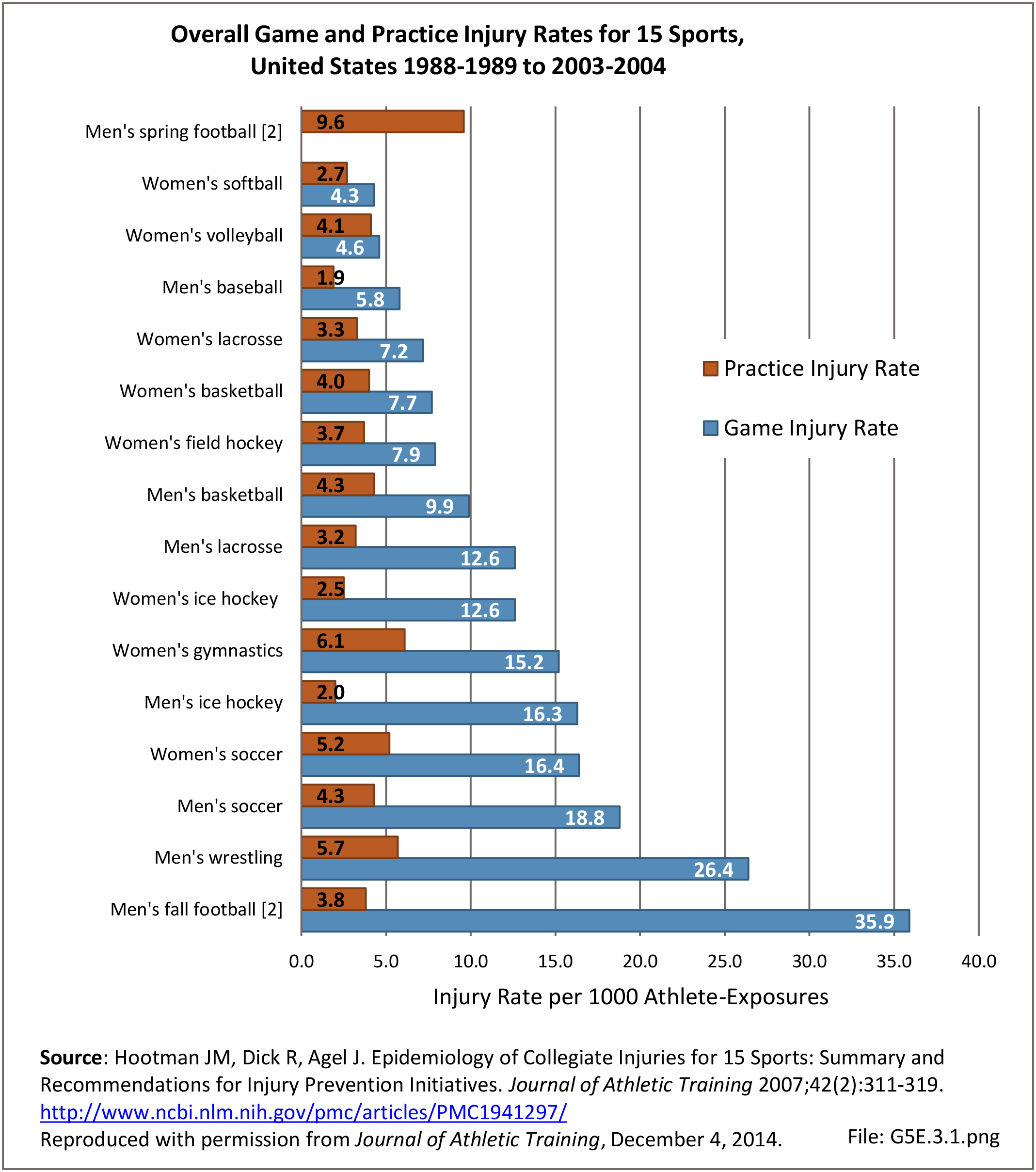
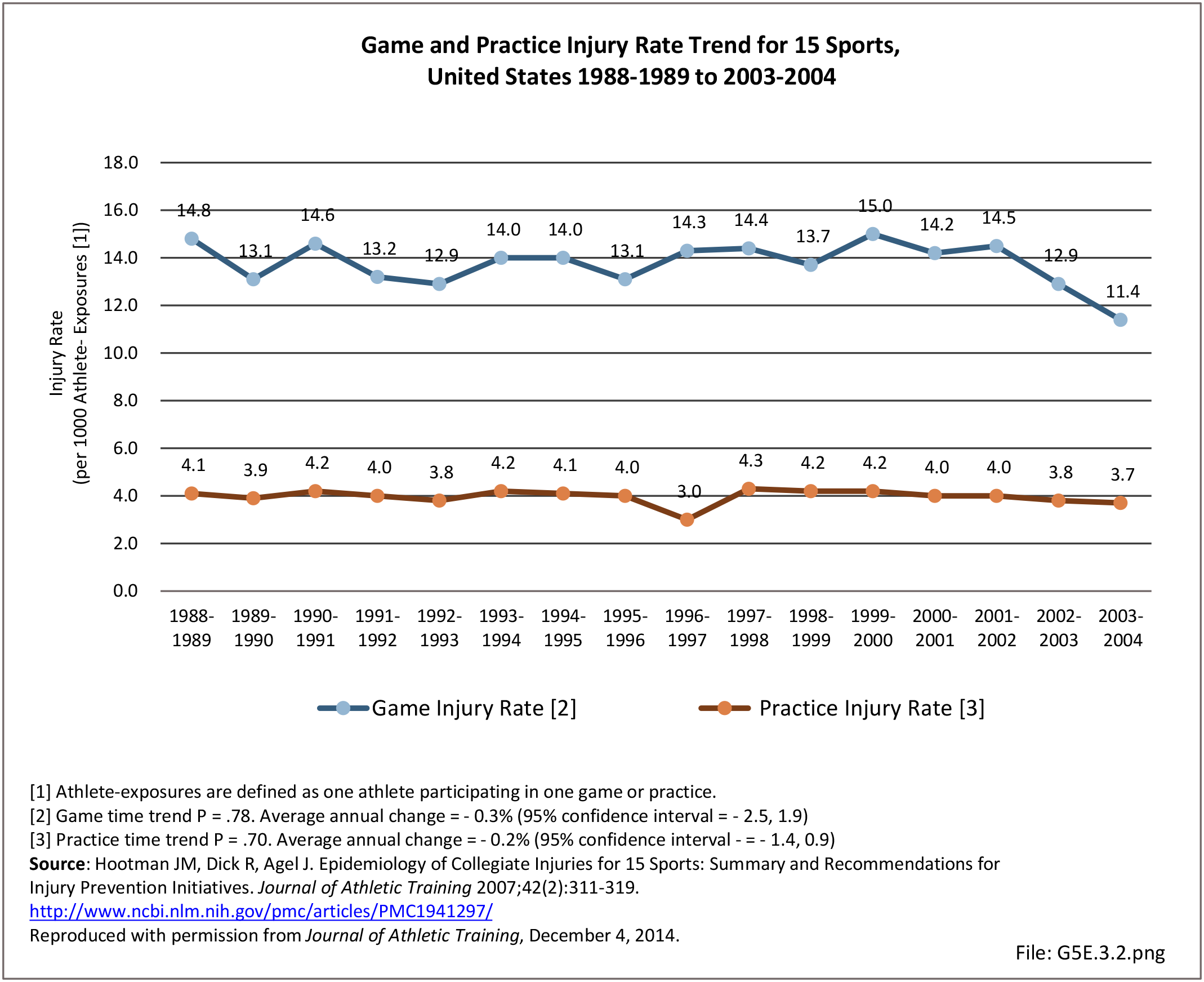
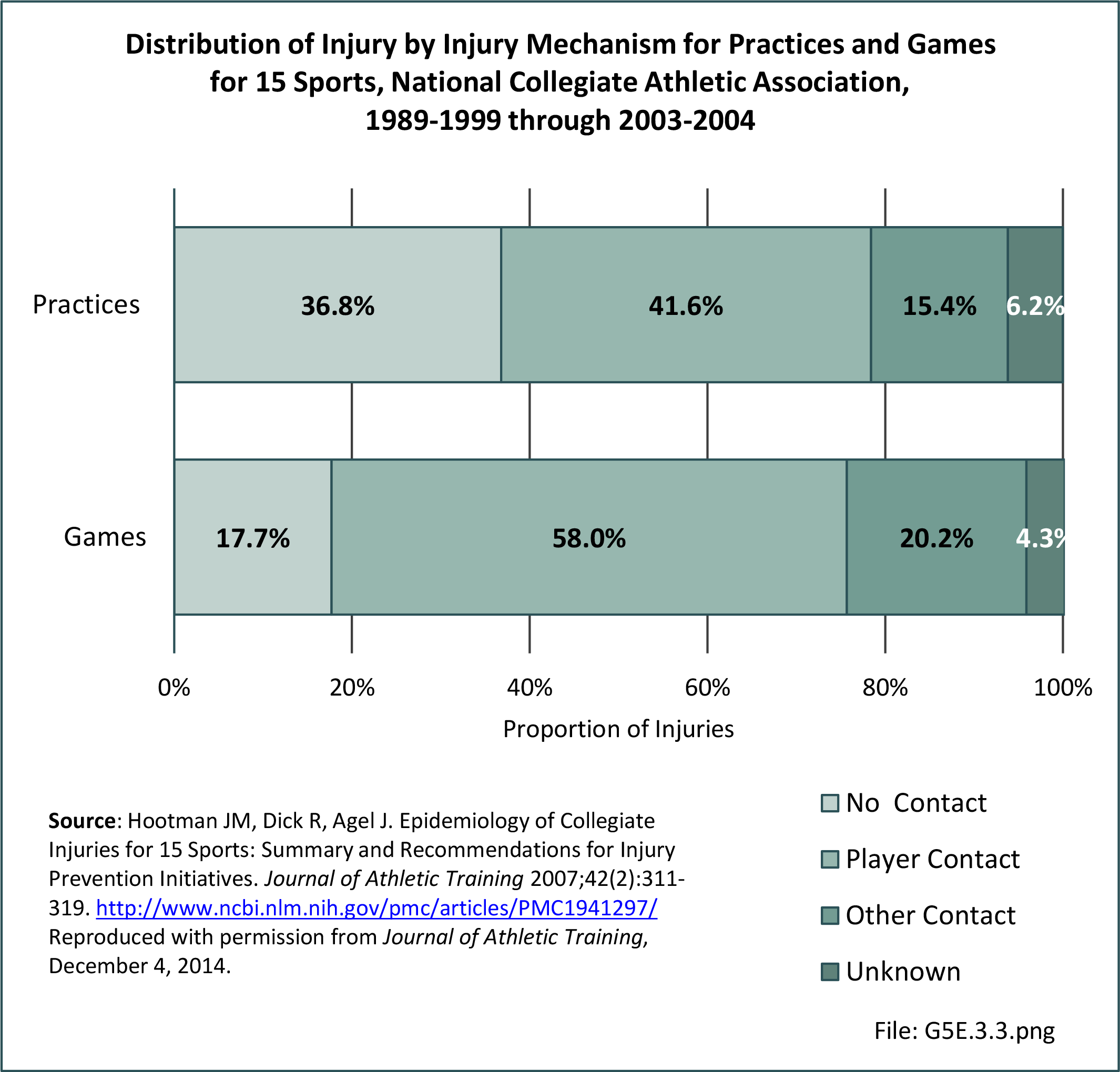
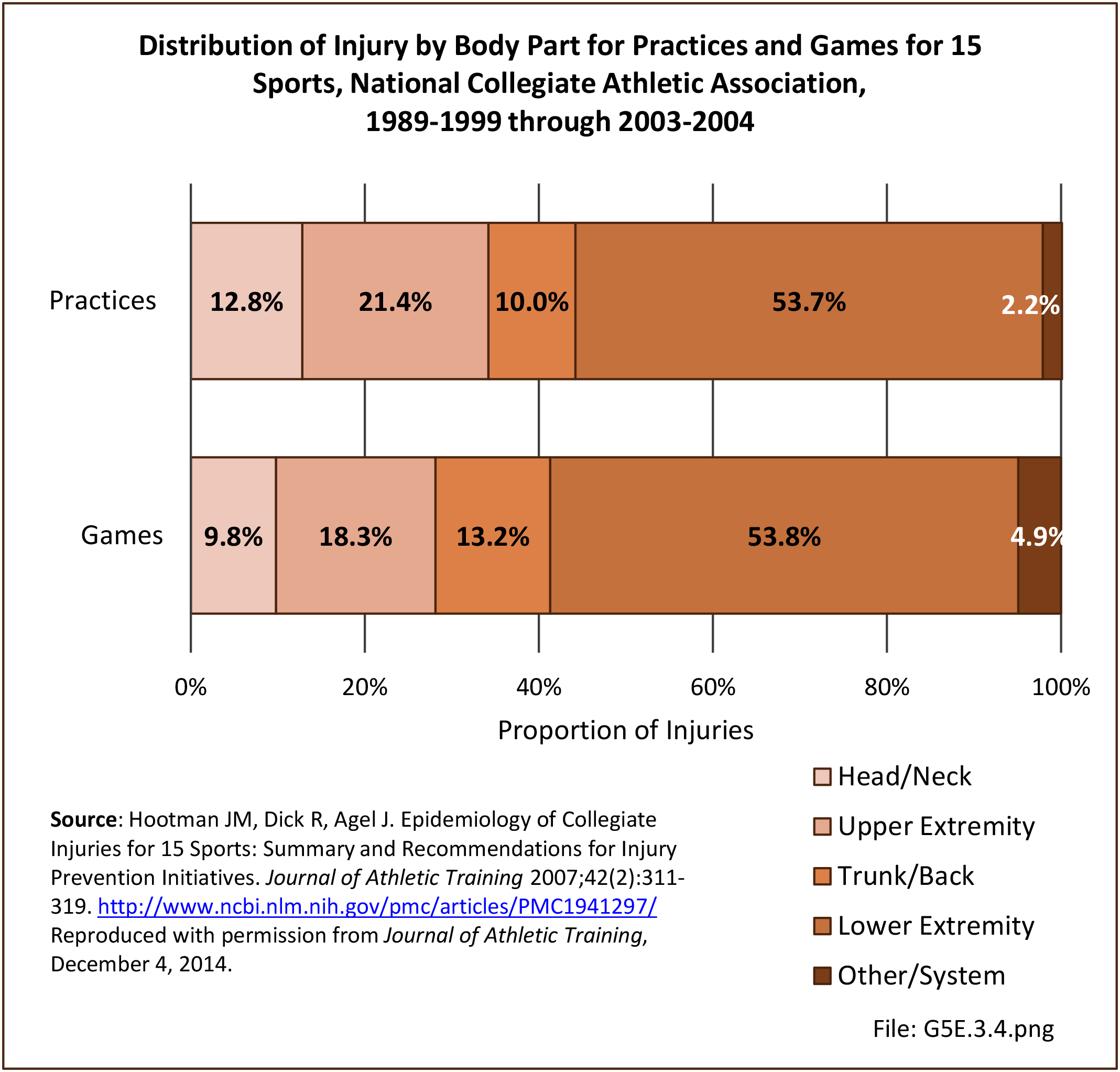
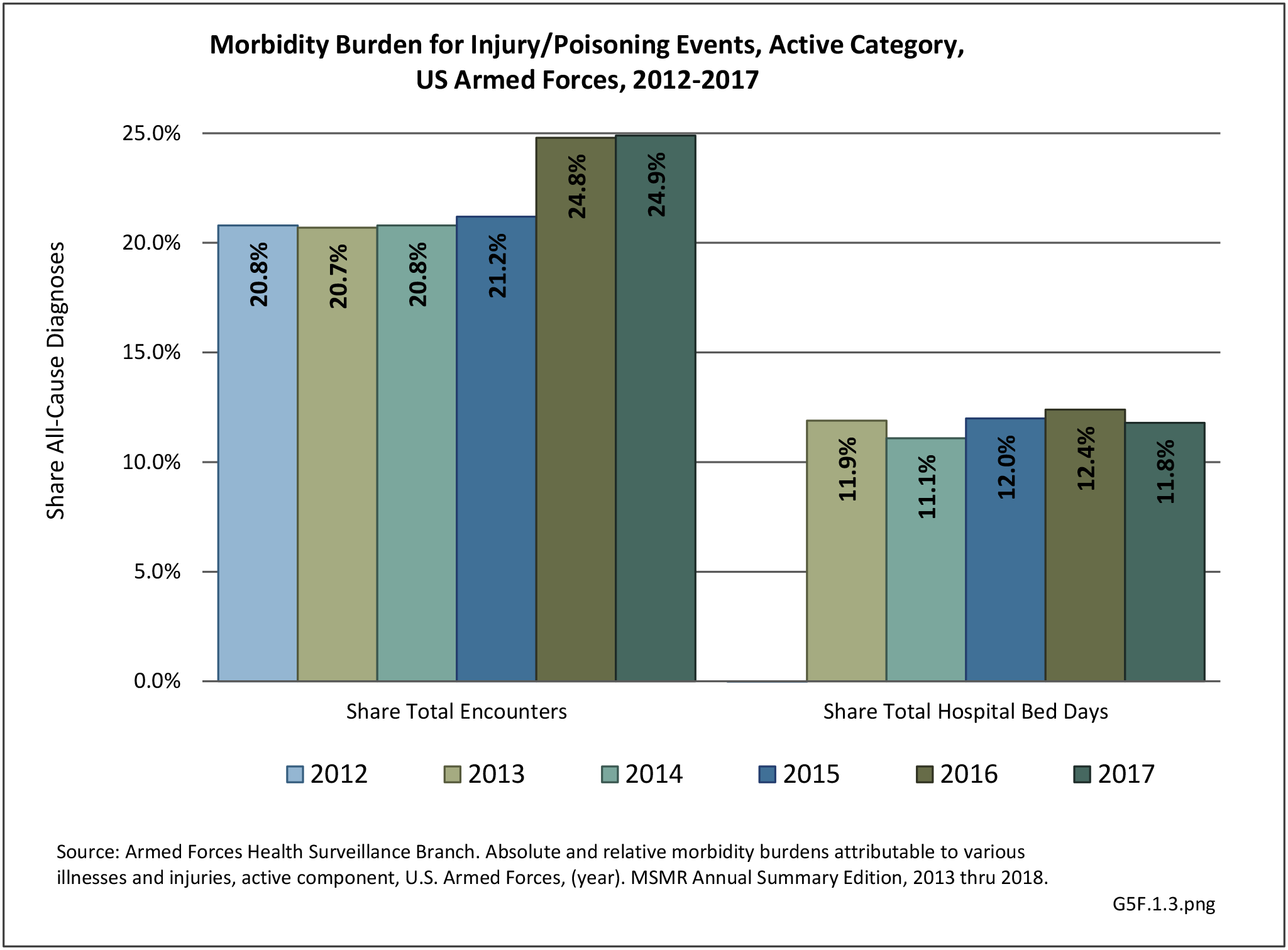
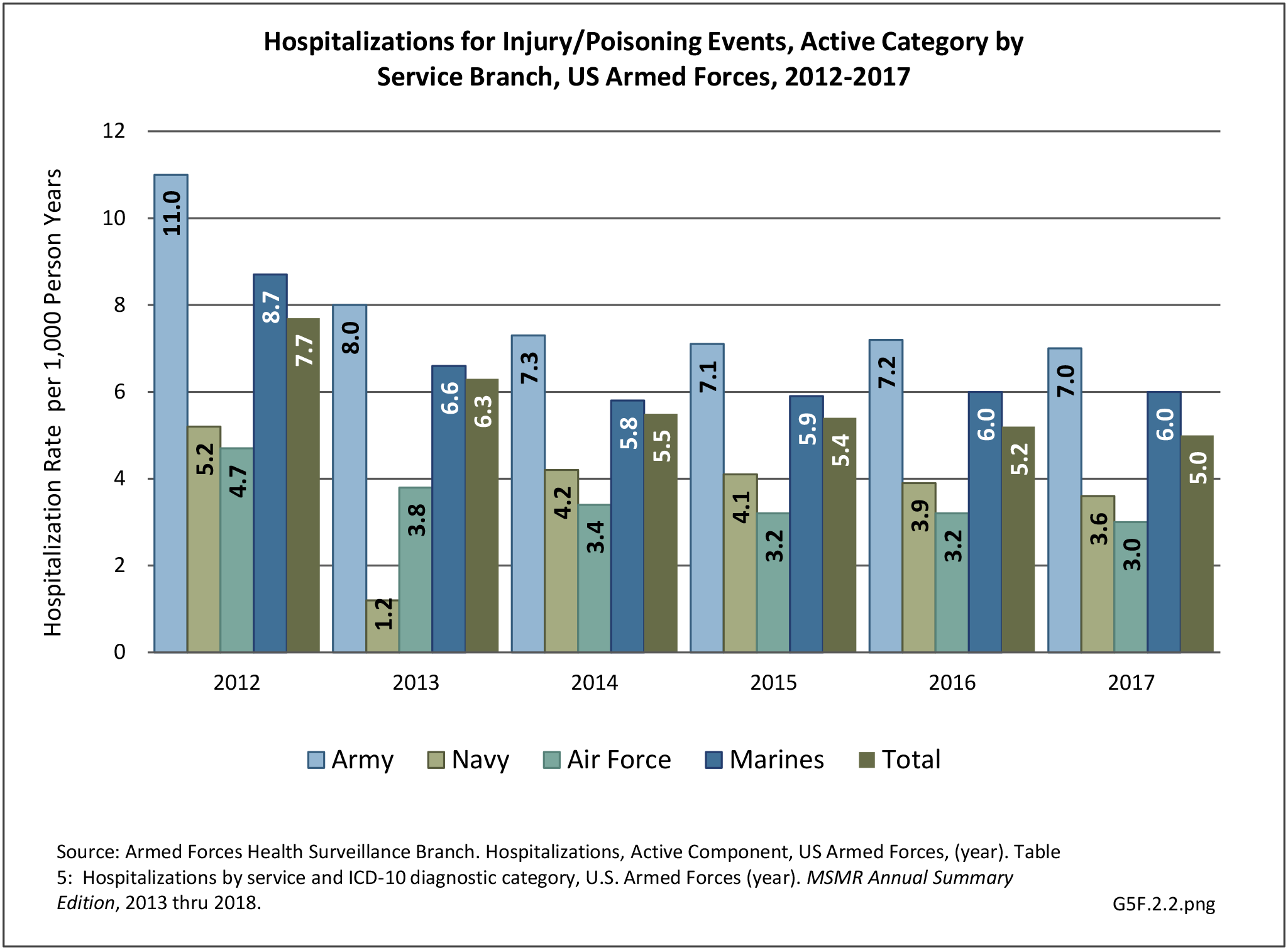
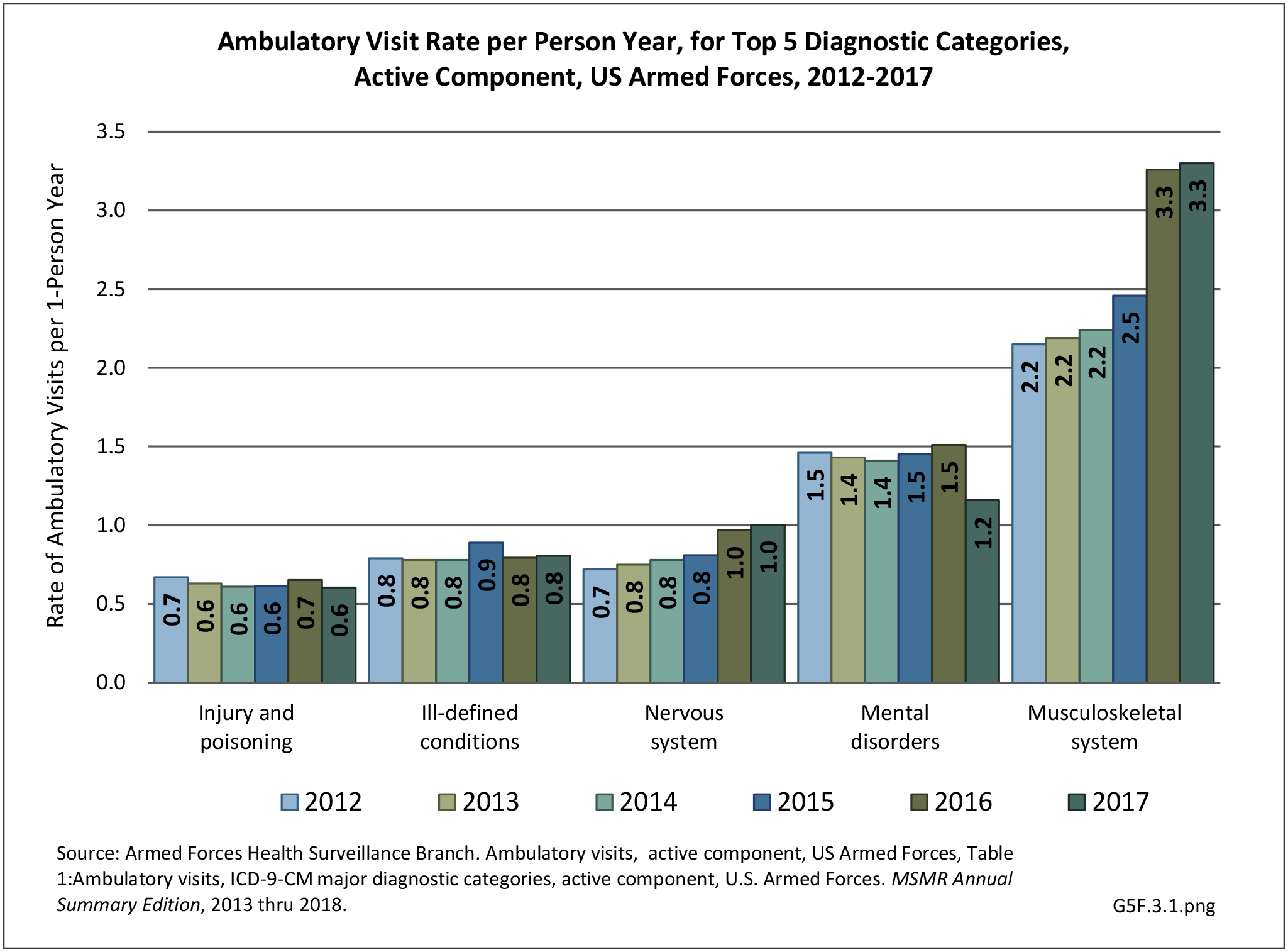
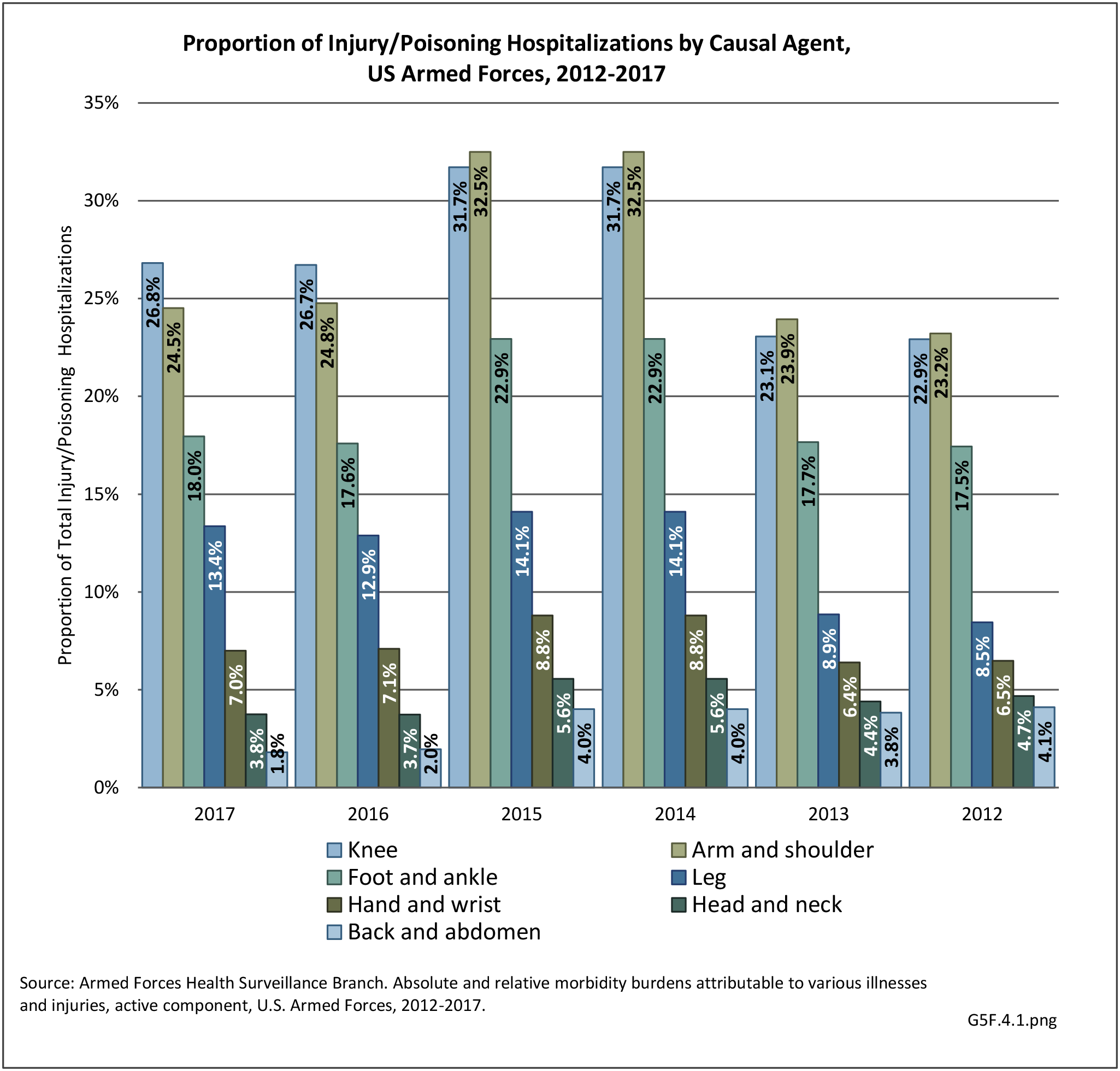
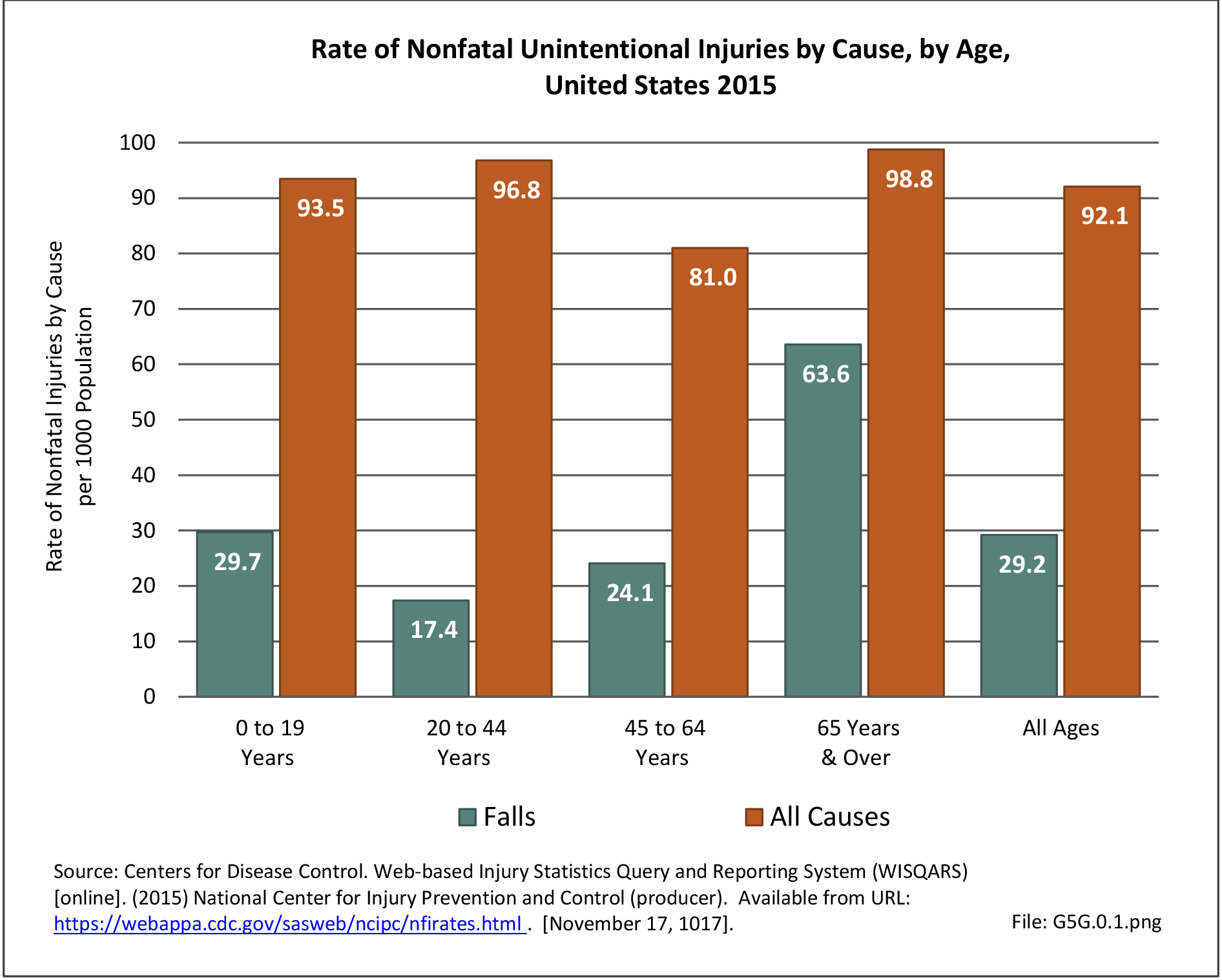
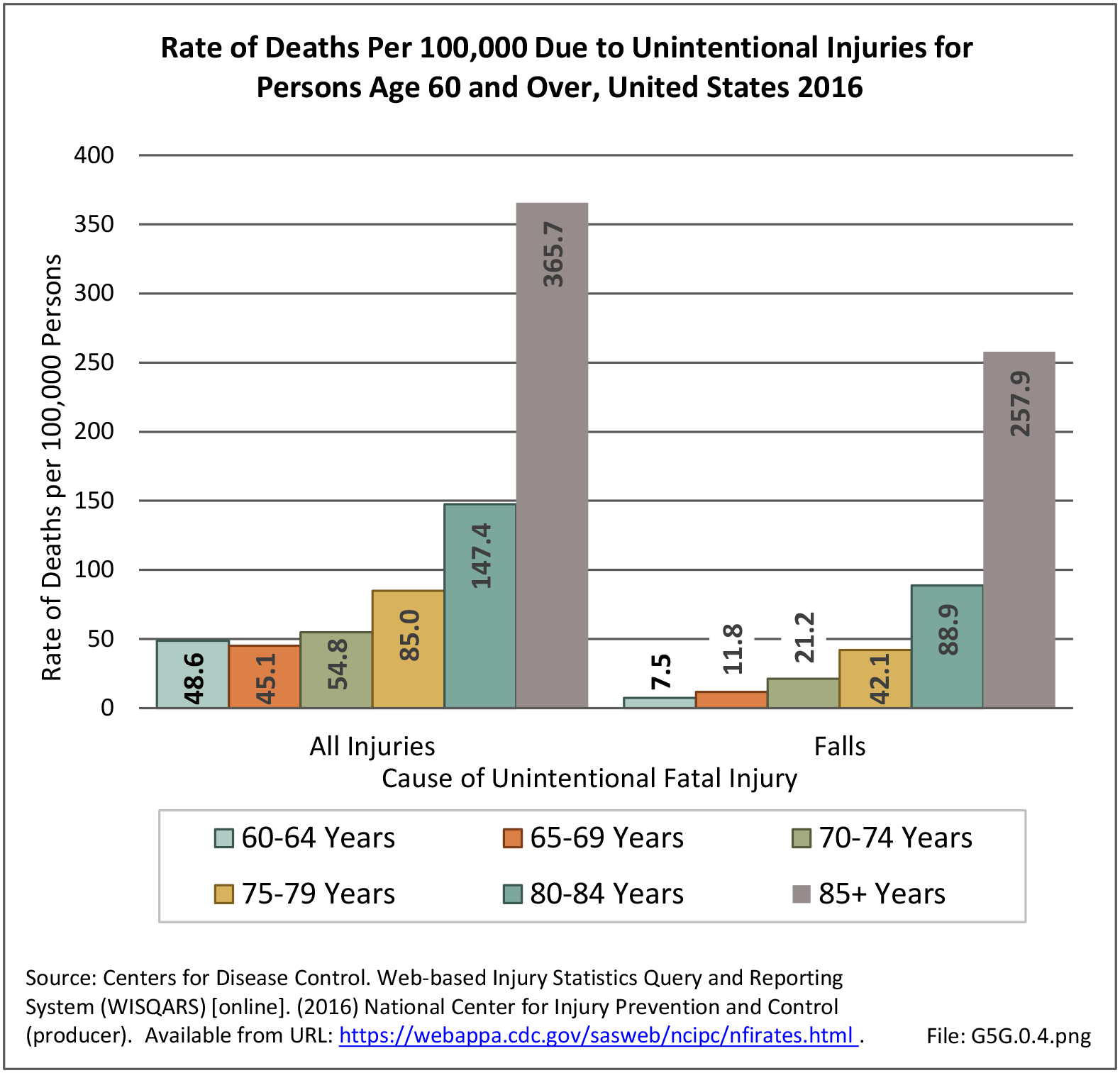
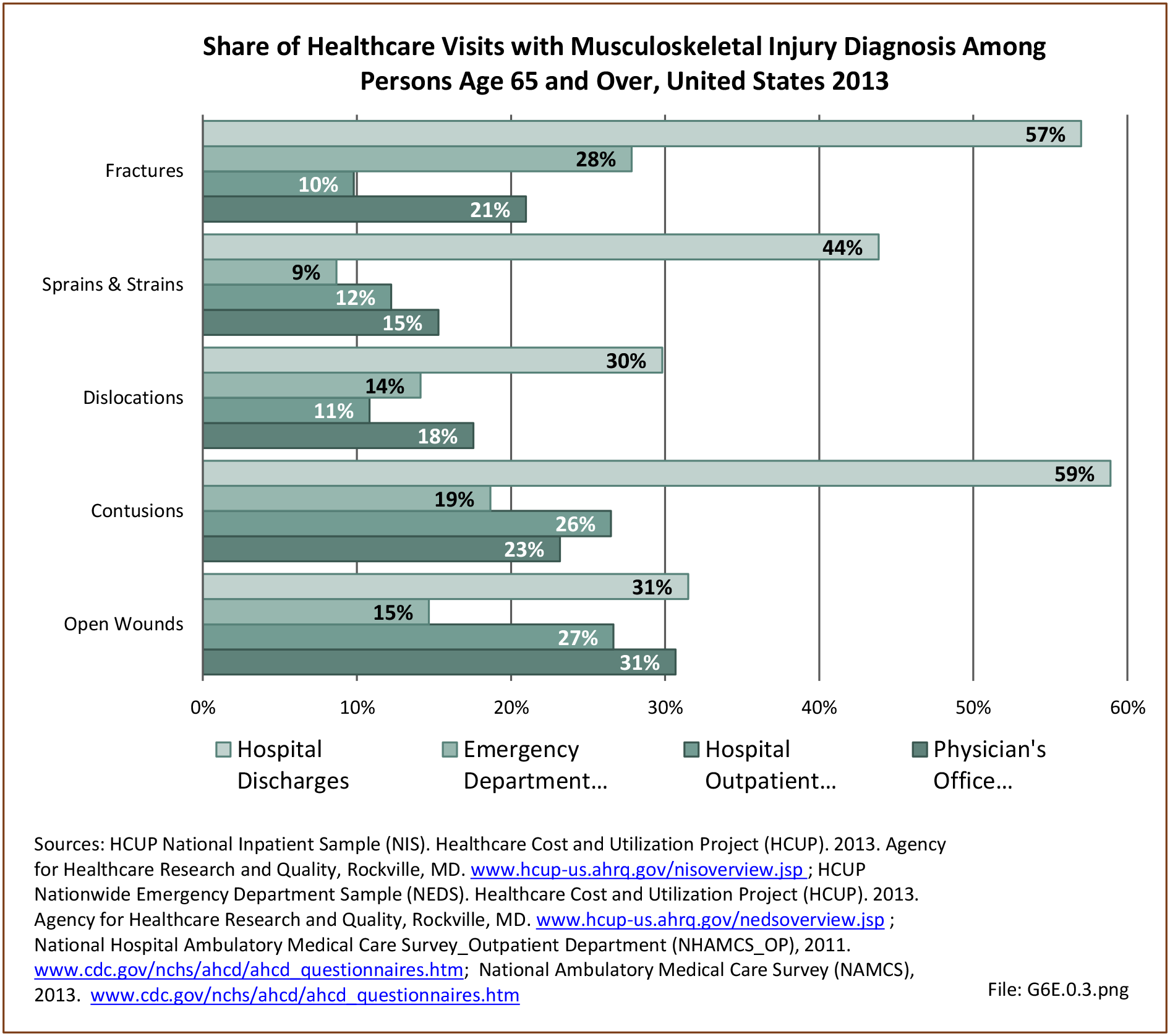
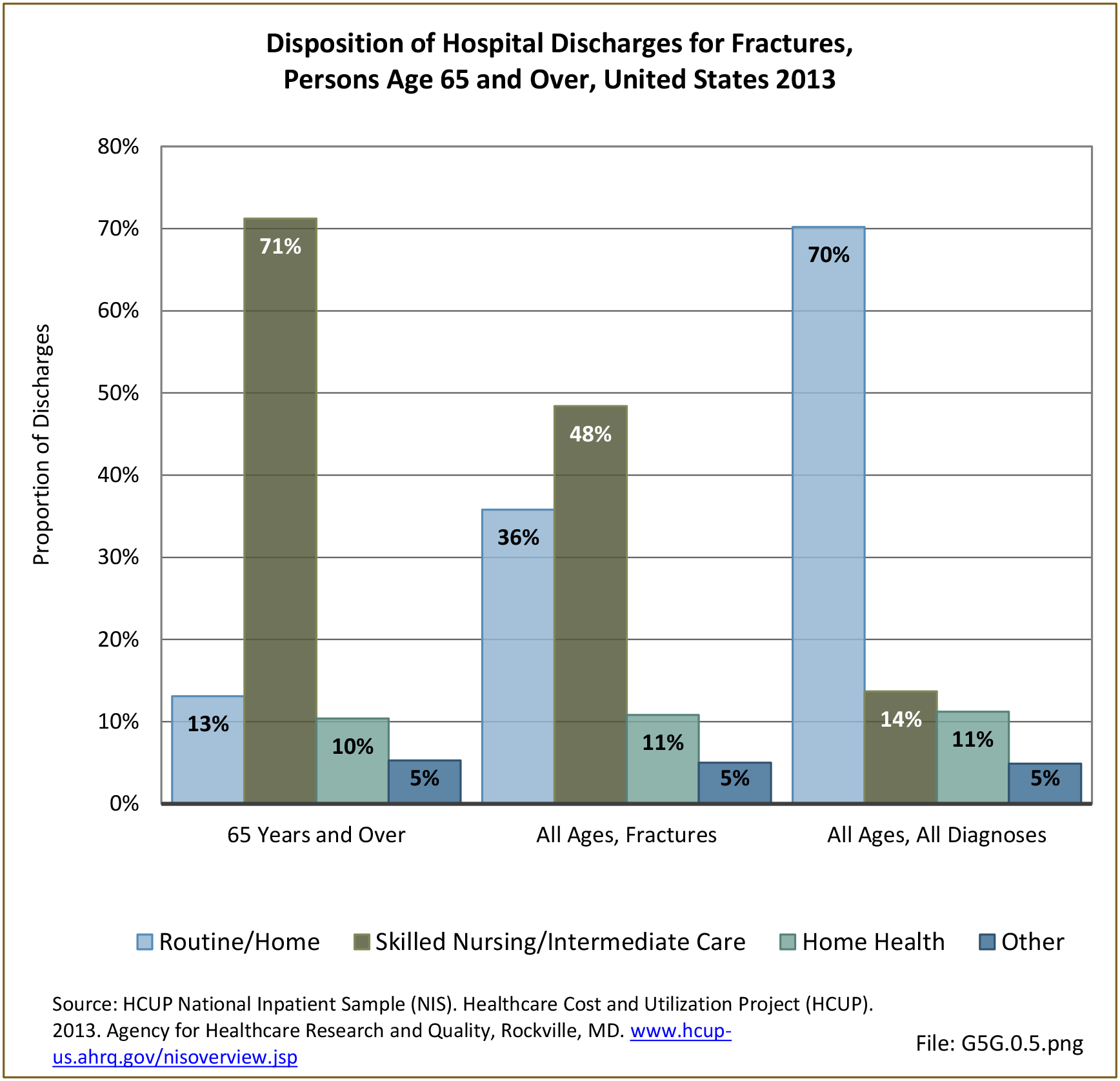
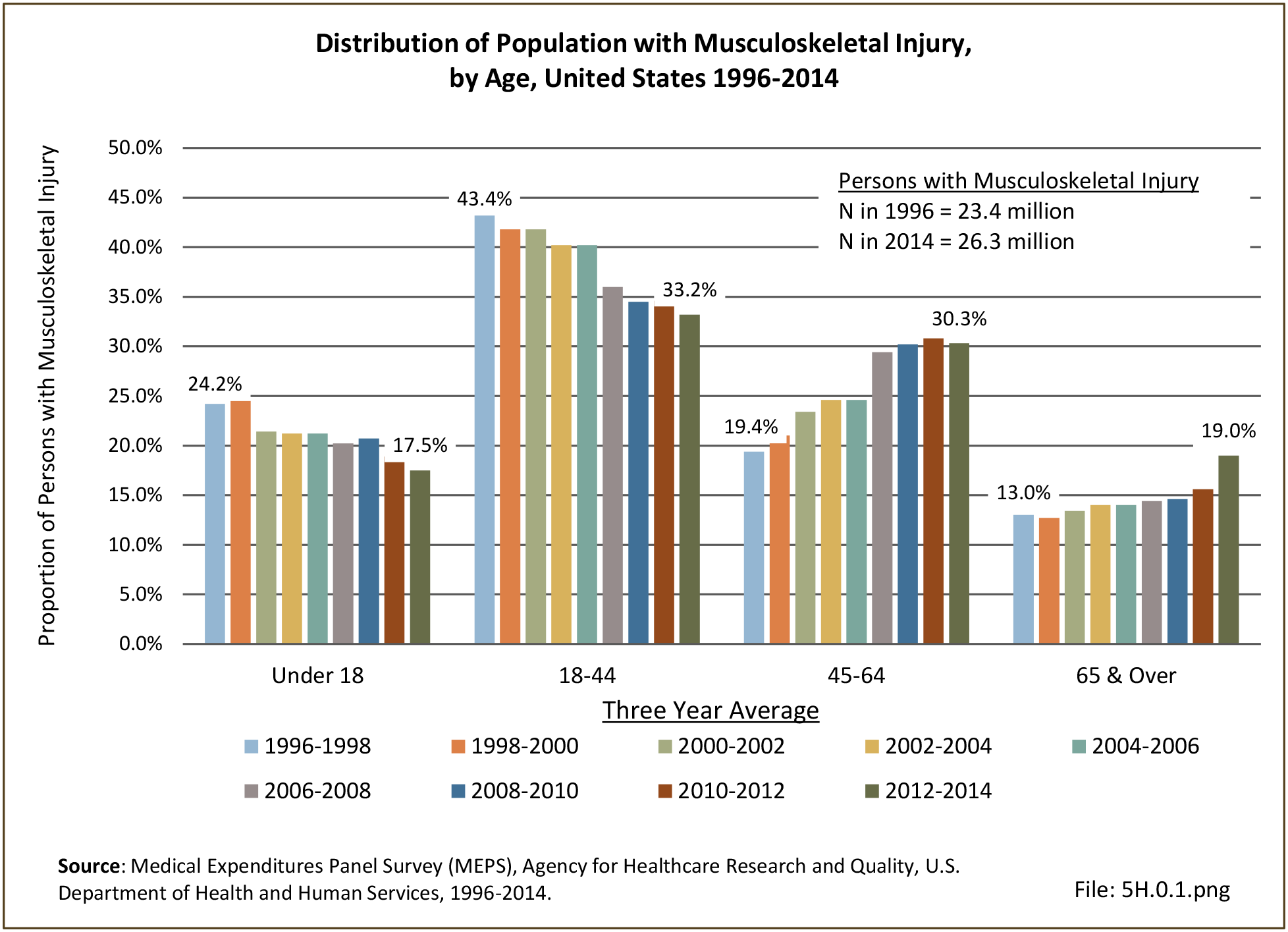
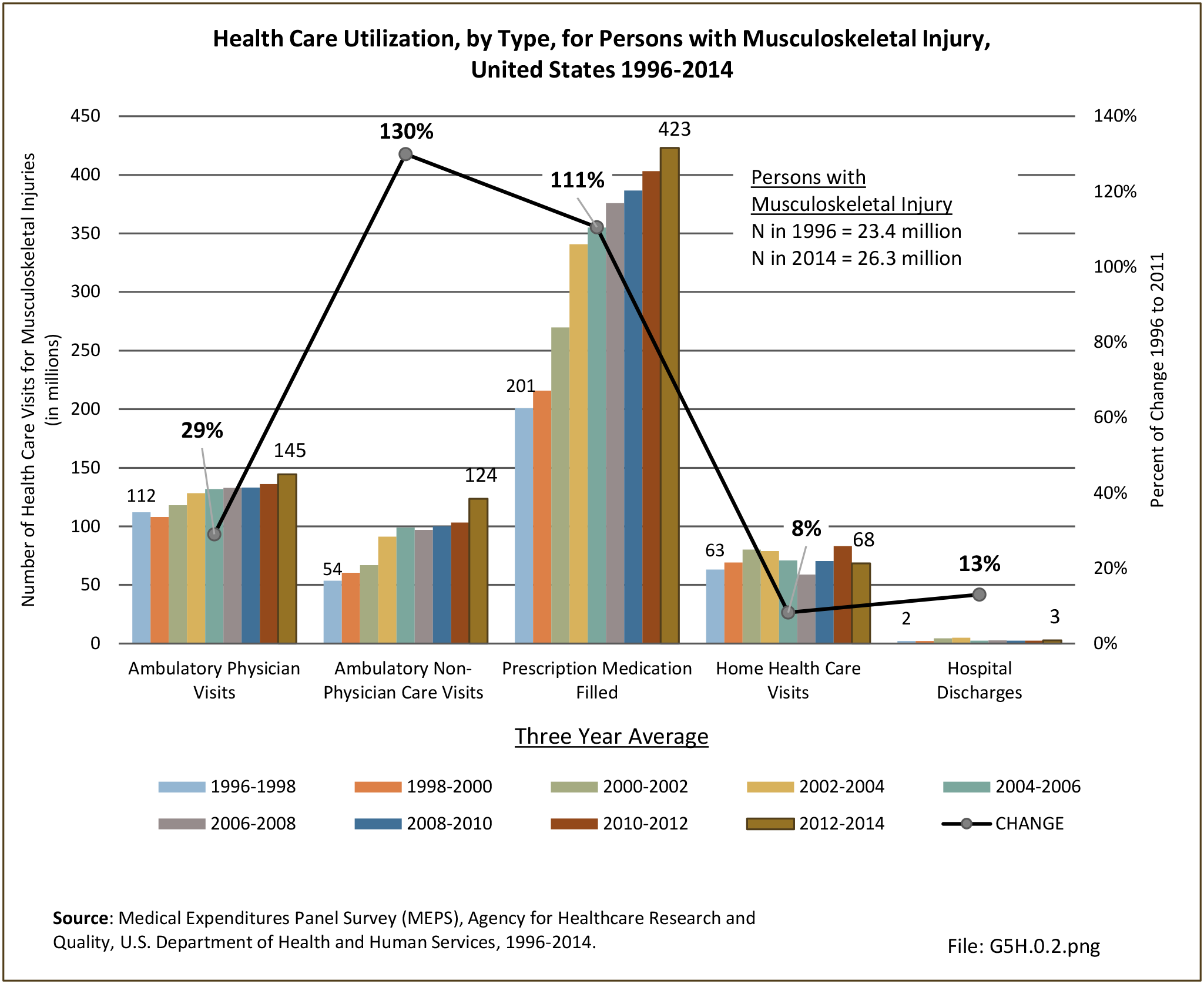
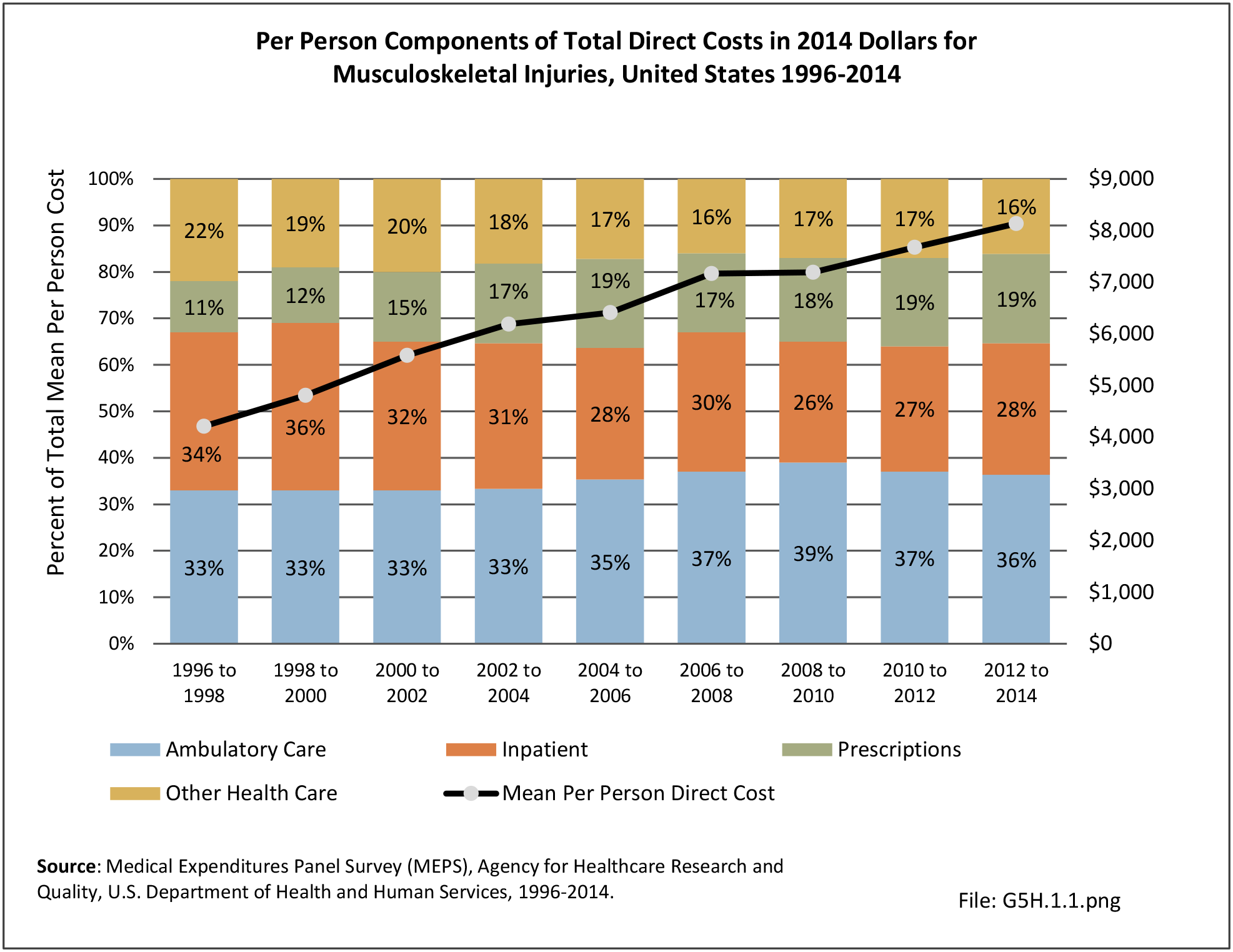
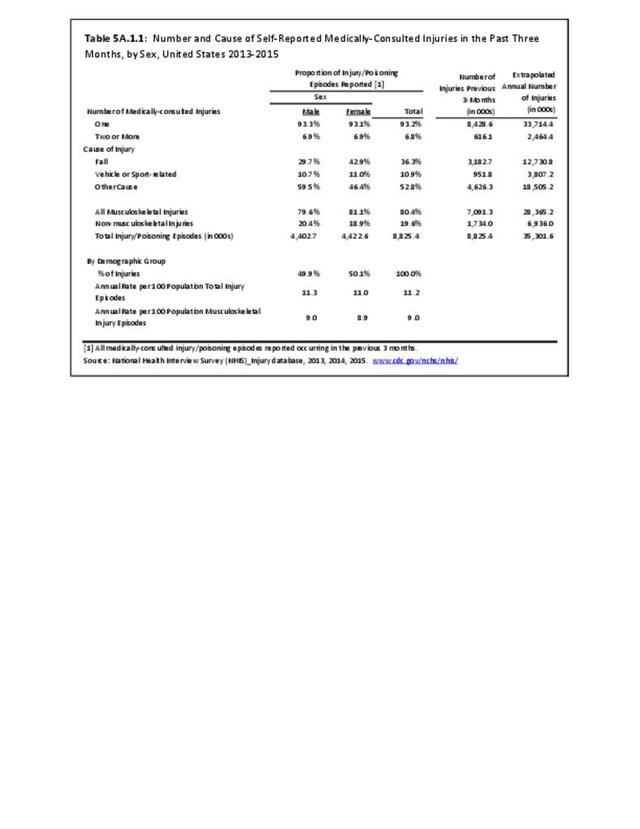
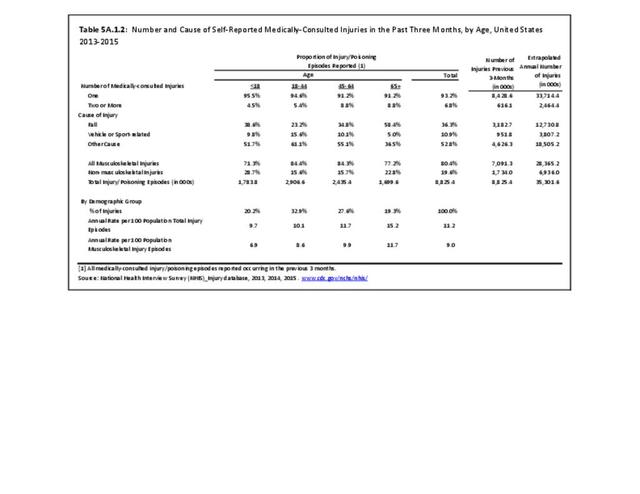
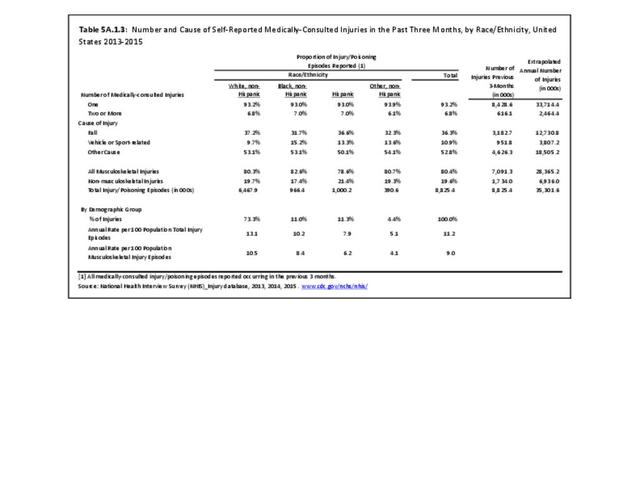
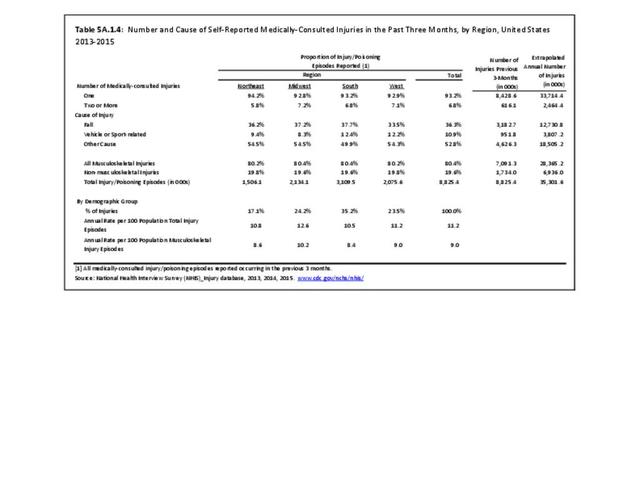
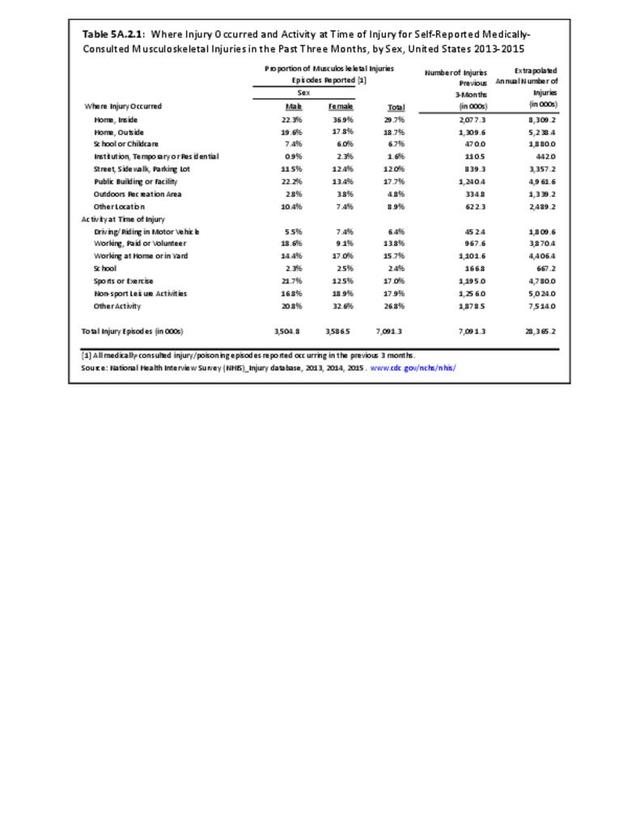
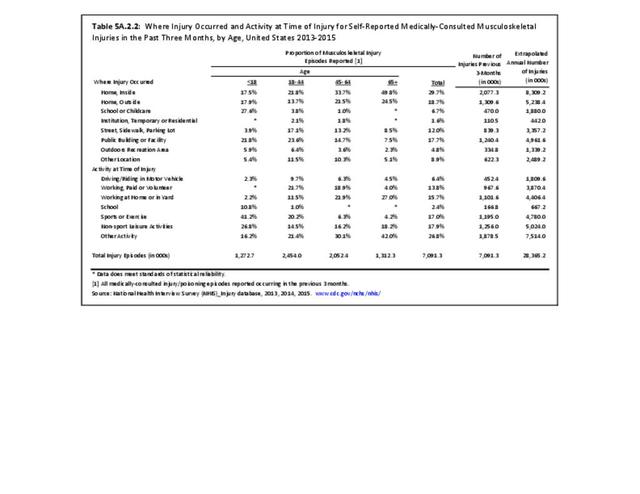
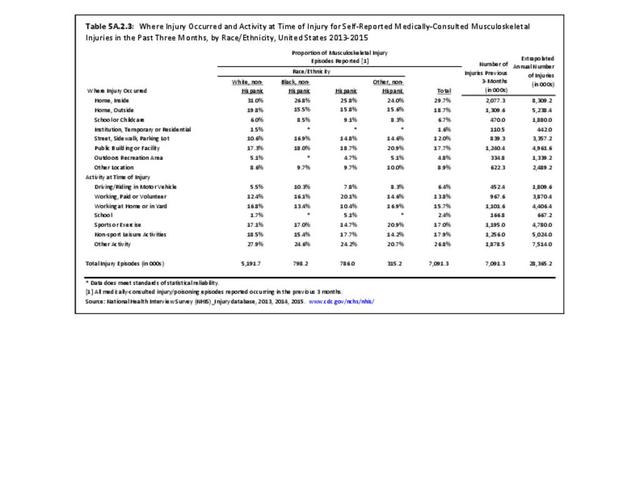
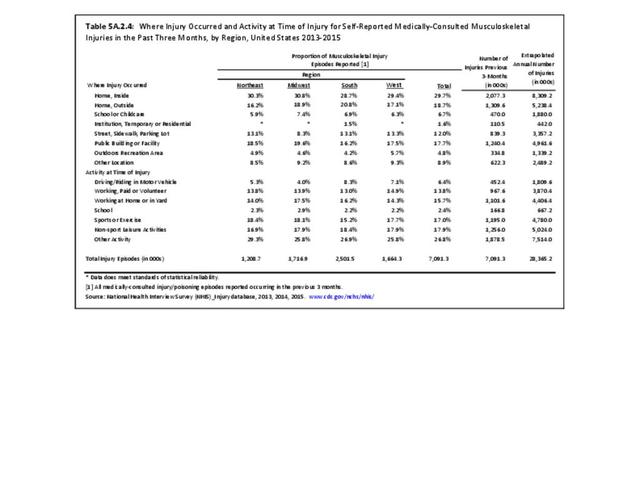
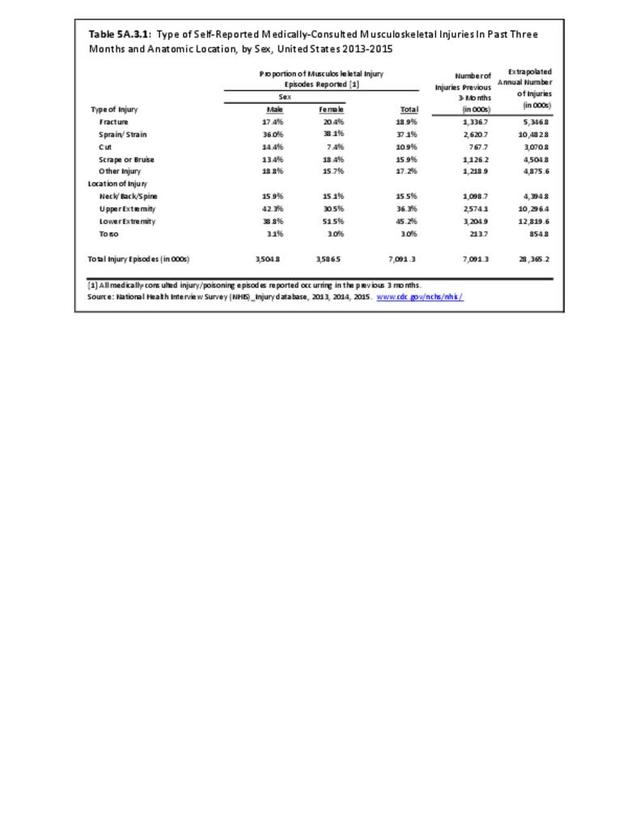
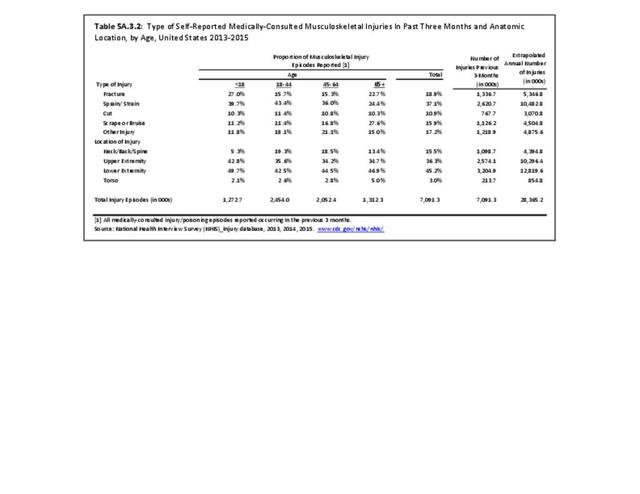
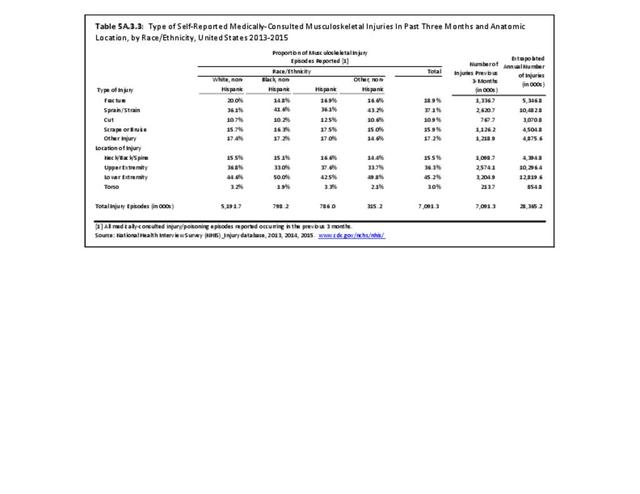
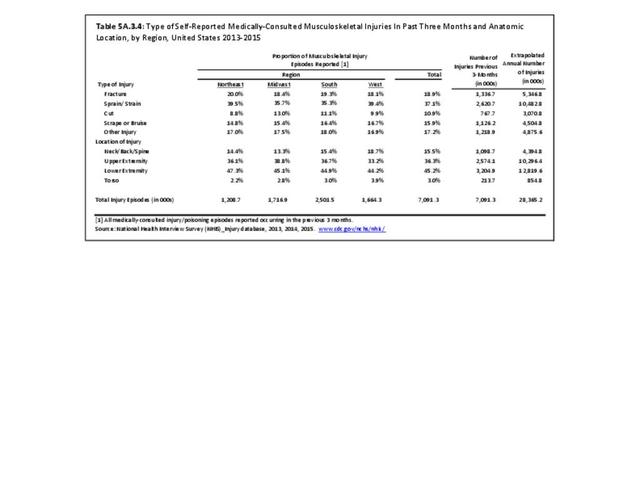
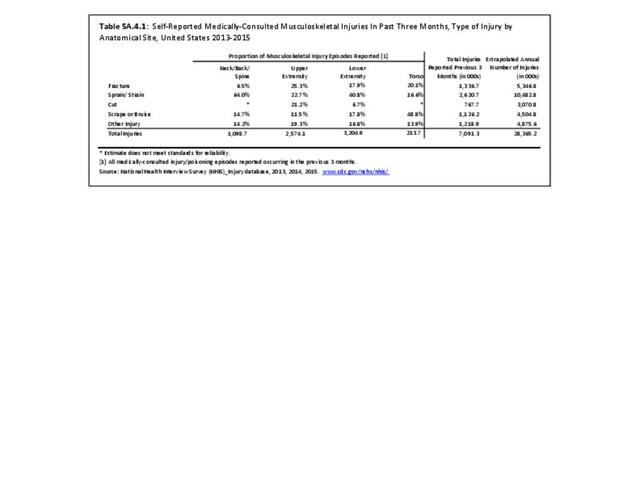
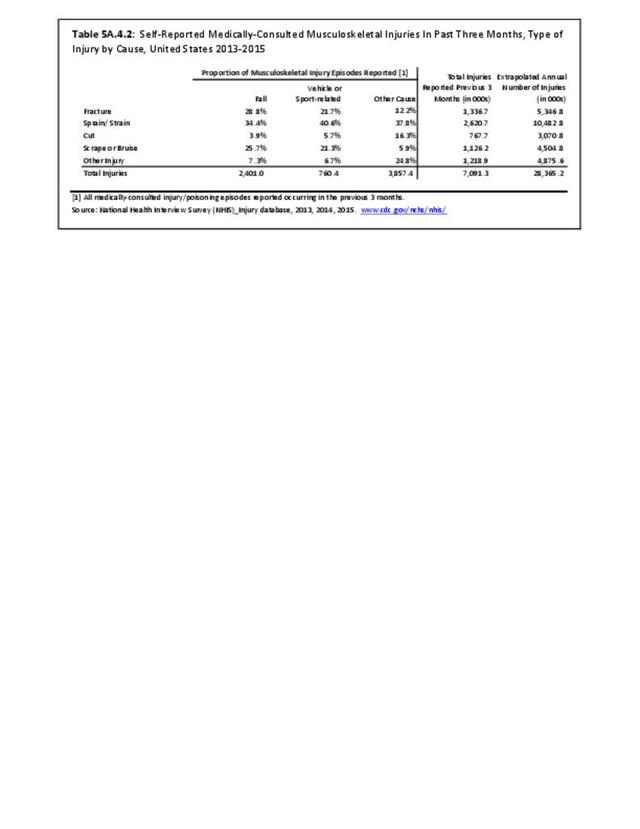
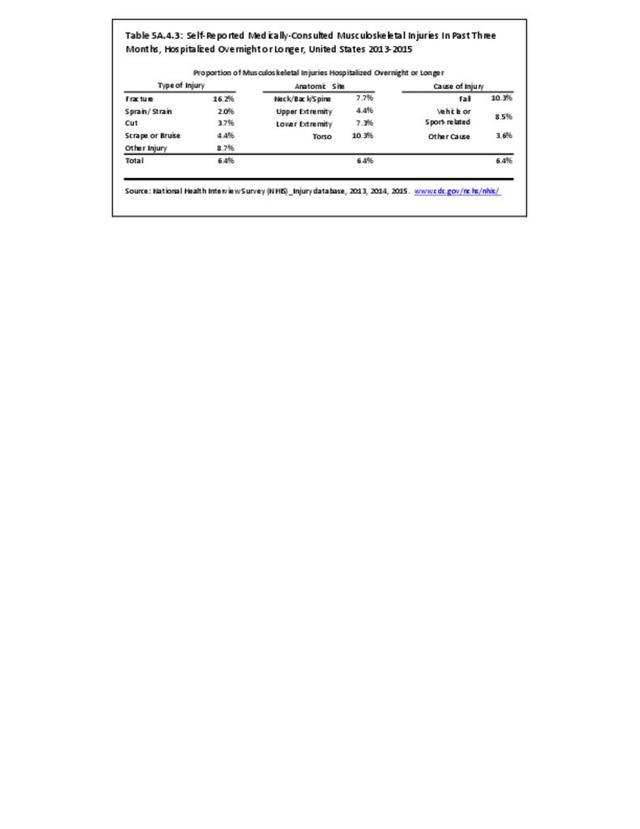
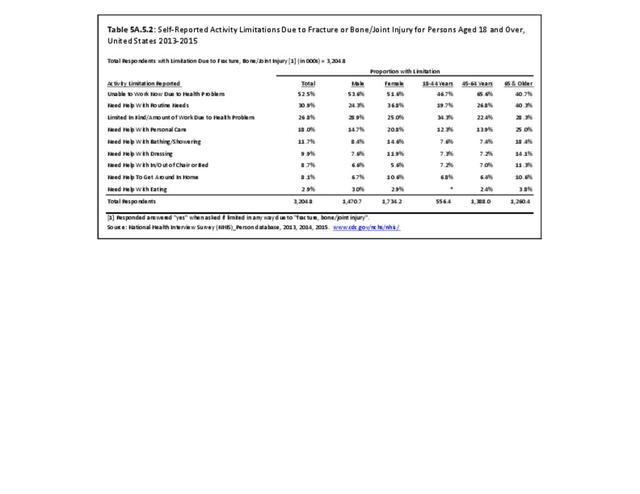
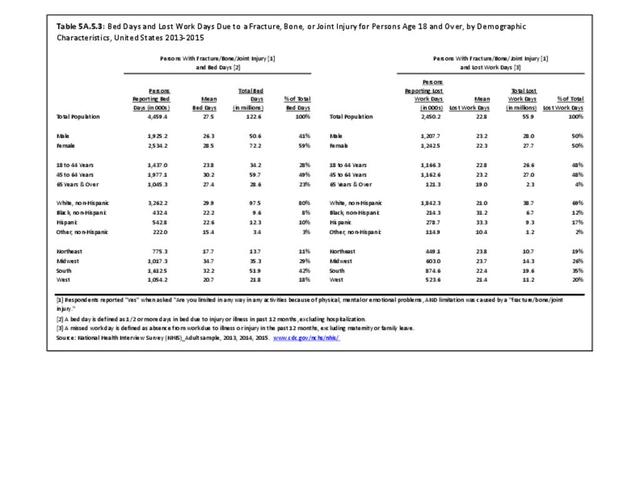
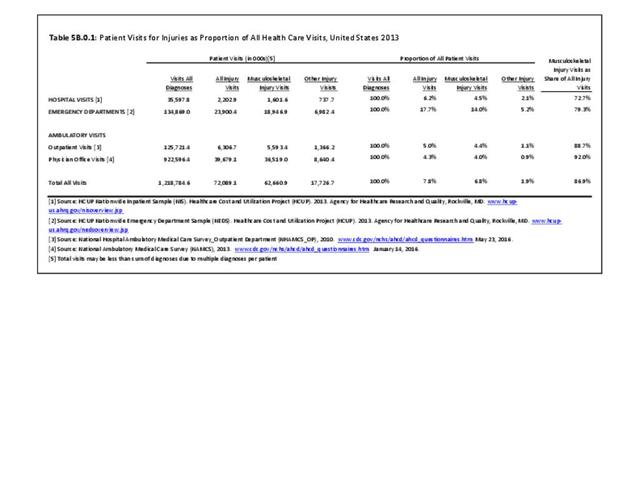
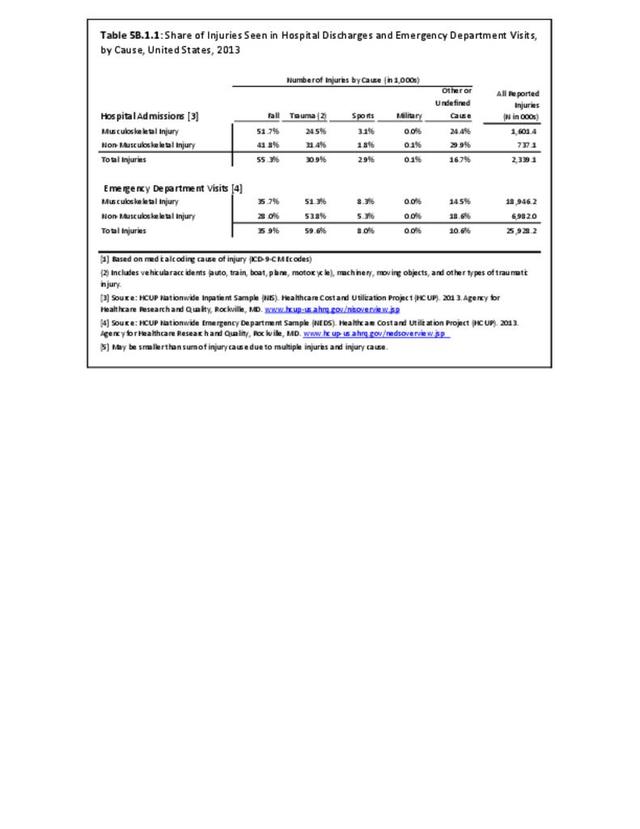
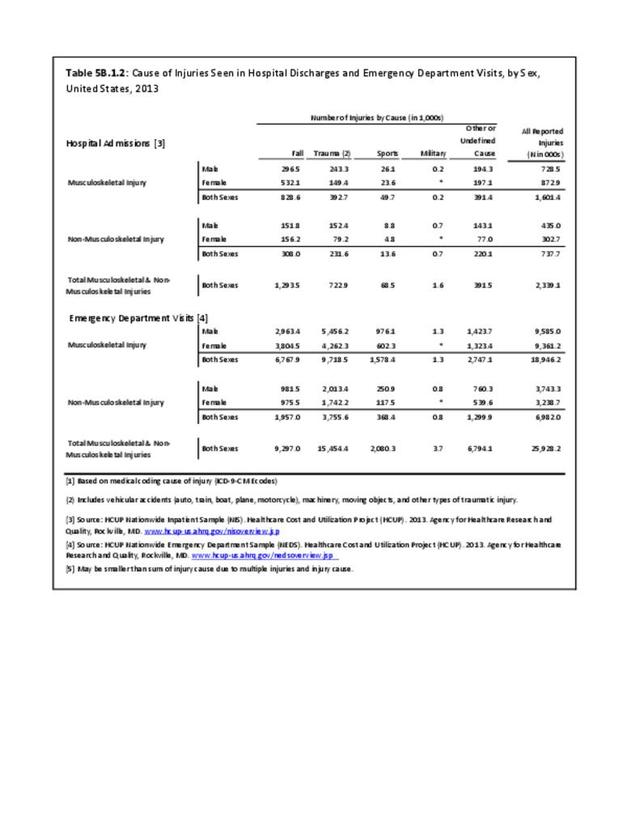
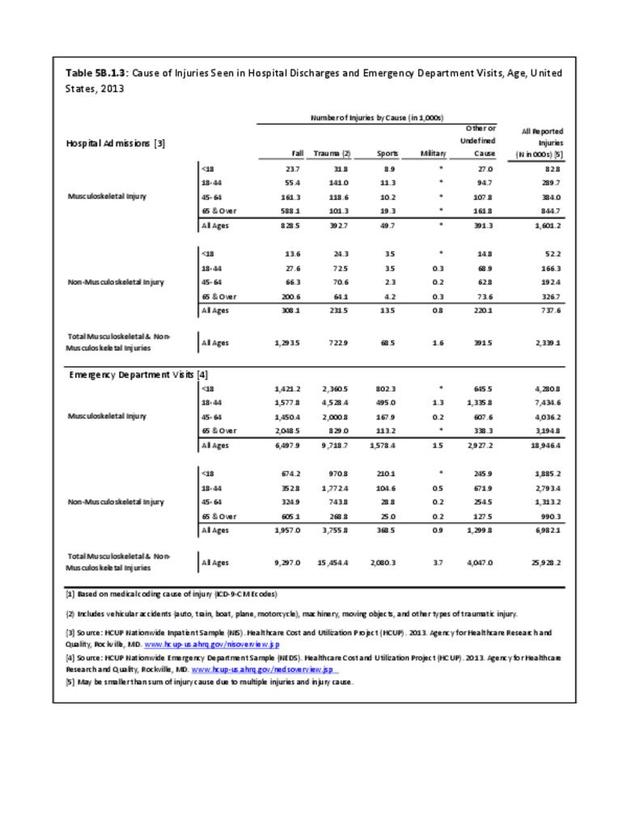
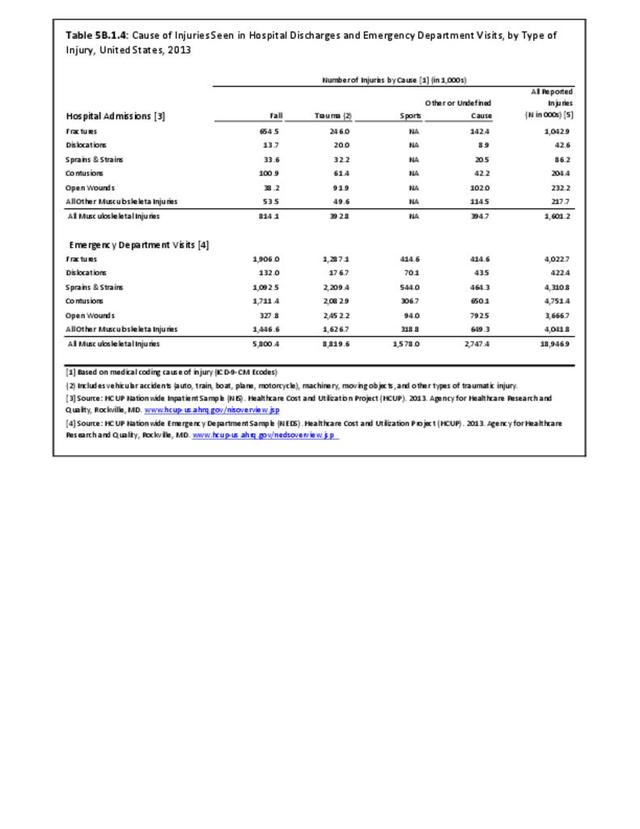
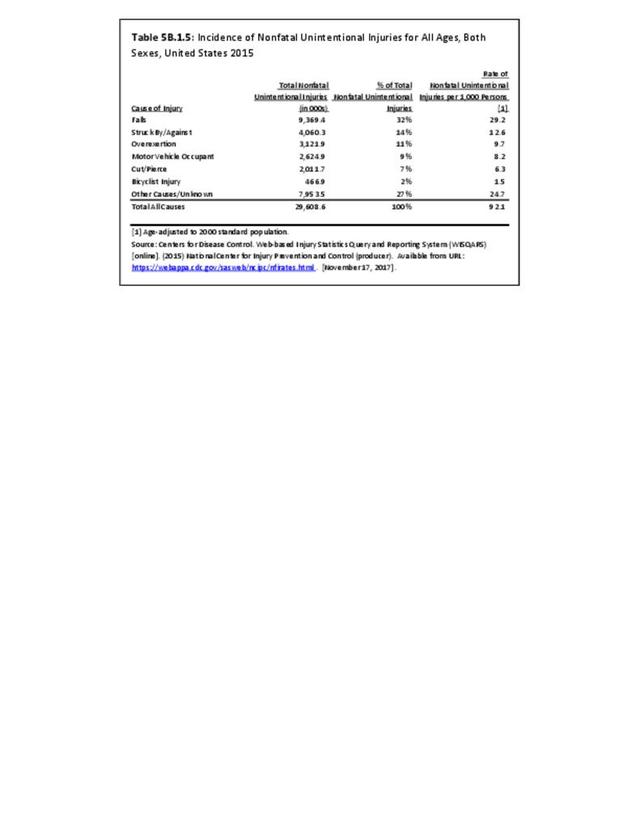
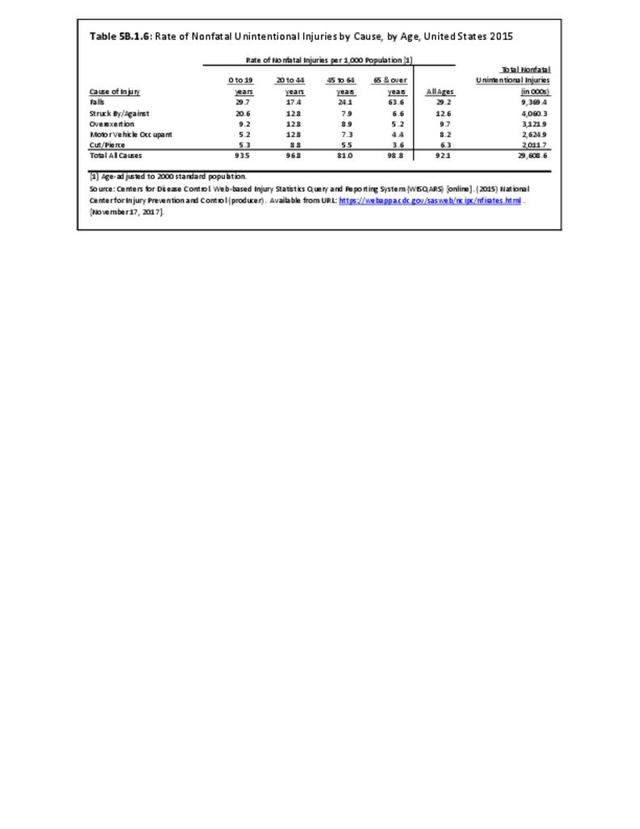
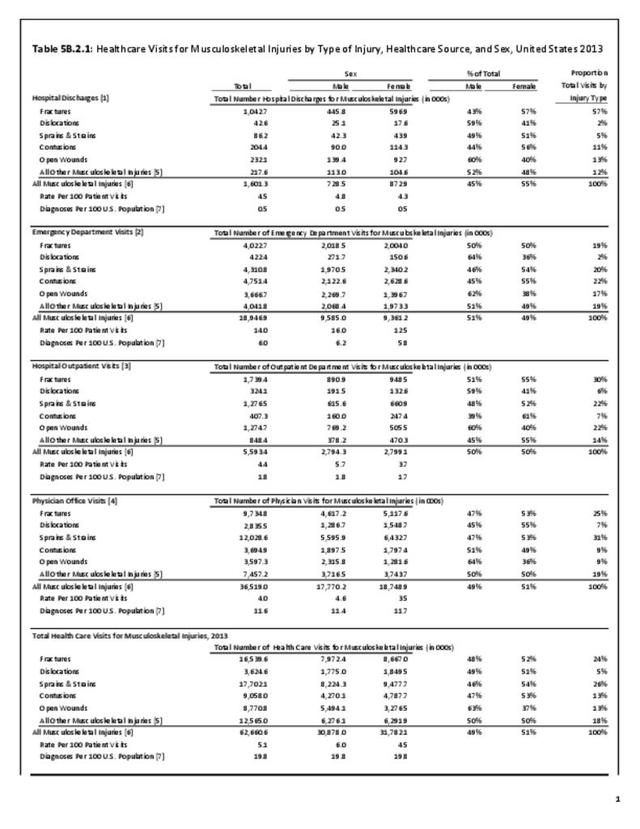
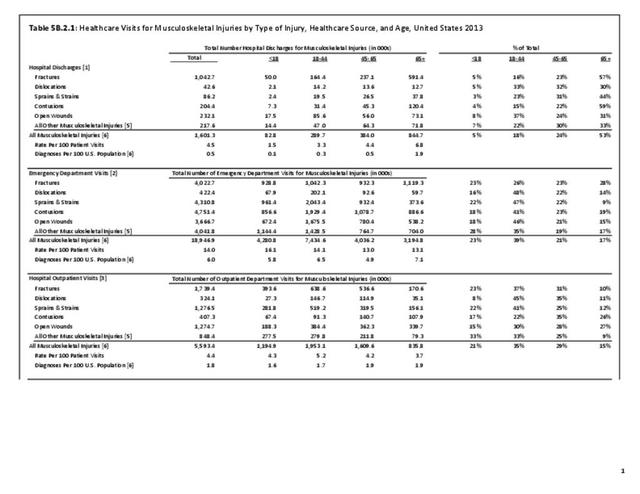
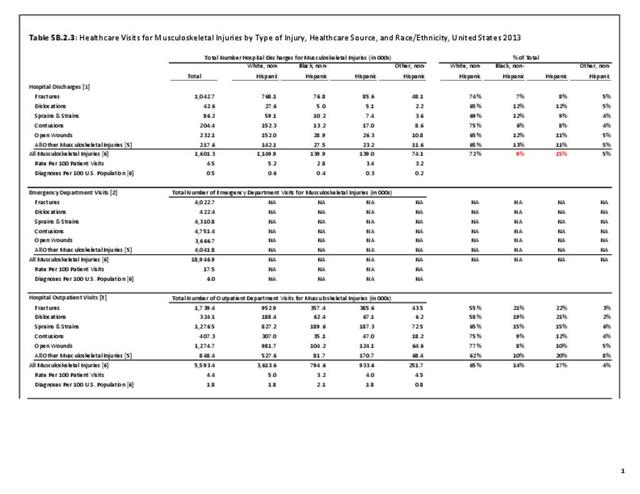
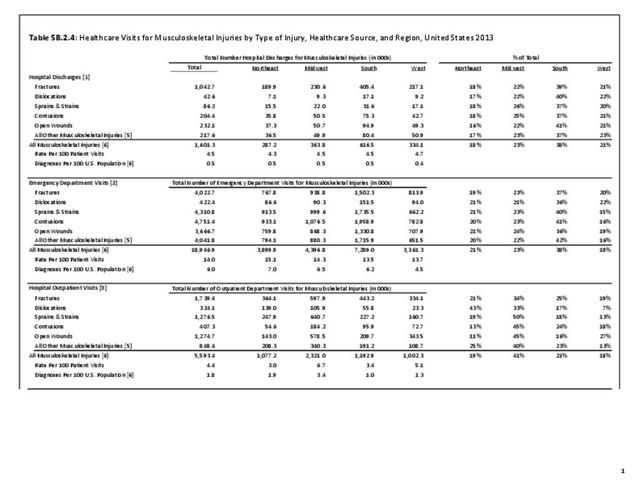
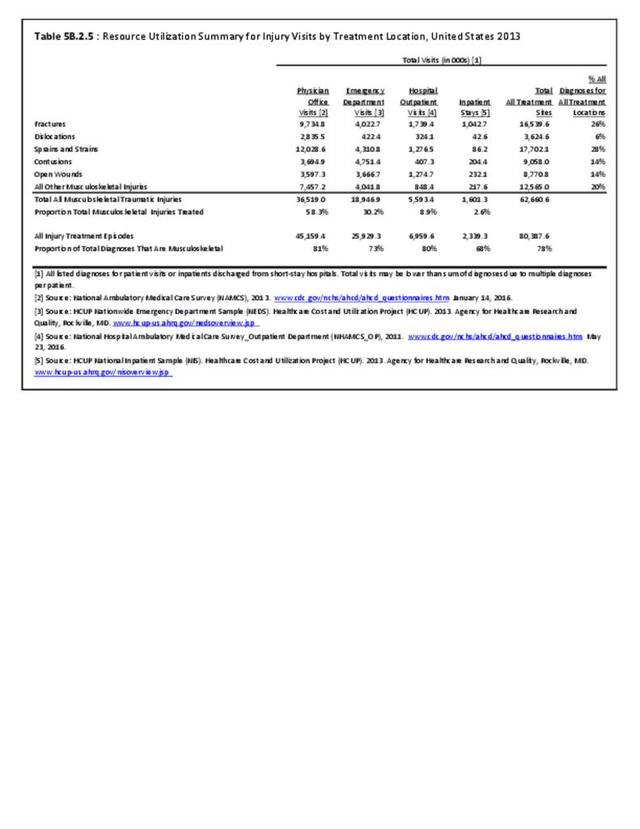
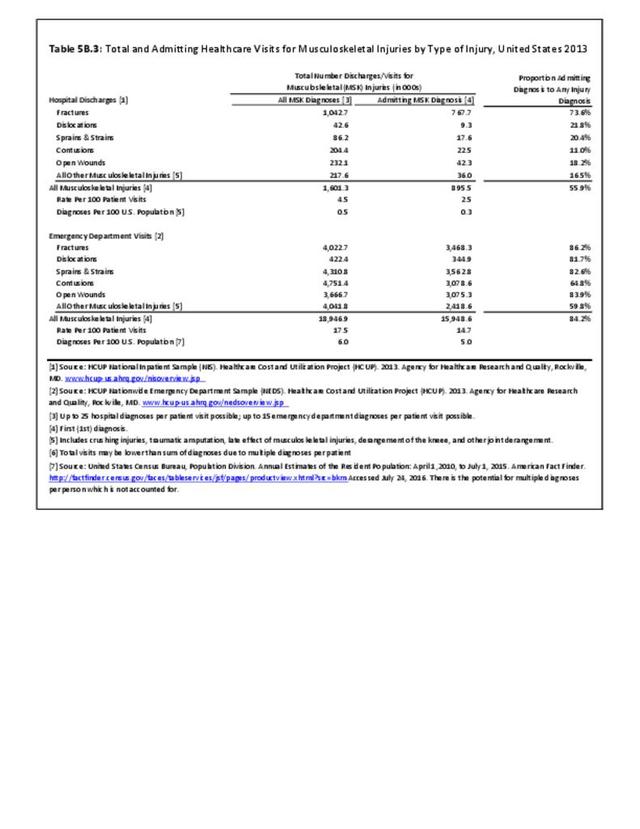
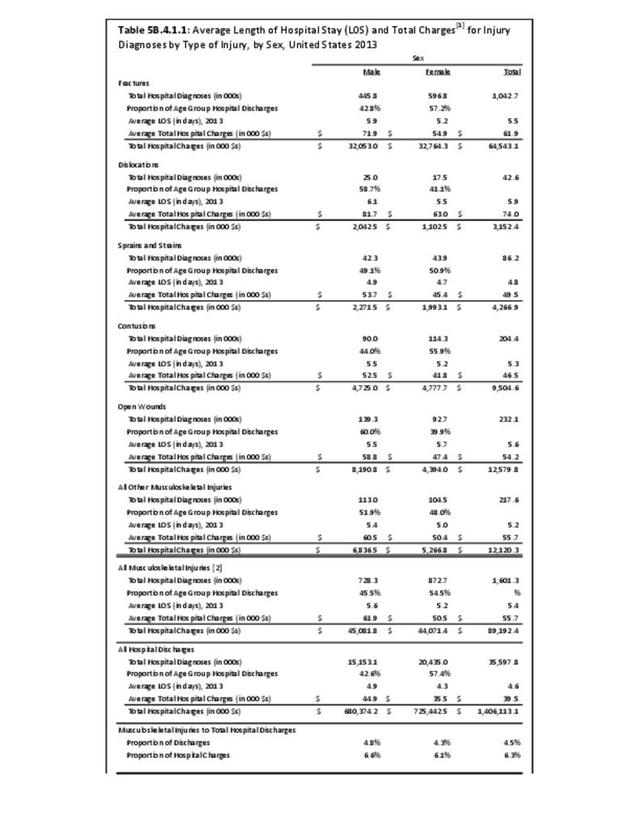
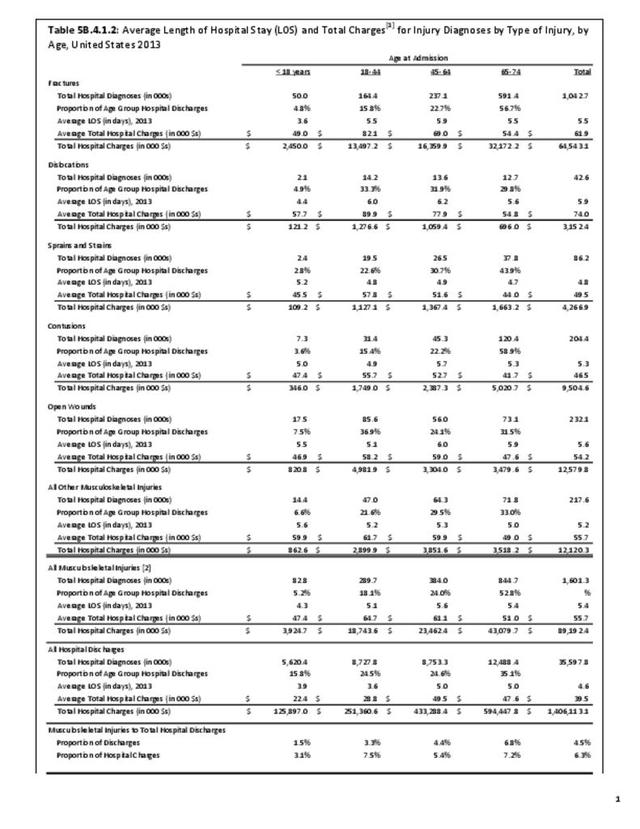
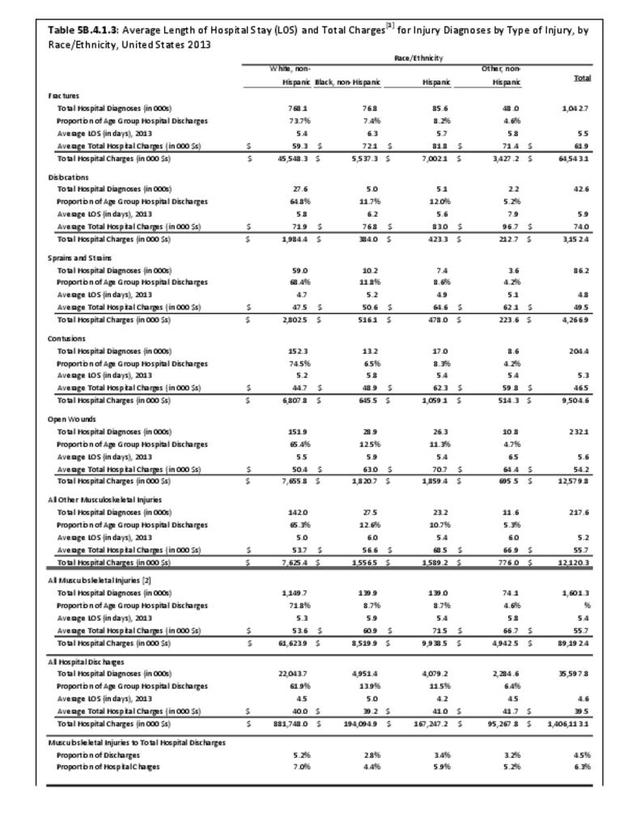
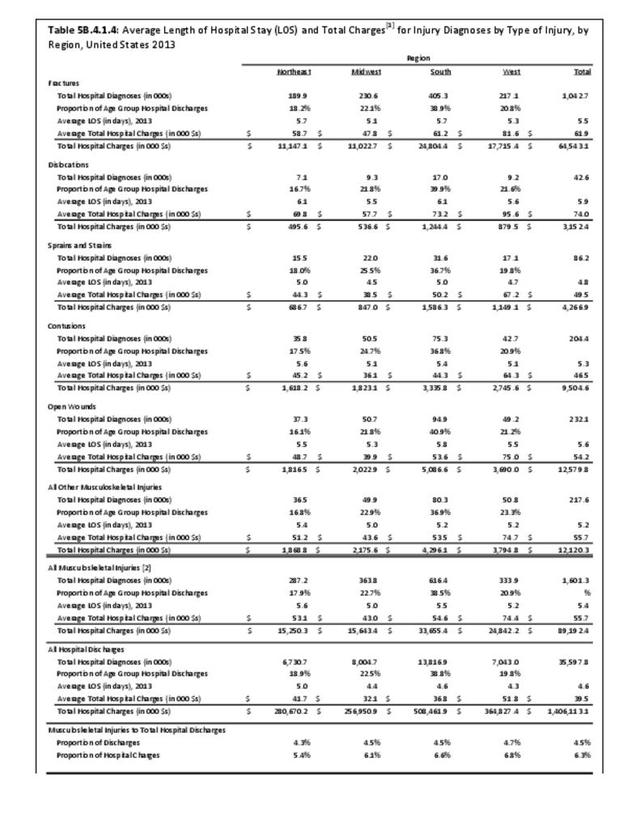
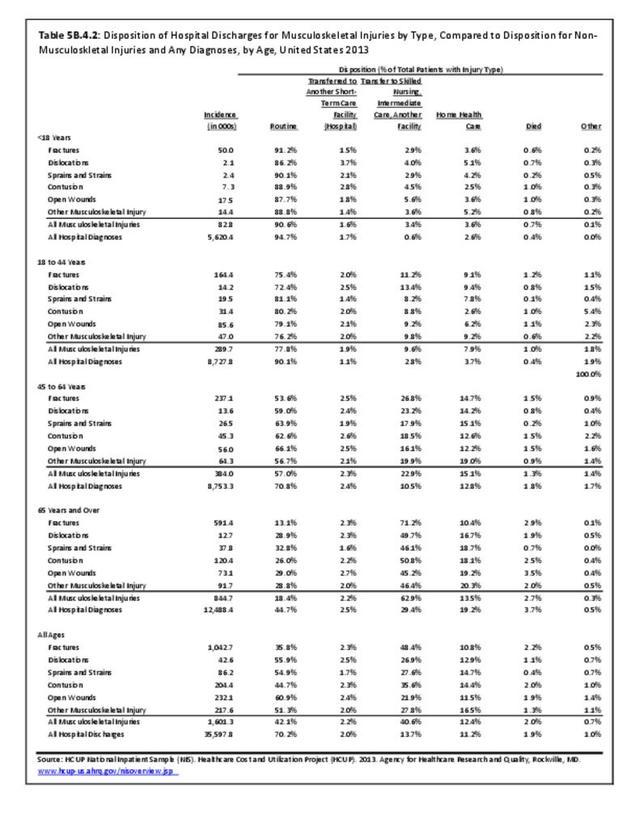
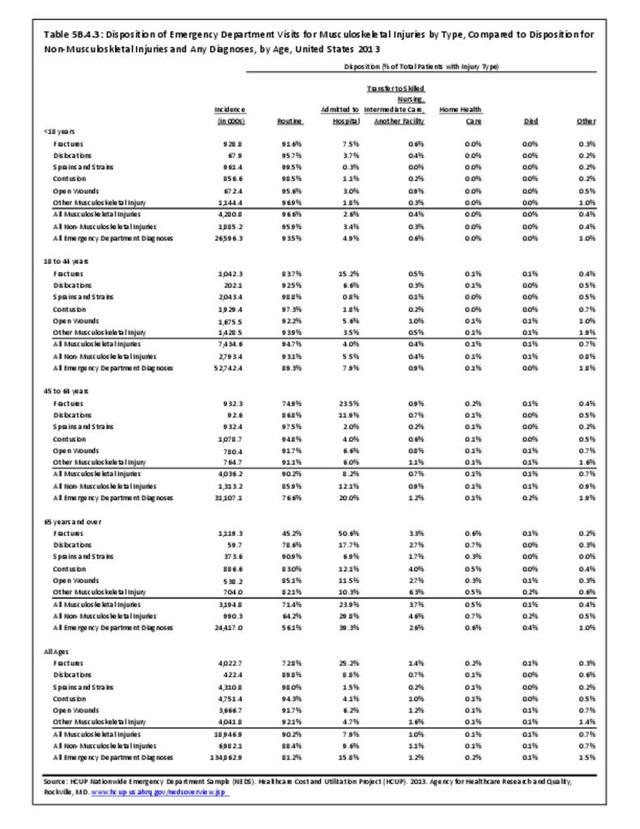
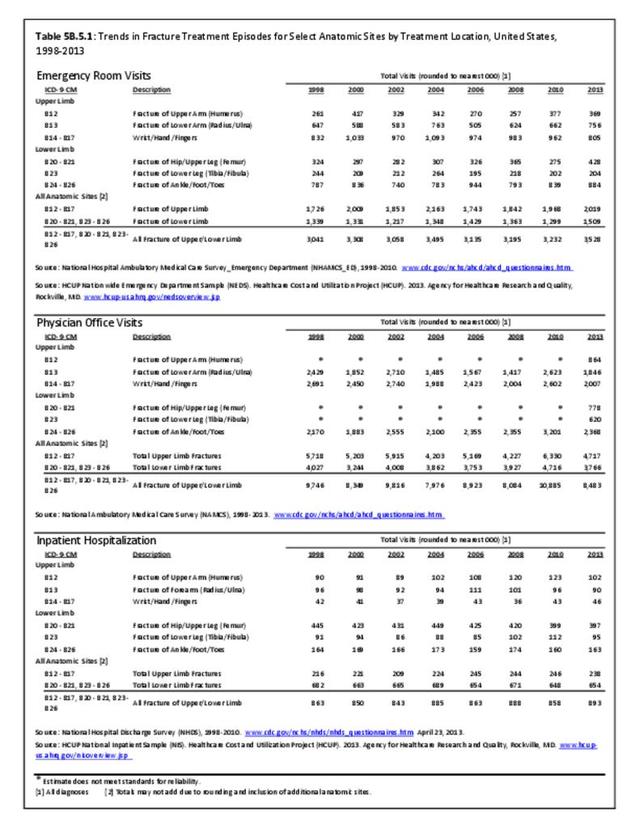
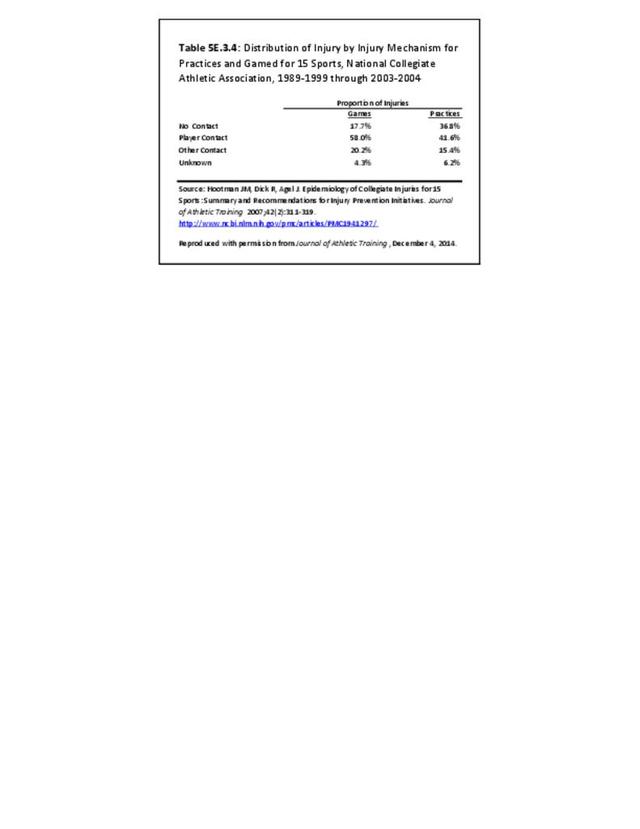
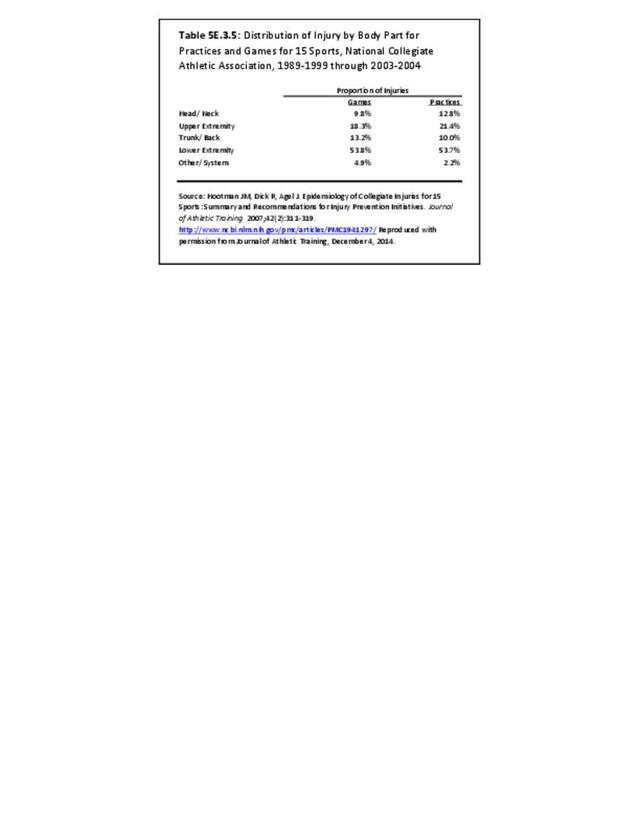
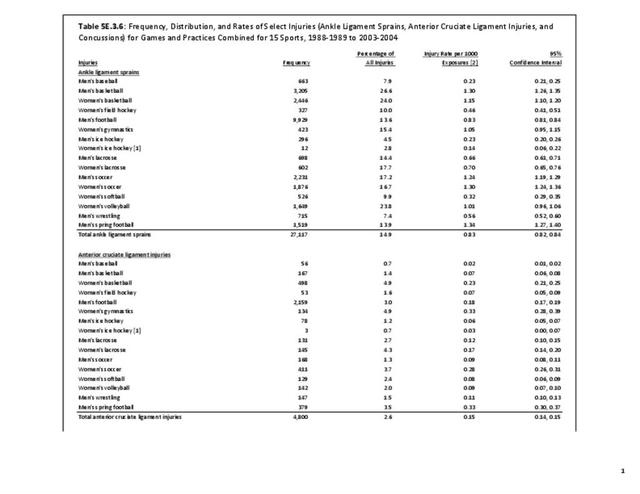
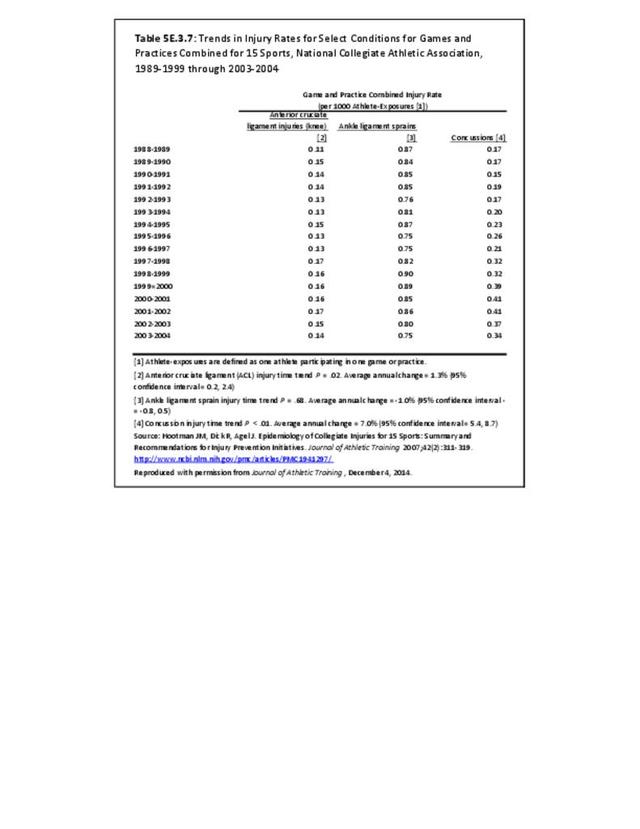
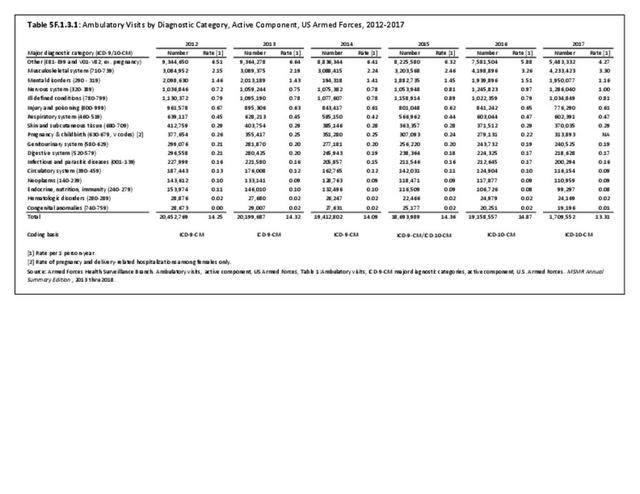
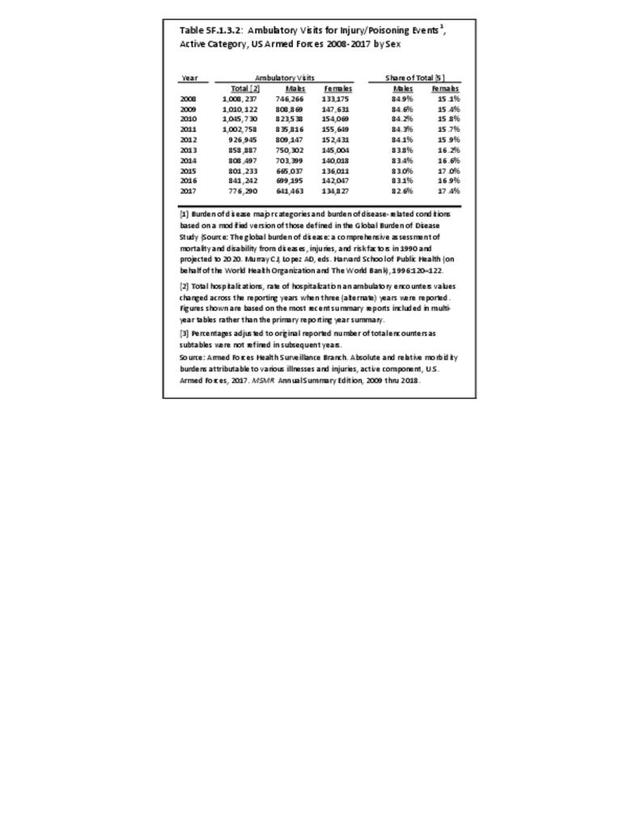
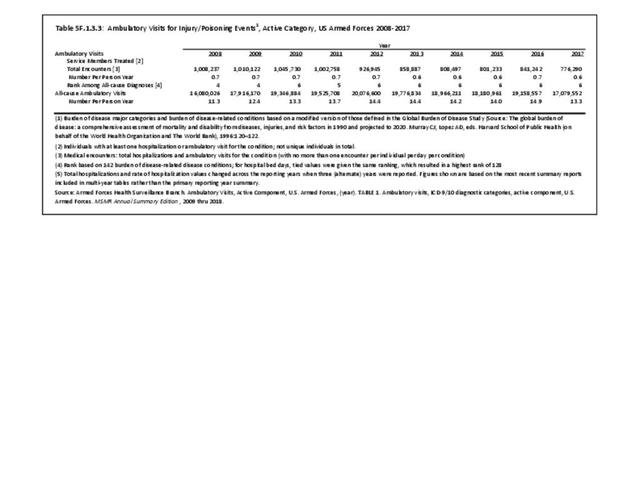
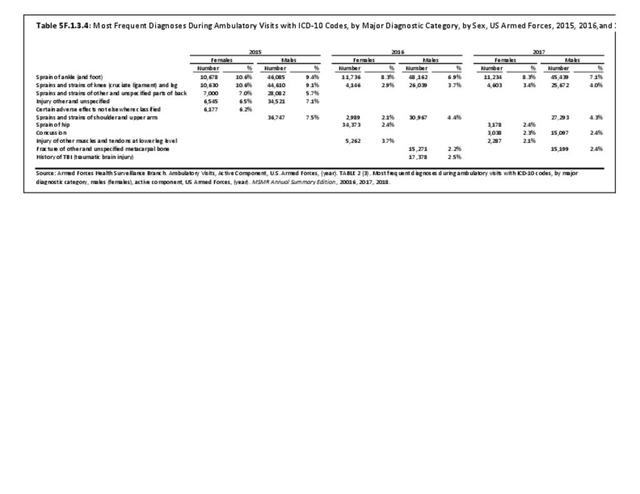
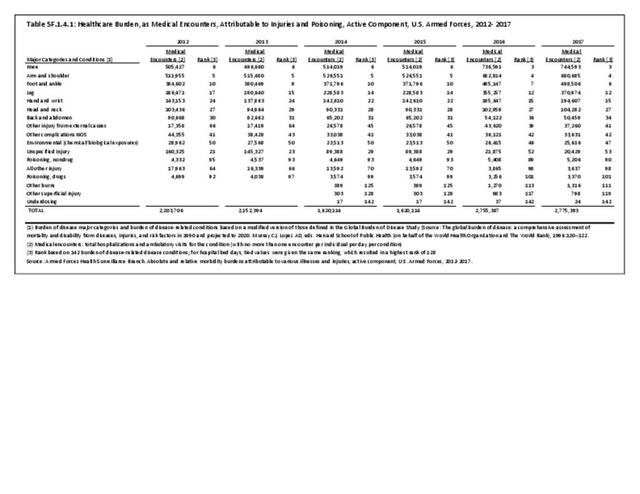
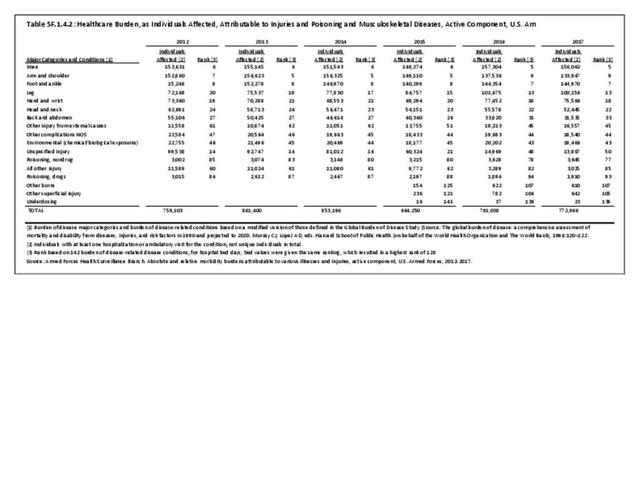
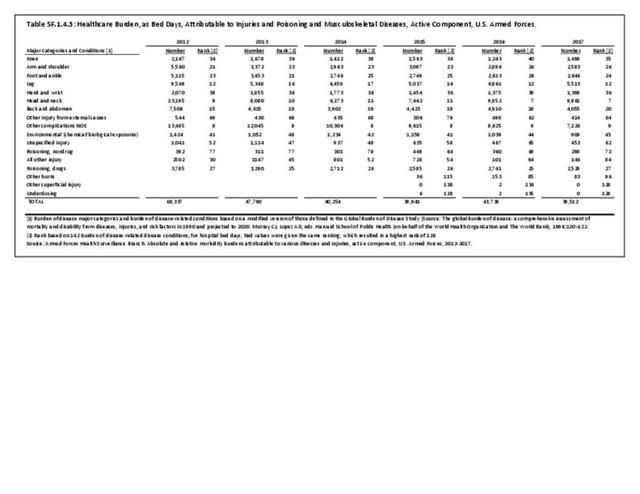
Musculoskeletal injuries may be specific to the category of injury (e.g., MSDs as described in Workplace Injuries above), but for the most part fall into five major groups, plus a group of less common injuries. These categories are based on ICD-9-CM diagnostic codes used primarily in national healthcare databases.
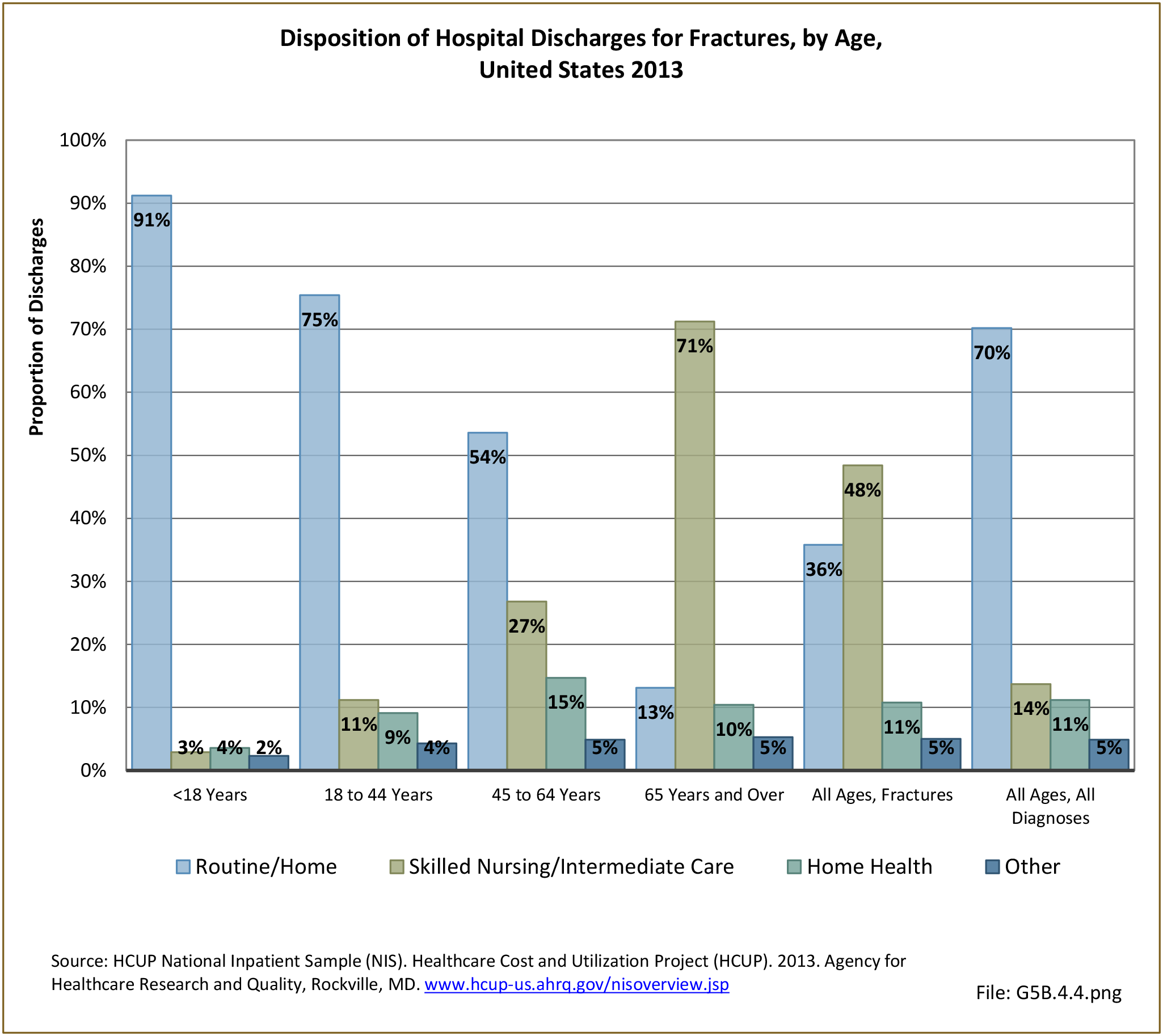
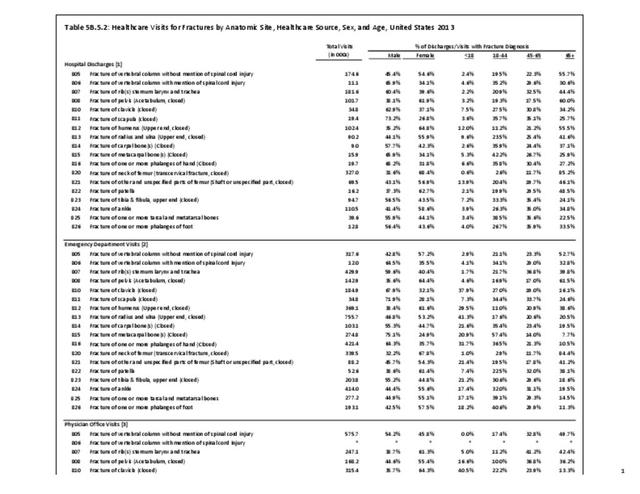
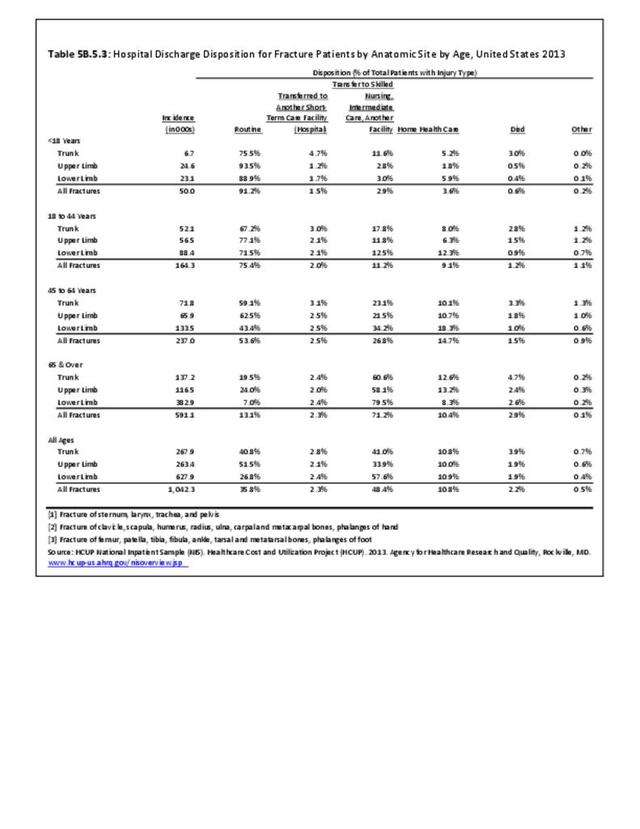
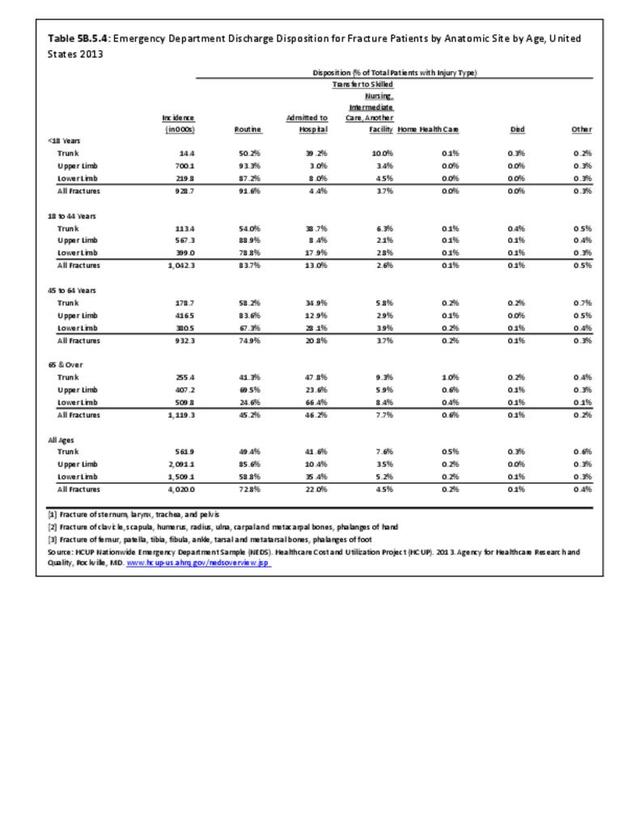
Fractures: Fractures occur when a bone is broken. Fractures fall into six types which are not exclusive of one another.
- Closed fractures: The bone is broken, but the skin remains intact.
- Open fractures: The bone is broken, and there is communication to the broken bone through disruption of the skin.
- Incomplete: The break does not occur through the whole bone.
- Complete: The break is completely through the bone.
- Comminuted: The bone is broken into many pieces.
- Long bone fractures occur in the bones of the extremities (arm and leg bones)
Dislocations: Dislocations are joint injuries that force the articular surfaces of bones out of position. An acutely dislocated joint is painful, swollen, and often visibly out of place. Movement becomes limited. Immediate medical attention is needed to reposition the bones, relieve pressure on soft tissue structures, and provide proper support for healing.
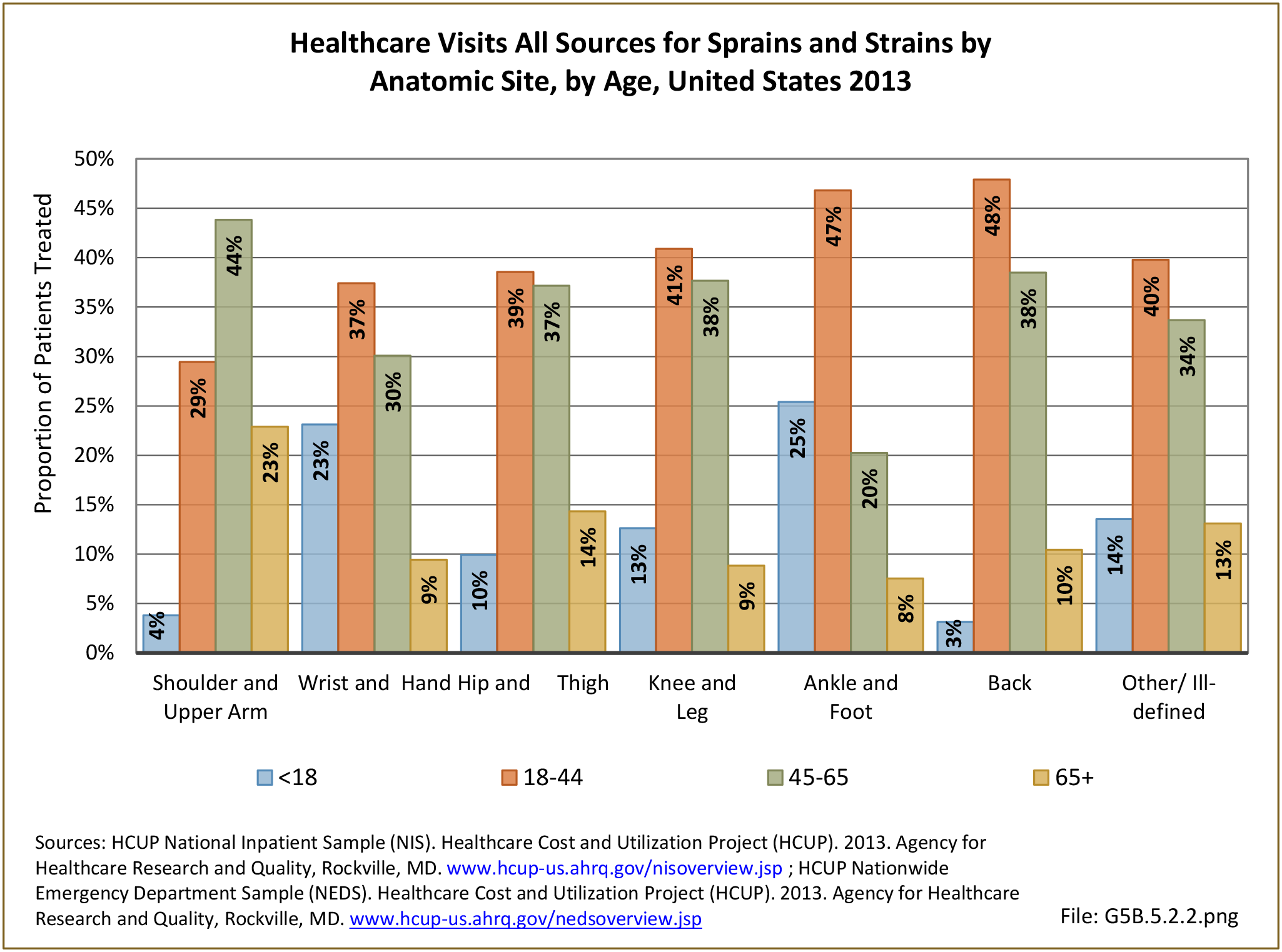
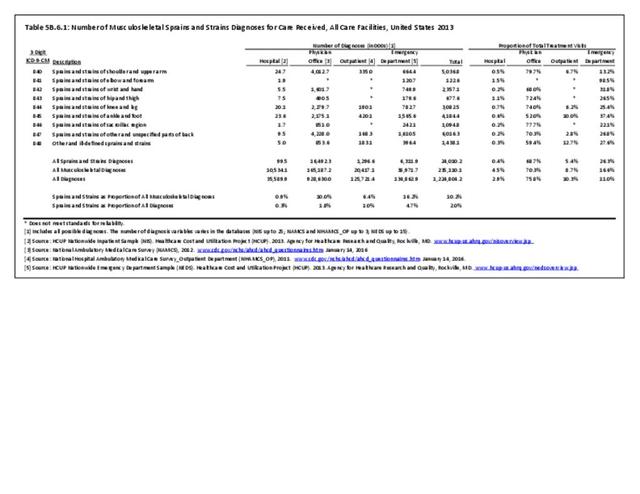
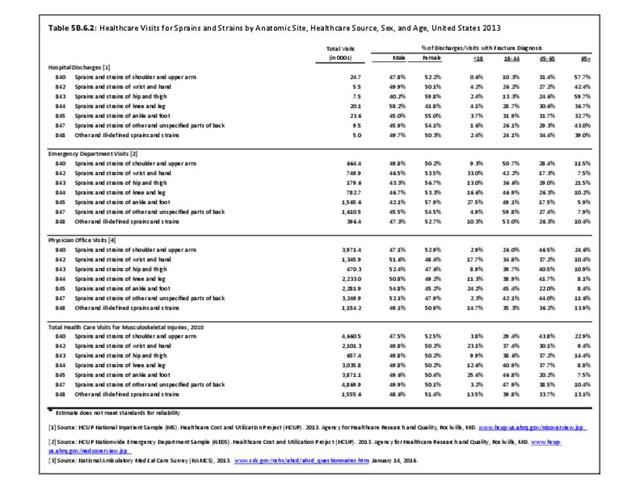
Sprains & strains: A sprain is a stretched or torn ligament, while a strain is a stretched or torn muscle or tendon. A strain can be caused by twisting or pulling tissues. The difference between a sprain and a strain is that a sprain injures the bands of tissue that connect two bones together, while a strain involves an injury to a muscle or to the band of tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone.
Contusions: A contusion, also referred to as a bruise, is damage to the body that doesn't break the skin but ruptures the blood capillaries beneath, resulting in discoloration to the injured area. Most contusions are minor and heal quickly, but they can be serious enough to cause deep tissue damage, swelling, lead to internal “degloving (a significant soft-tissue injury), and limit joint range of motion near the injury. Bruises do not only occur under the skin, but also in deeper tissues, organs, and bones. While these deeper bruises may not show visible signs of bleeding, they can cause pain. They are the second most common sports injury.
Open wounds:
- Abrasion: Occurs when, at minimum, the epidermal skin is disrupted by rubbing or scraping against a rough or hard surface.
- Incision: A sharp object, such as a knife, shard of glass, or razor blade, causes an incision.
- Laceration: A laceration is a deep cut or tearing of the skin.
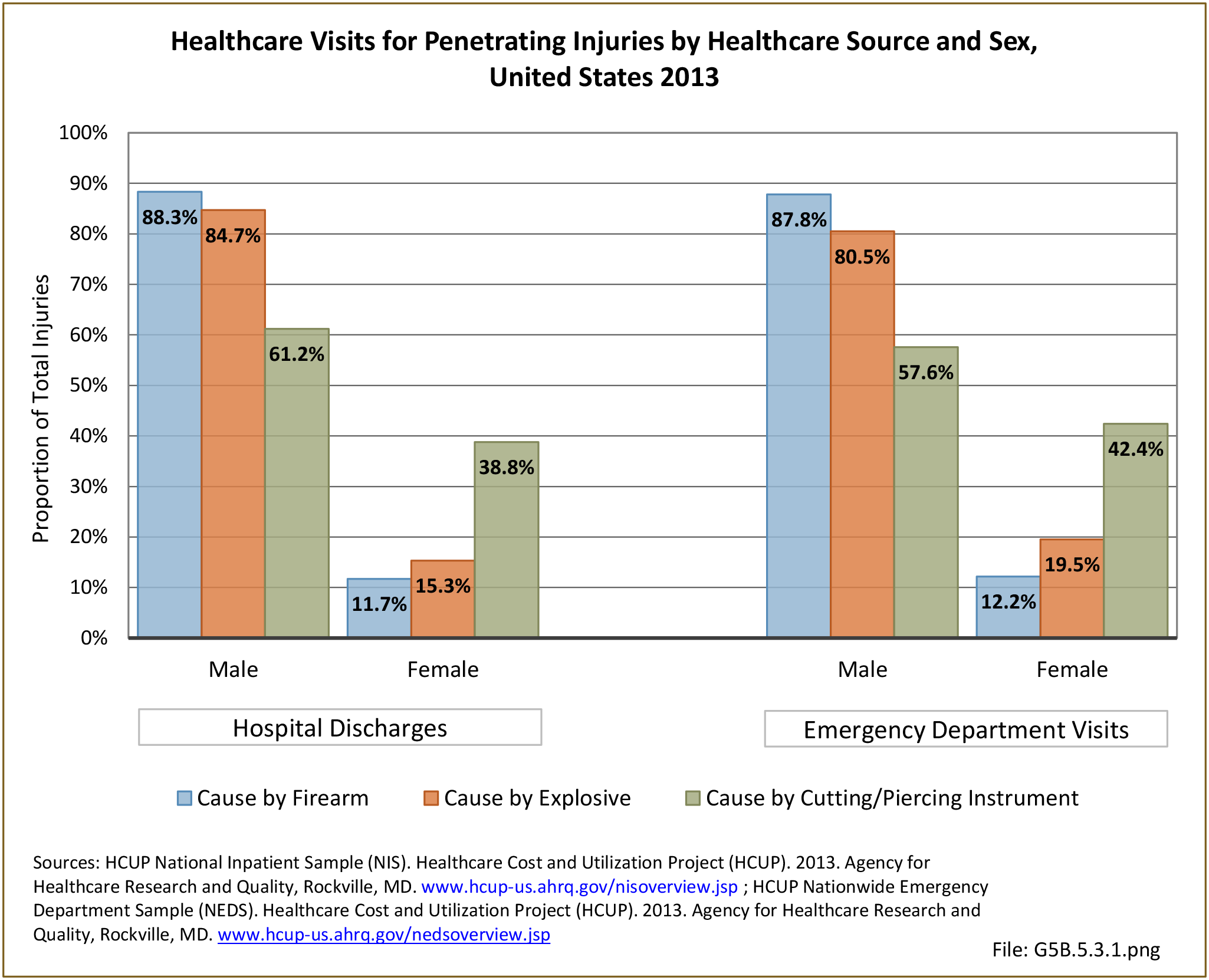
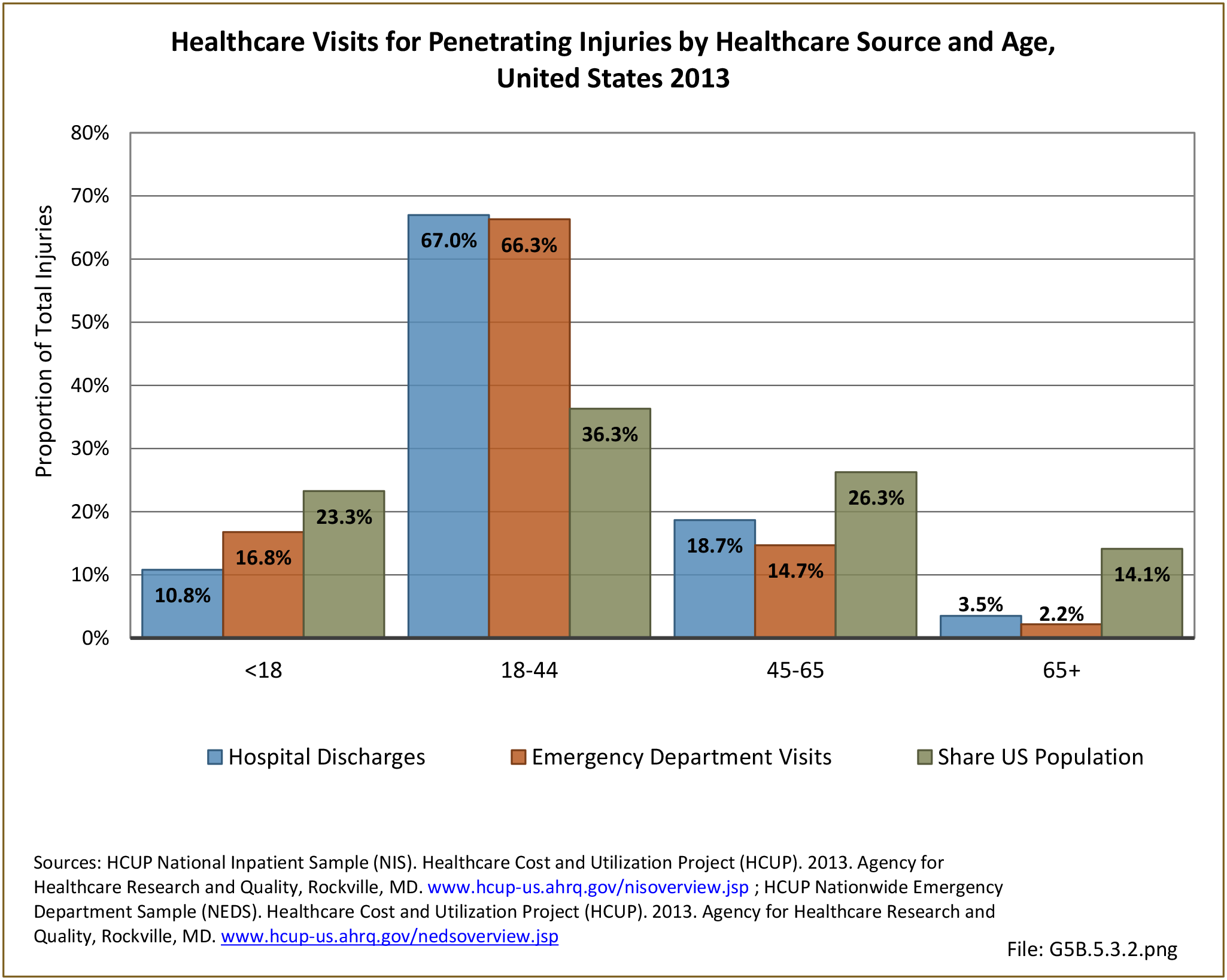
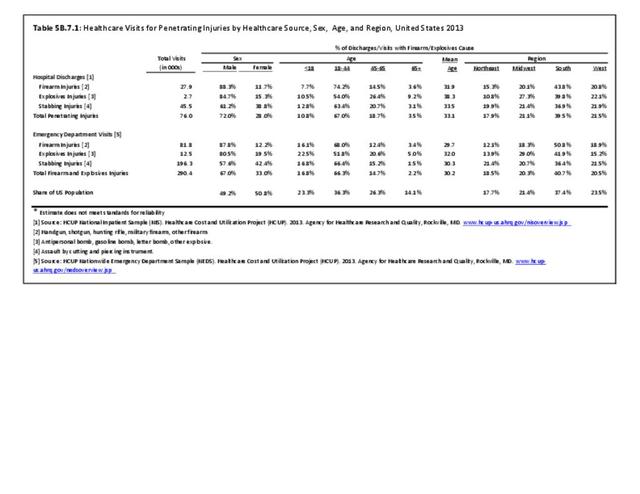
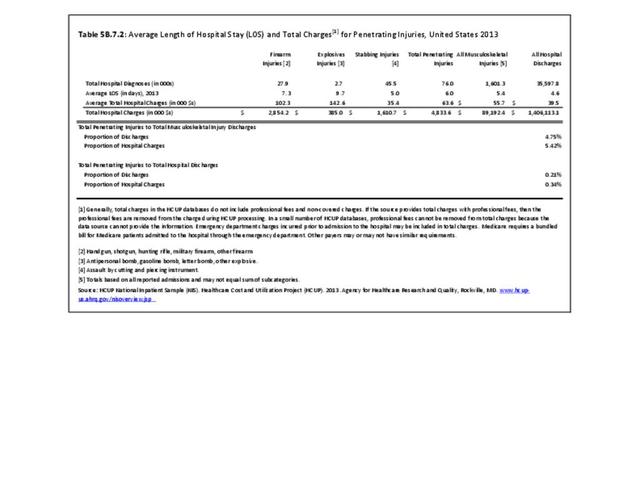
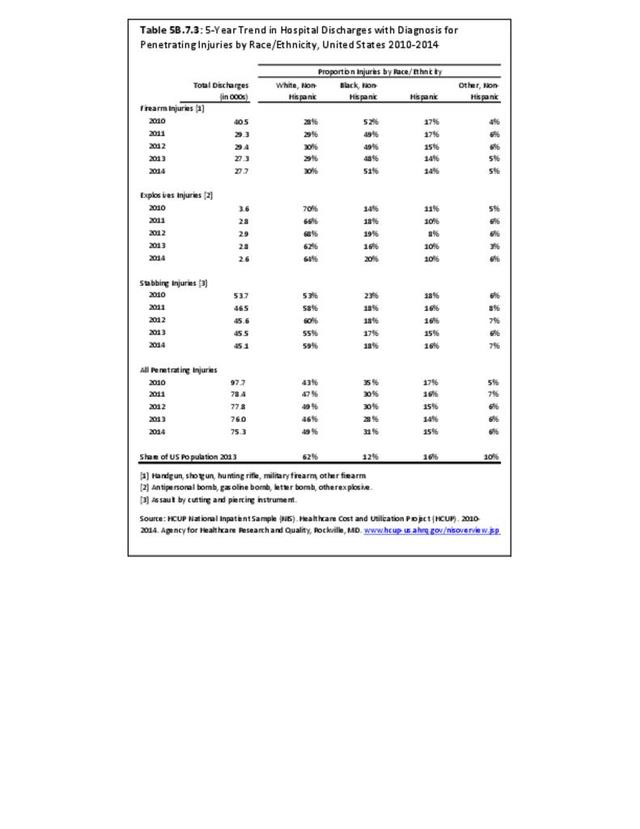
- Puncture or penetrating trauma: A puncture wound is a deep wound that occurs due to something sharp and pointed, such as a nail or a bullet. The opening on the skin is small, and the puncture wound may not bleed much.
- Avulsion: An avulsion fracture is an injury to the bone in a location where a tendon or ligament attaches to the bone. When an avulsion fracture occurs, the tendon or ligament pulls off a piece of the bone. Avulsion fractures can occur anywhere in the body. Skin avulsion is a wound that happens when skin is torn from the body during an accident or other injury. The torn skin may be lost or too damaged to be repaired, and it must be removed.
Other musculoskeletal injuries:
- Traumatic amputation: The accidental loss of some or all of a body part. A complete amputation detaches a limb from the rest of the body. In a partial amputation, some tissue remains attached.
- Burns: Tissue damage that results from scalding, overexposure to the sun or other radiation, contact with flames, chemicals or electricity, or smoke inhalation.
- Electrical injuries: Injury damage caused by generated electrical current passing through the body. Electric current can cause injury in four ways: Cardiac arrest due to the electrical effect on the heart; muscle, nerve, and tissue destruction from a current passing through the body; thermal burns from contact with the electrical source; and falling or injury after contact with electricity.
- Bites: Human bite injuries that can result in a wide range of injuries from minor bruising to punctures and lacerations to partial loss of body parts.
Edition:
- Fourth Edition